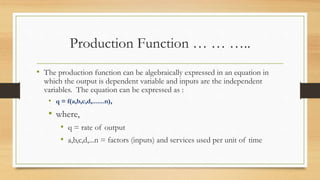
The document discusses the production function in economics, emphasizing that production creates utilities rather than material. It defines key factors of production—land, labor, capital, and organization—and explains their roles in the production process. Additionally, it describes how inputs transform into outputs and introduces the concept of a production function as the relationship between these inputs and outputs.