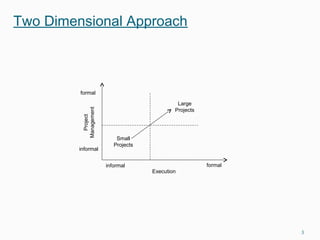
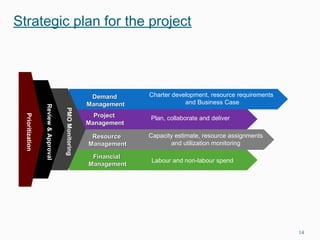
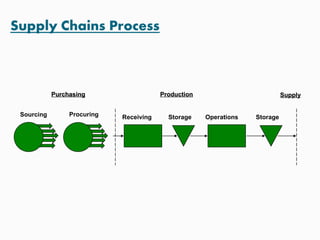
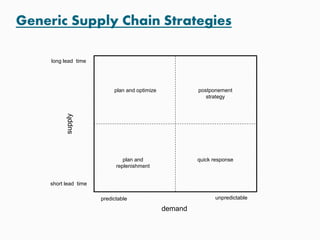
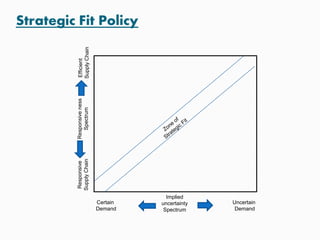
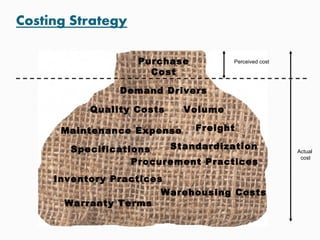
This document discusses goals and processes for managing a supply chain at Sasmos. It aims for customer satisfaction through cost, schedule and quality commitments. It takes a two-dimensional approach to project management, applying different levels of formality for small and large projects. Key areas covered include purchasing, operations, distribution, integration, organization, planning, scheduling, resources, quality, risk management and tracking. The document also discusses trends toward strategic sourcing, alliances and partnerships to improve performance and reduce costs.