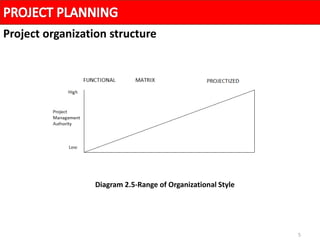
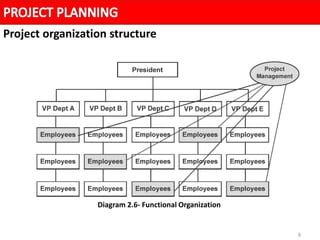
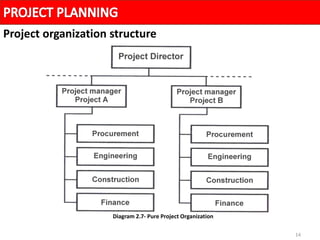
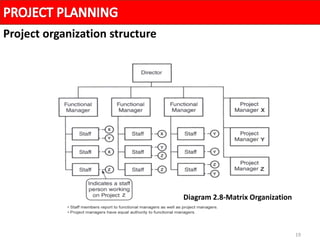
A project organization structure facilitates coordination and implementation of project activities. The structure considers the organization environment, project characteristics, and the project manager's authority level. There are three main types of project organization structures: functional/pure line, pure project, and matrix. A matrix structure shares resources across projects and regular work, with team members reporting to both a project manager and functional manager. This splits authority but allows optimization of resource usage and integration of expertise from different functions.