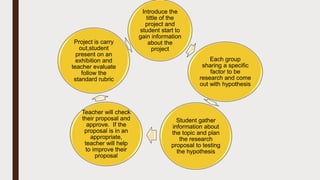
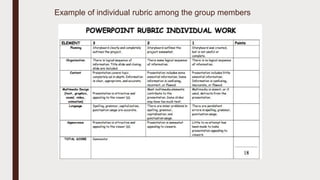
Project based learning (PBL) is a teaching method where students gain knowledge and skills by investigating and responding to an engaging question or challenge over an extended period of time. It focuses on 21st century skills like inquiry, innovation, and developing solutions to present publicly. PBL is conducted through sections that introduce the project, provide examples, establish foundations like receiving feedback, and provide guidance on execution and building a culture for excellence. It can ignite passion for learning, foster varied skills needed later in life, and tailor to different student abilities while letting projects drive the curriculum over tests. For example, a photosynthesis project has student groups research factors that affect it, develop hypotheses to test, gather information, design proposals, conduct their project