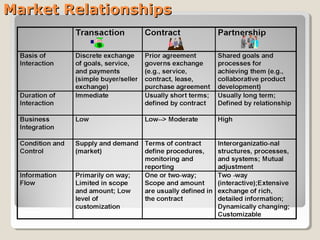
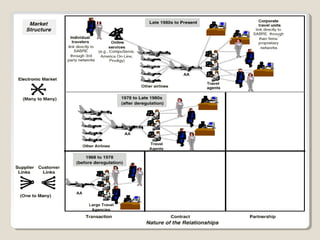
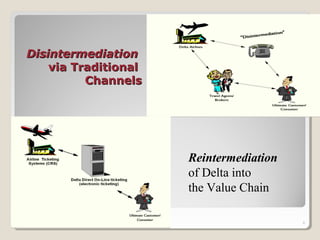
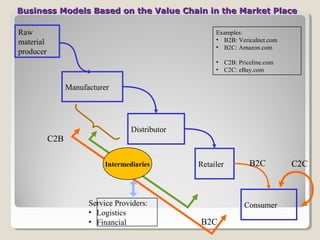
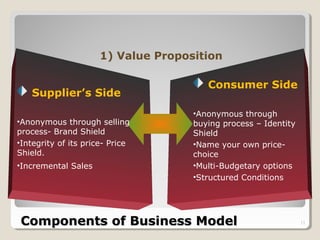
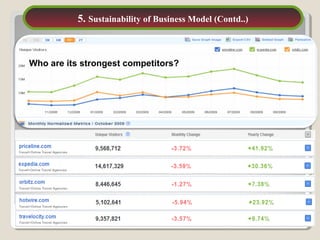
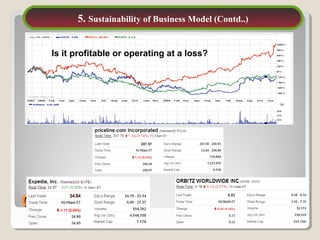
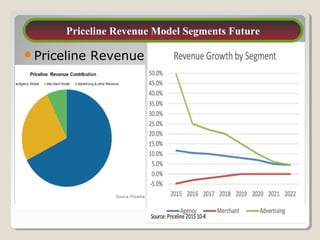
This document discusses Priceline's business model. It describes how Priceline operates as an intermediary between suppliers (hotels, airlines) and consumers by allowing consumers to "name their own price" for travel services. Priceline earns transaction fees from suppliers when consumer offers are accepted. The model was initially unprofitable but became profitable in the early 2000s as the company expanded internationally and integrated additional travel booking services. The document analyzes factors that affect the sustainability of Priceline's business model, such as competition from other online travel sites and flexibility in adapting to new technologies and market conditions.