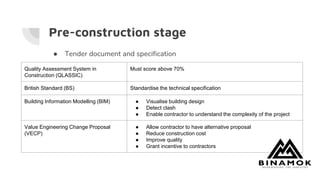
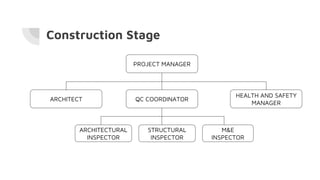
This document analyzes a proposed development project. It provides details on the project team, project description including land size and development area, strengths and weaknesses of the site location, a benchmark project for comparison, proposed concept design which allocates percentages of development to low cost housing, shops and terrace houses. It also discusses quality management considerations including pre-construction, construction, and post-construction stages. Risk management is analyzed through identification, assessment, response, and monitoring of risks.