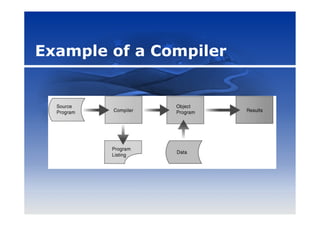
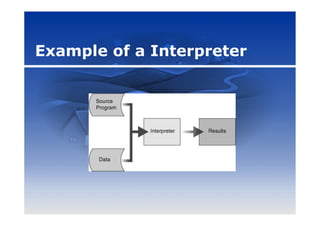
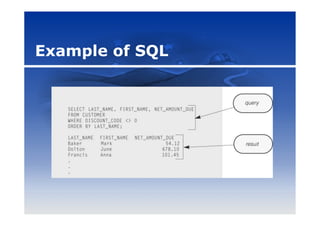
This document discusses programming languages and development tools. It defines programming languages and categorizes them from low-level machine languages to high-level languages. Popular languages today include Visual Basic, C, C++, Java, and SQL. The document also outlines tools for application development, macros, RAD, web pages using HTML and XML, and multimedia programs.