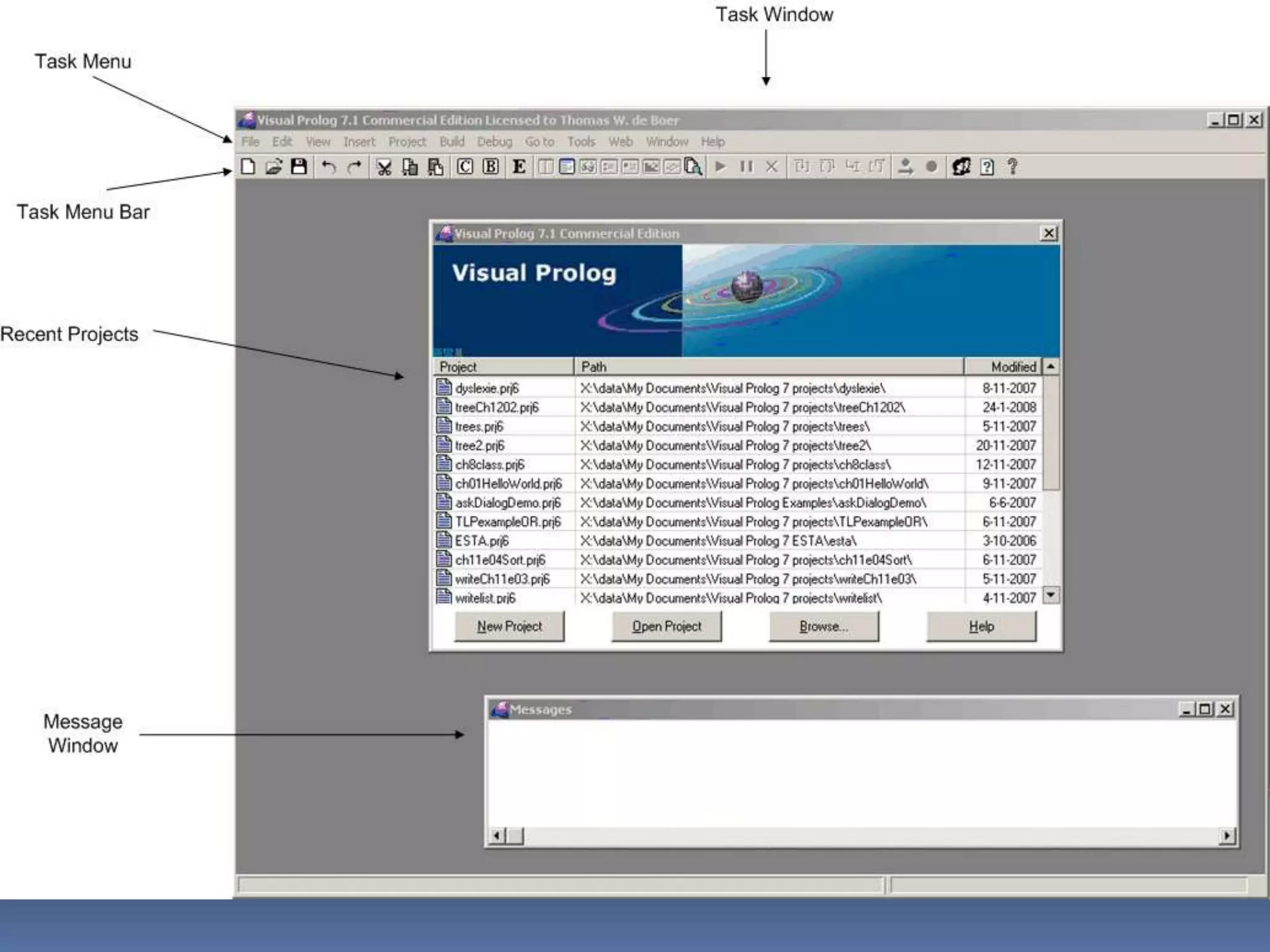
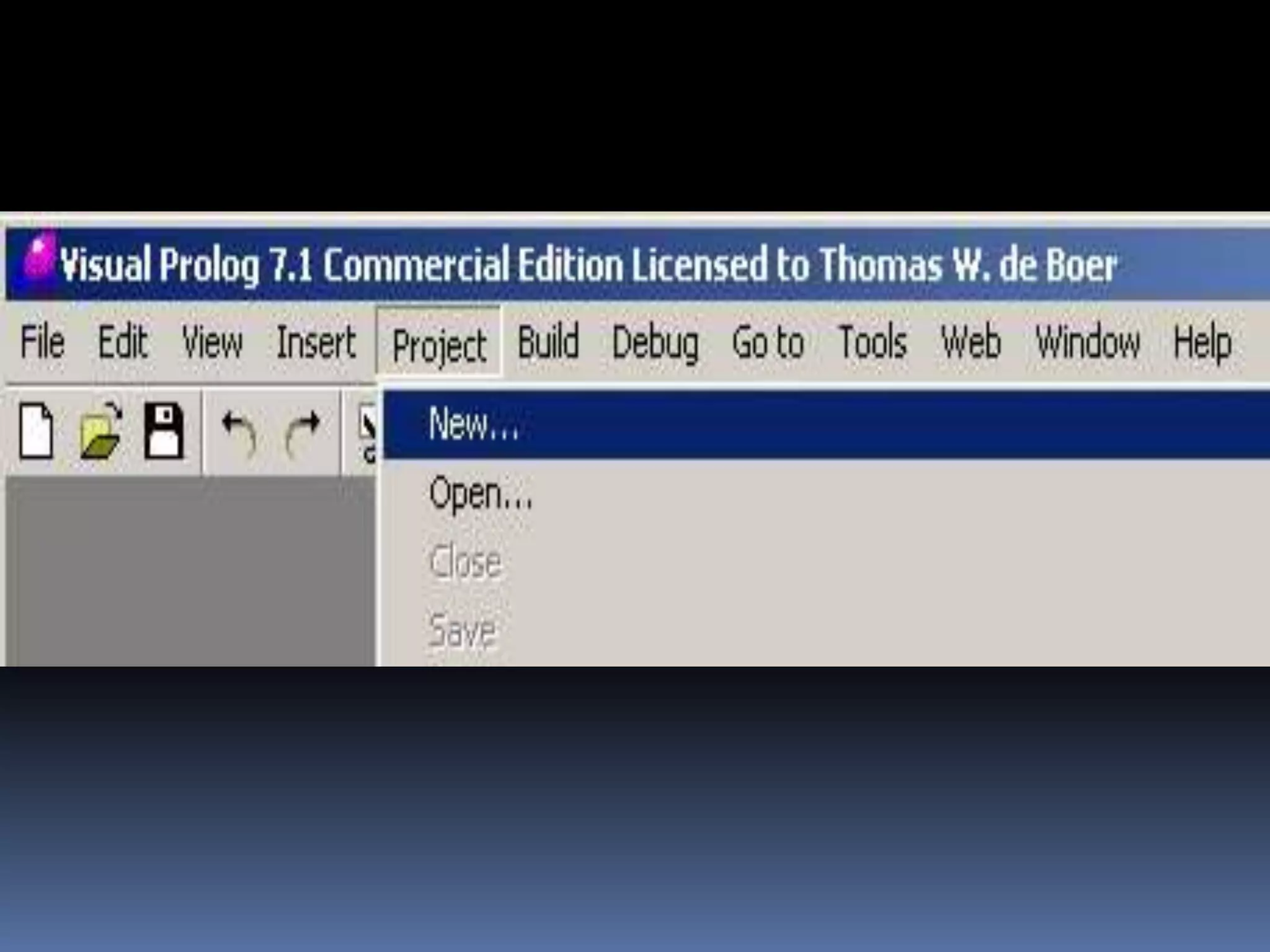
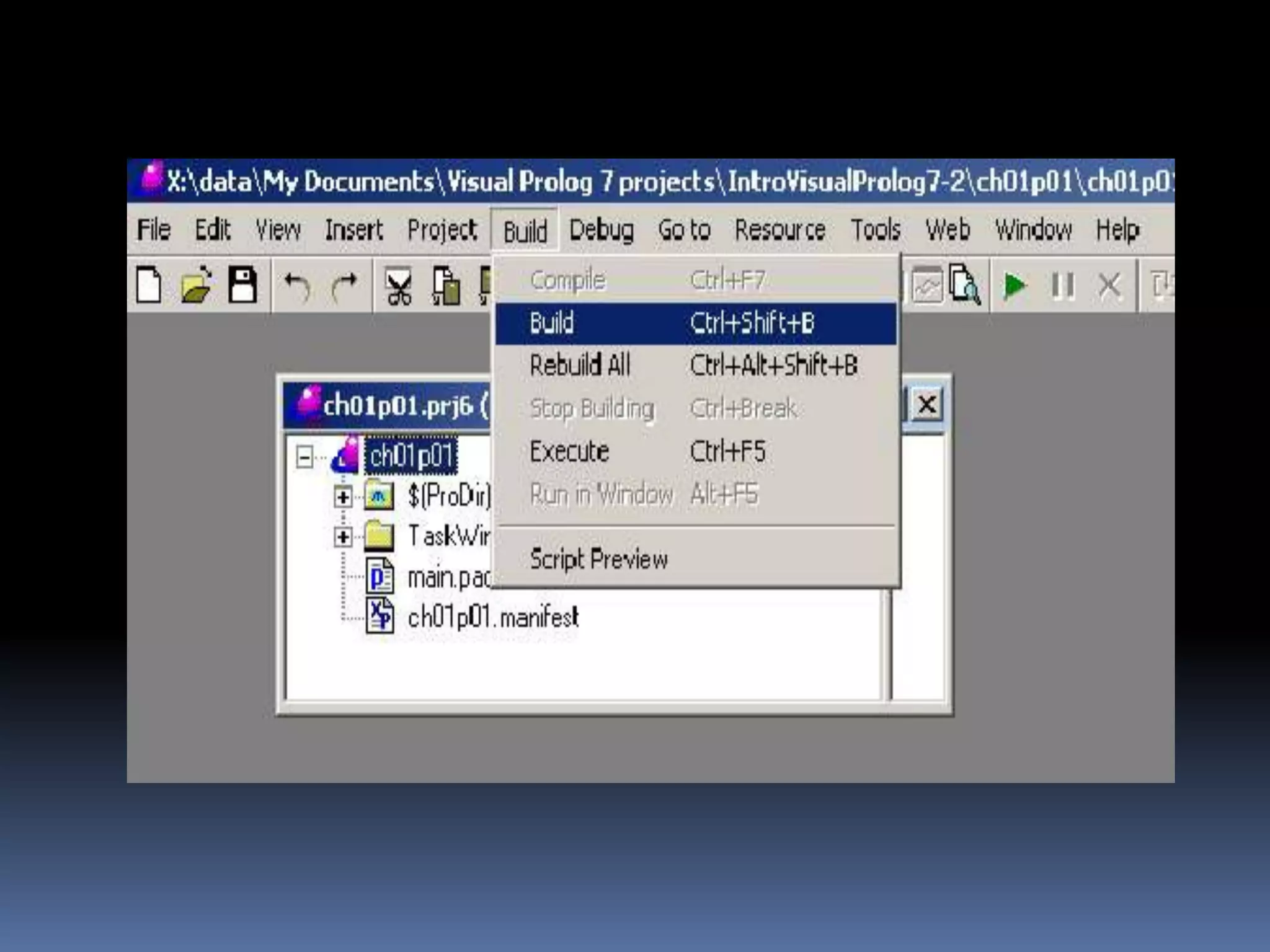
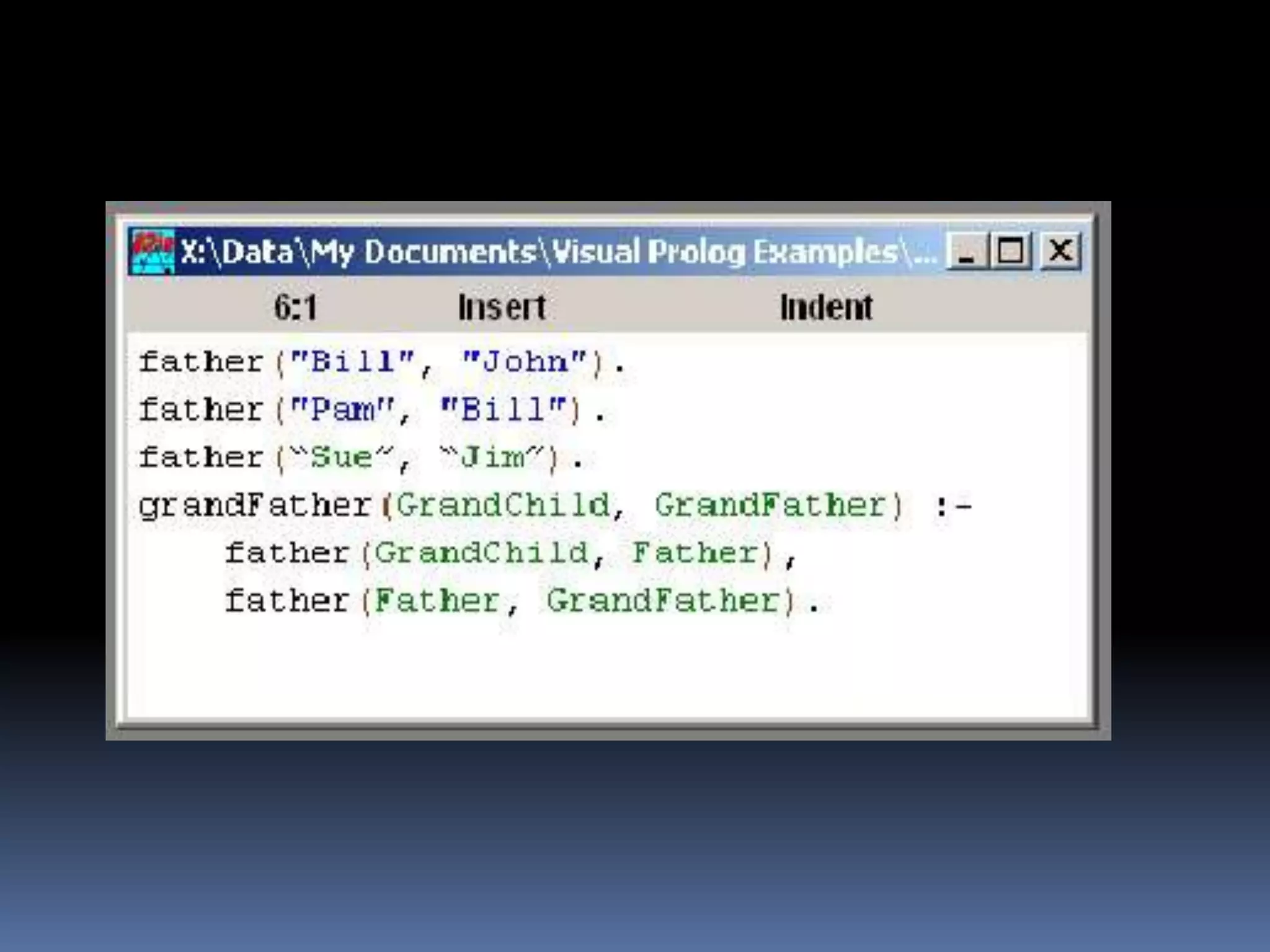
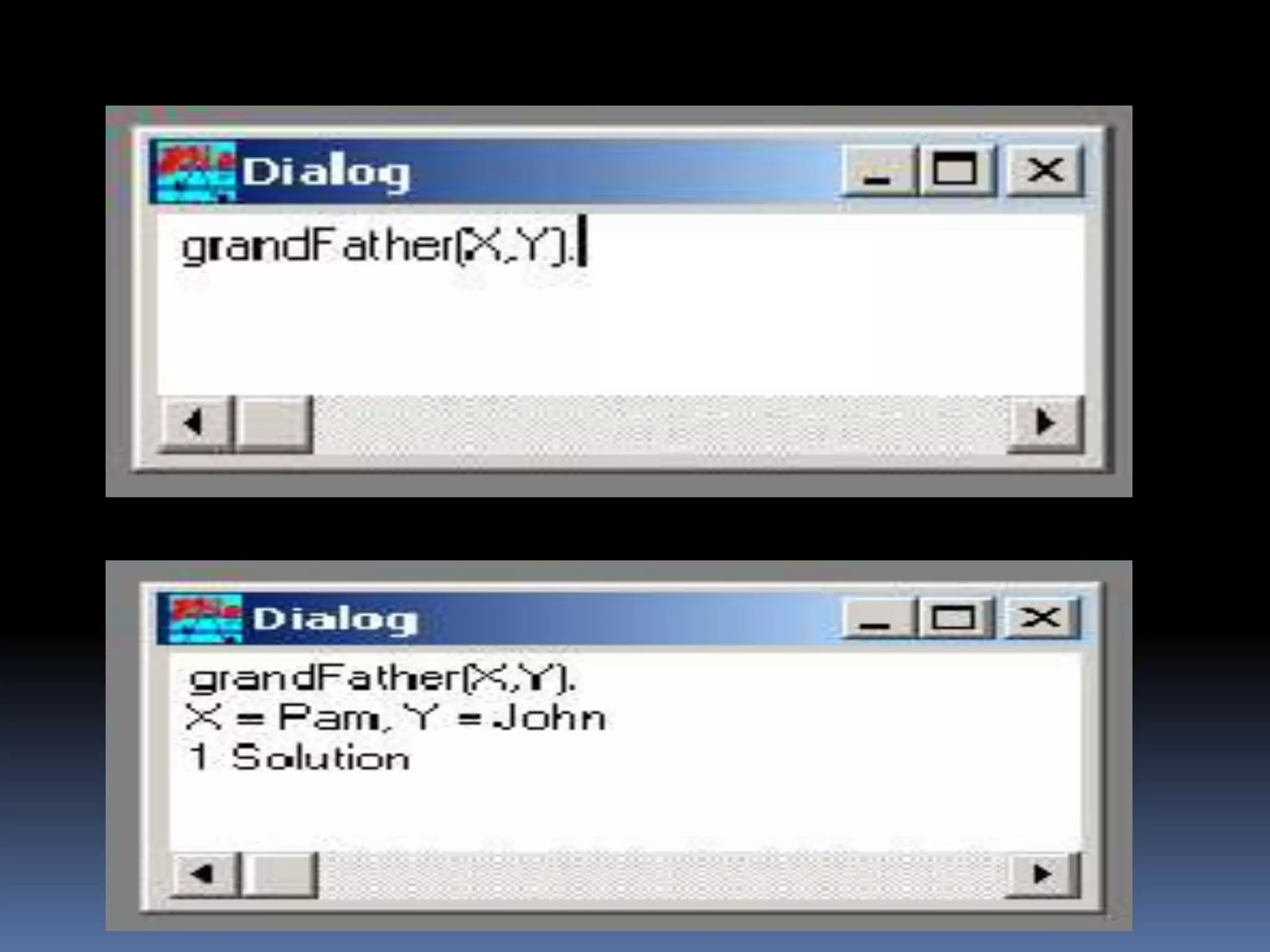
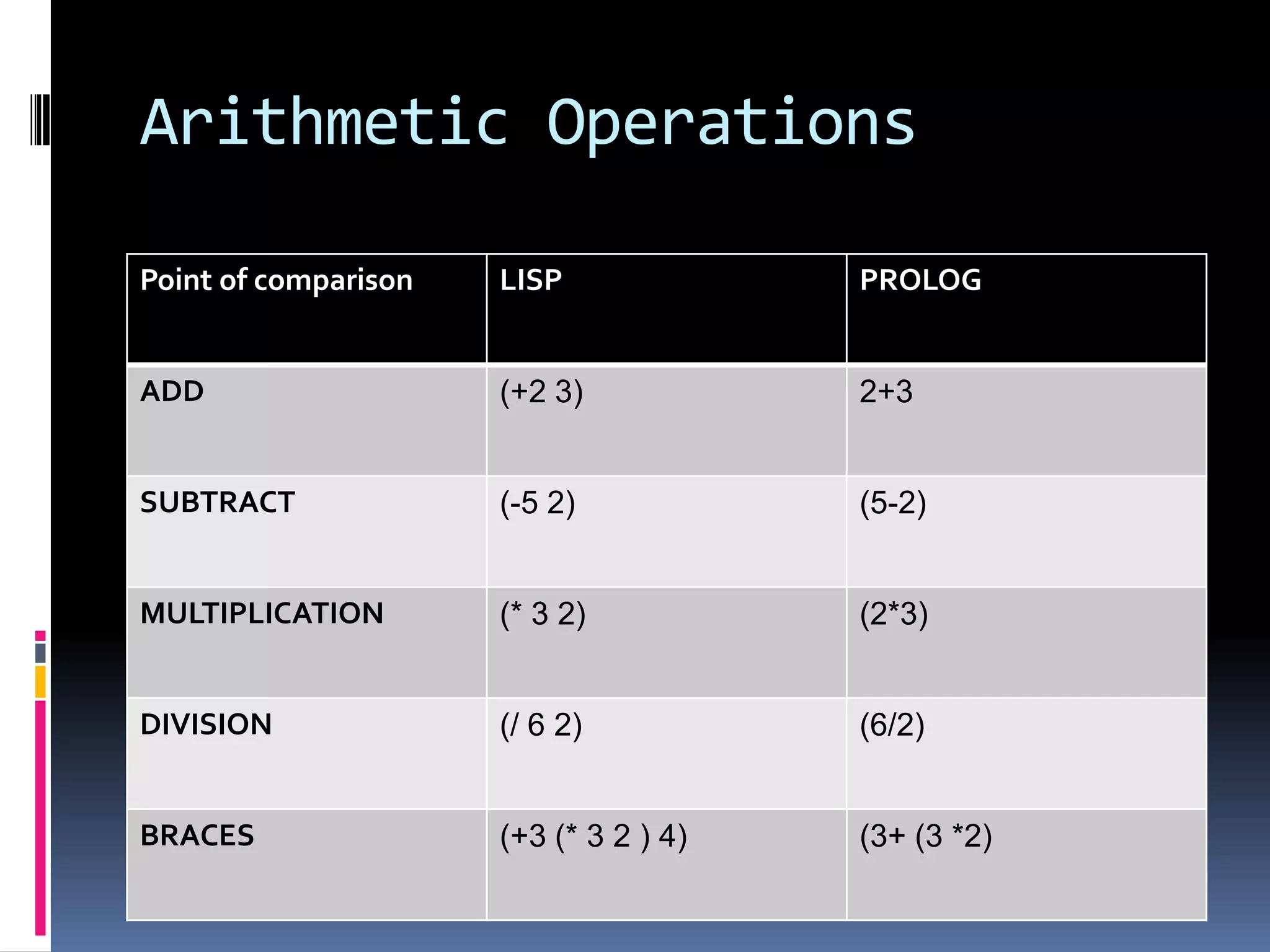
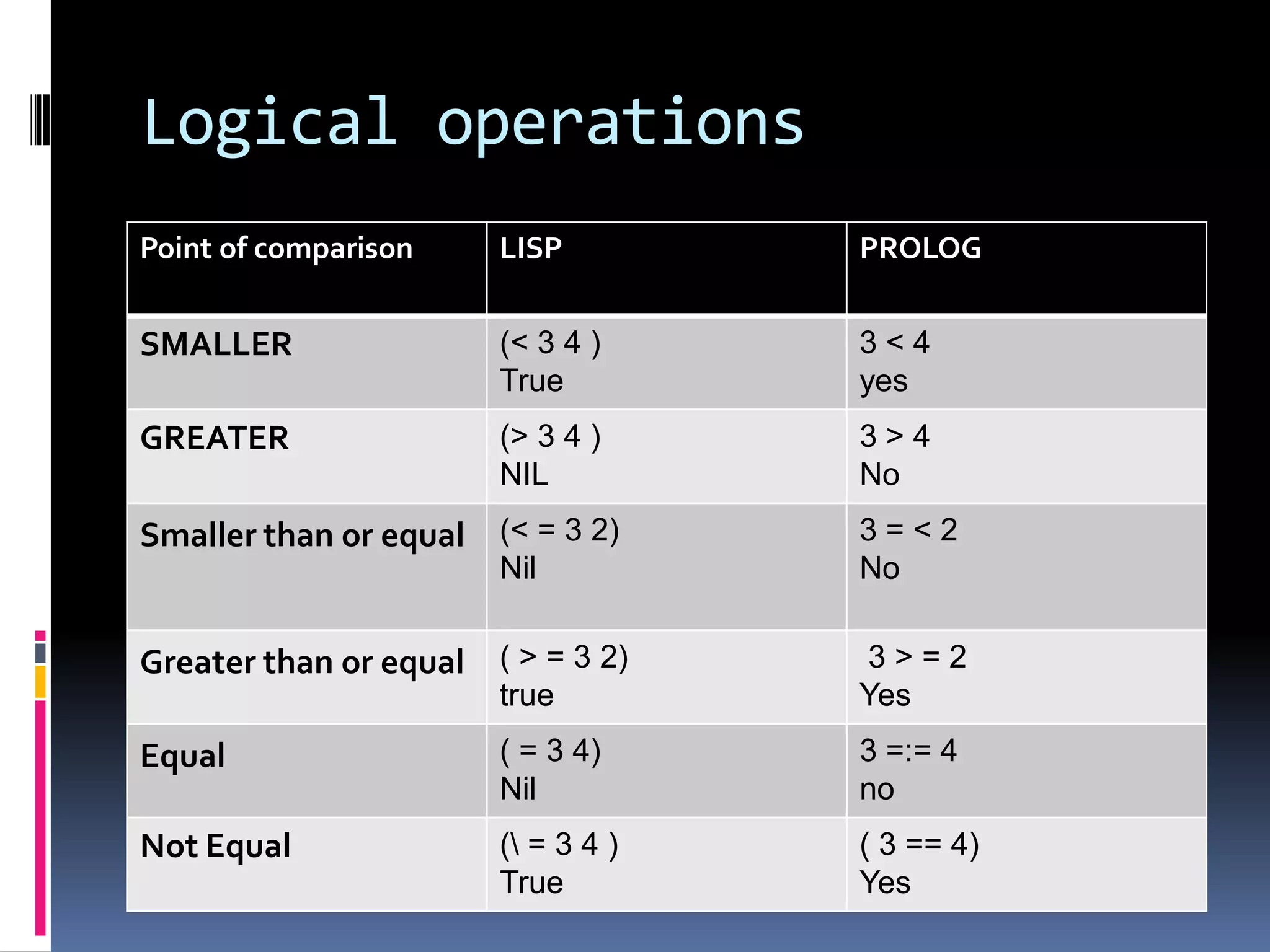
This document provides information about the LISP and PROLOG programming languages. It defines LISP as a list processing language invented in 1958 that manipulates lists. PROLOG is described as a declarative language where programs are expressed in terms of relations. Examples of simple programs are provided in both LISP using recursion and factorials, and in PROLOG using logic rules. The document outlines some applications and advantages of each language such as artificial intelligence and natural language processing for LISP and expert systems for PROLOG. Similarities and differences between the languages are also summarized.



![LISP Discription:
A list is either empty or non-empty.
[a, b, c, d]
Empty: []
Non-empty: head=[a] tail=[b, c, d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-140122100634-phpapp02/75/Presentation1-4-2048.jpg)