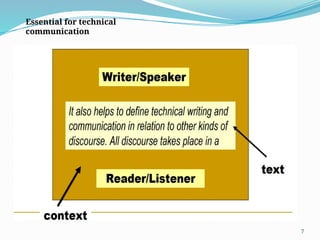
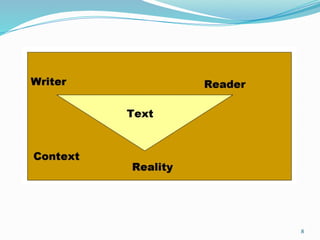
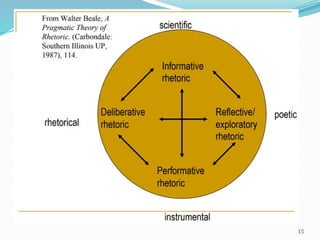
The document outlines the vision and mission of an institute and its technical communication course objectives, focusing on developing students' skills in technical writing, understanding audience needs, and fostering research aptitude. It emphasizes the importance of clear communication through various forms such as emails and business letters, highlighting techniques for effective writing and document design. Additionally, it discusses the significance of meeting minutes as a record of decisions and responsibilities for group discussions.