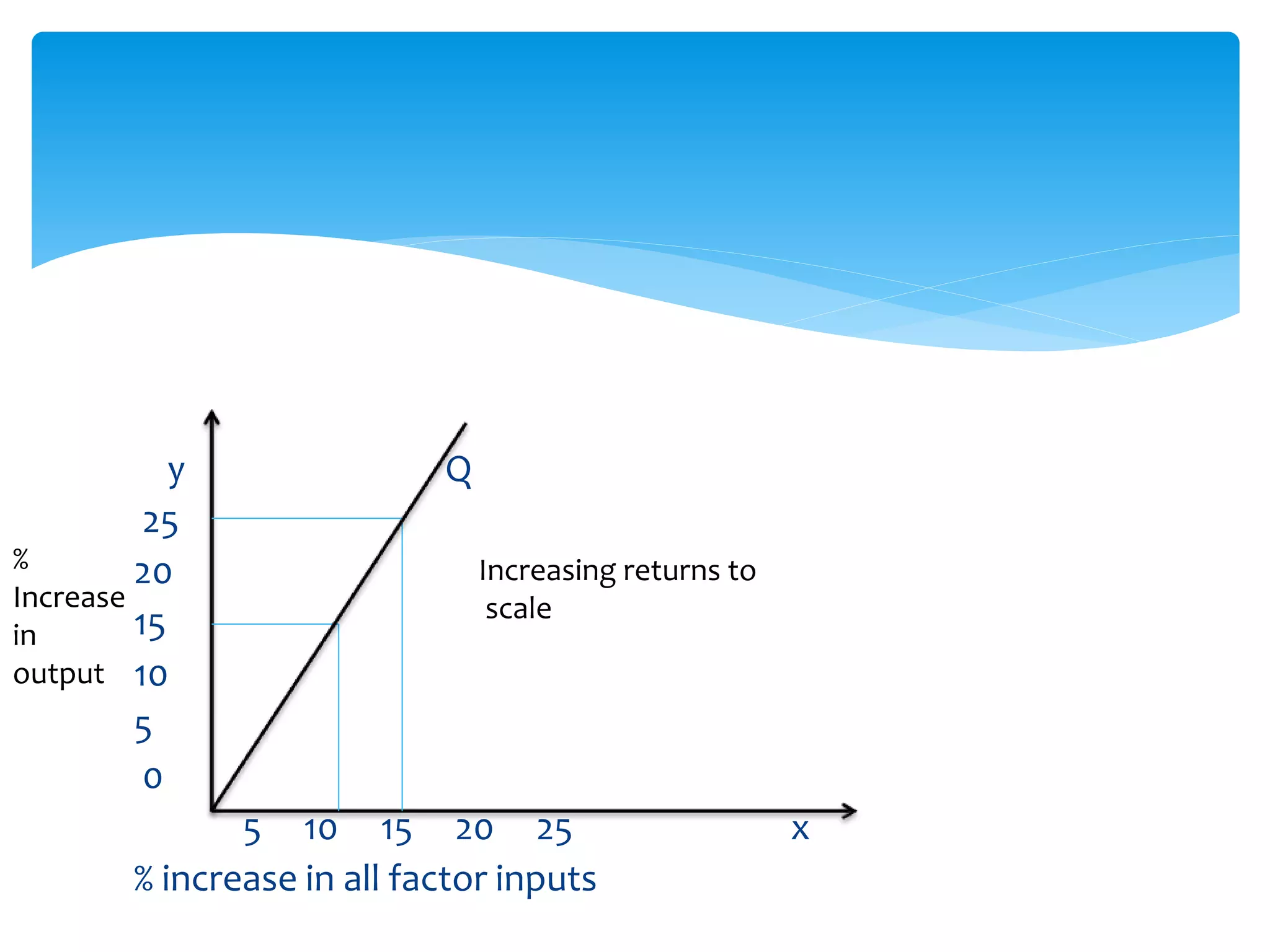
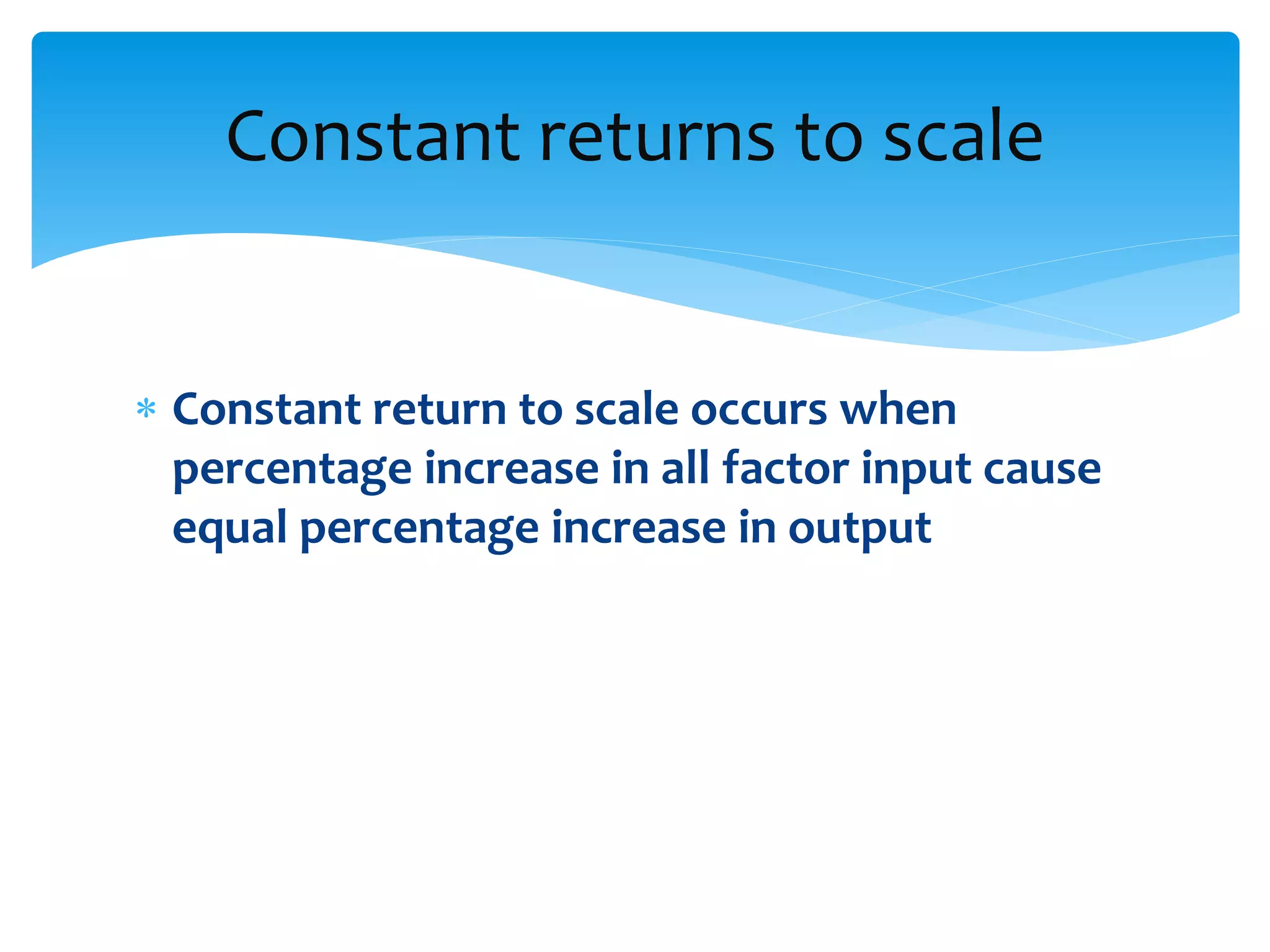
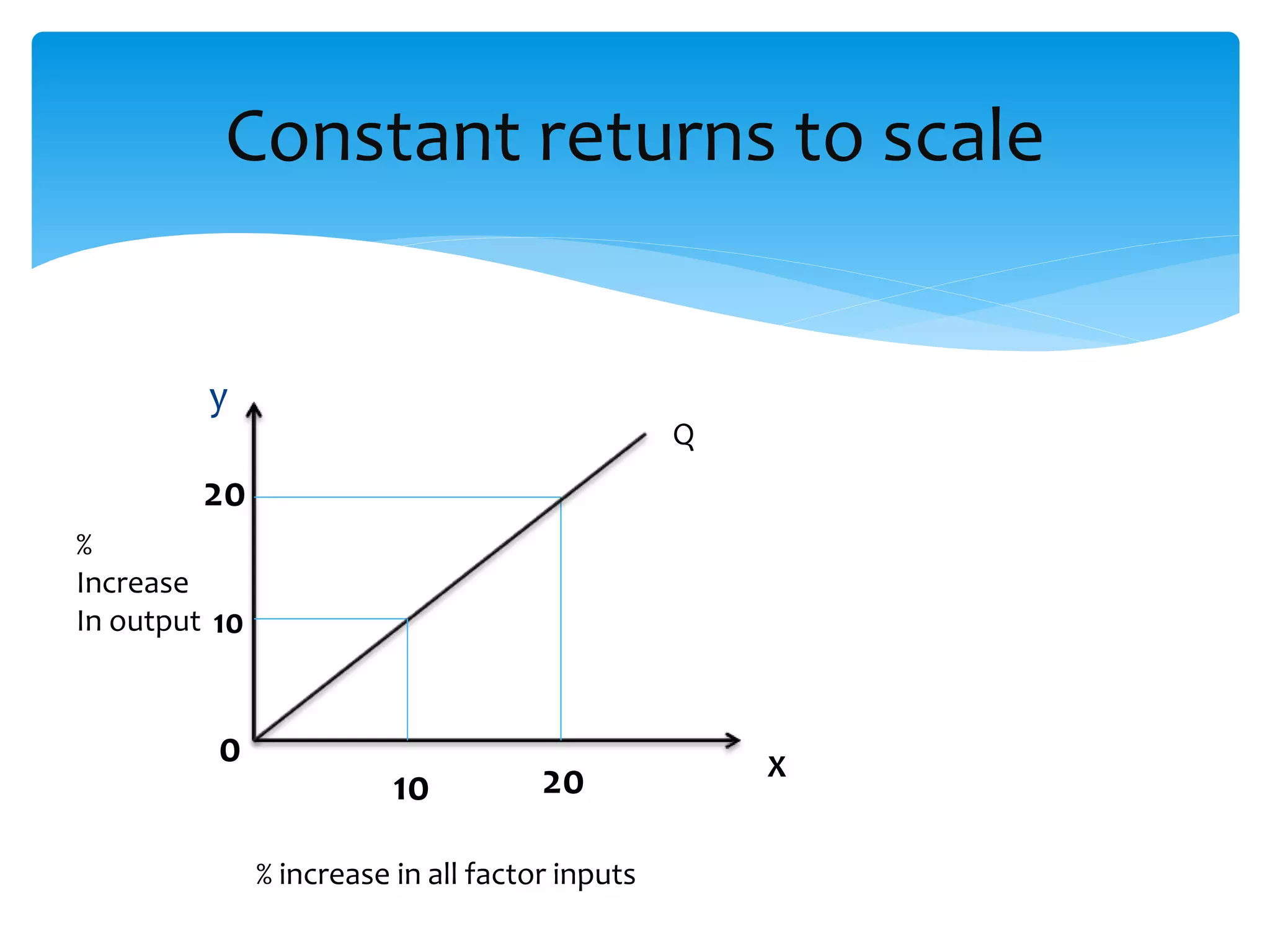
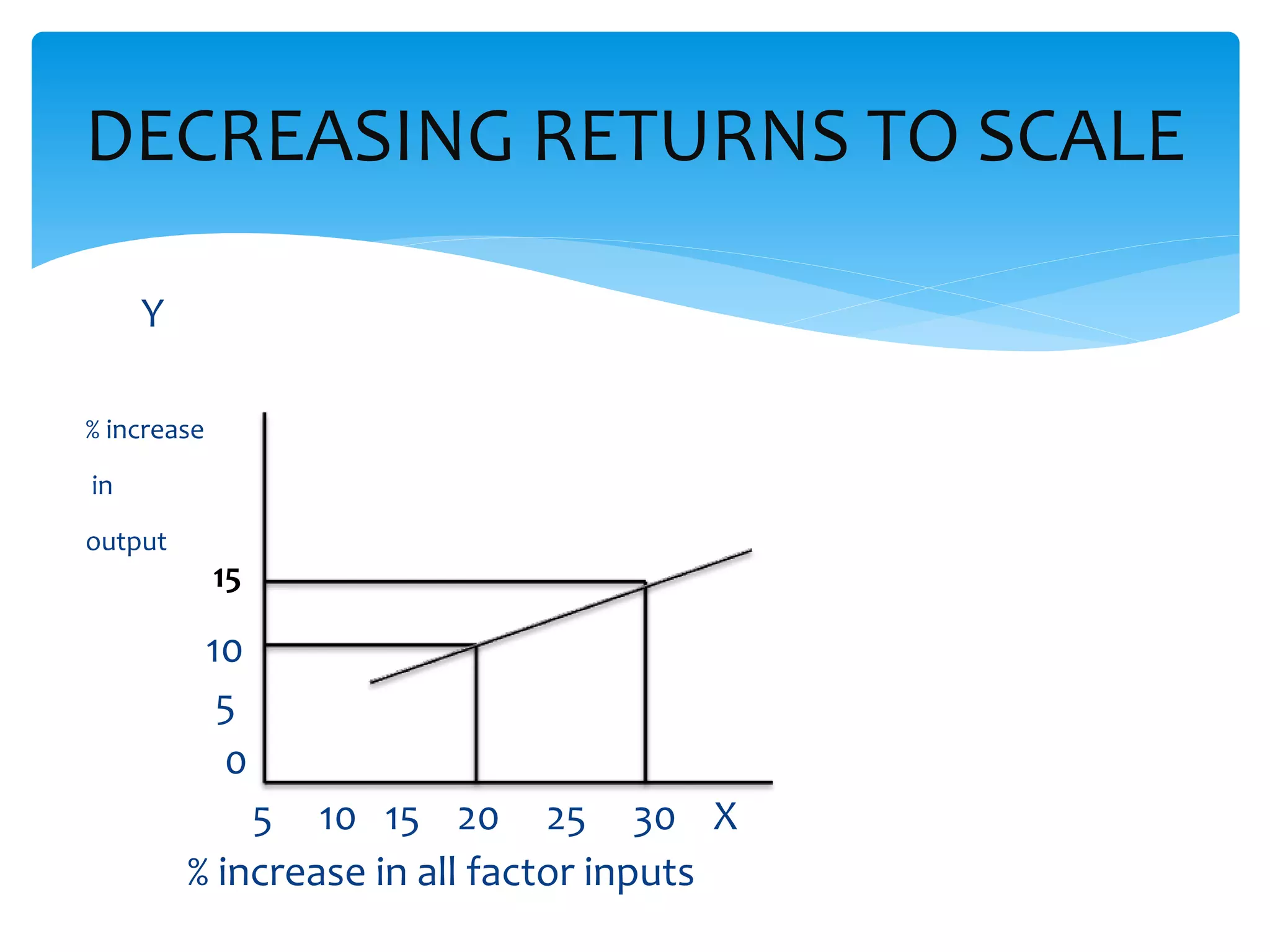
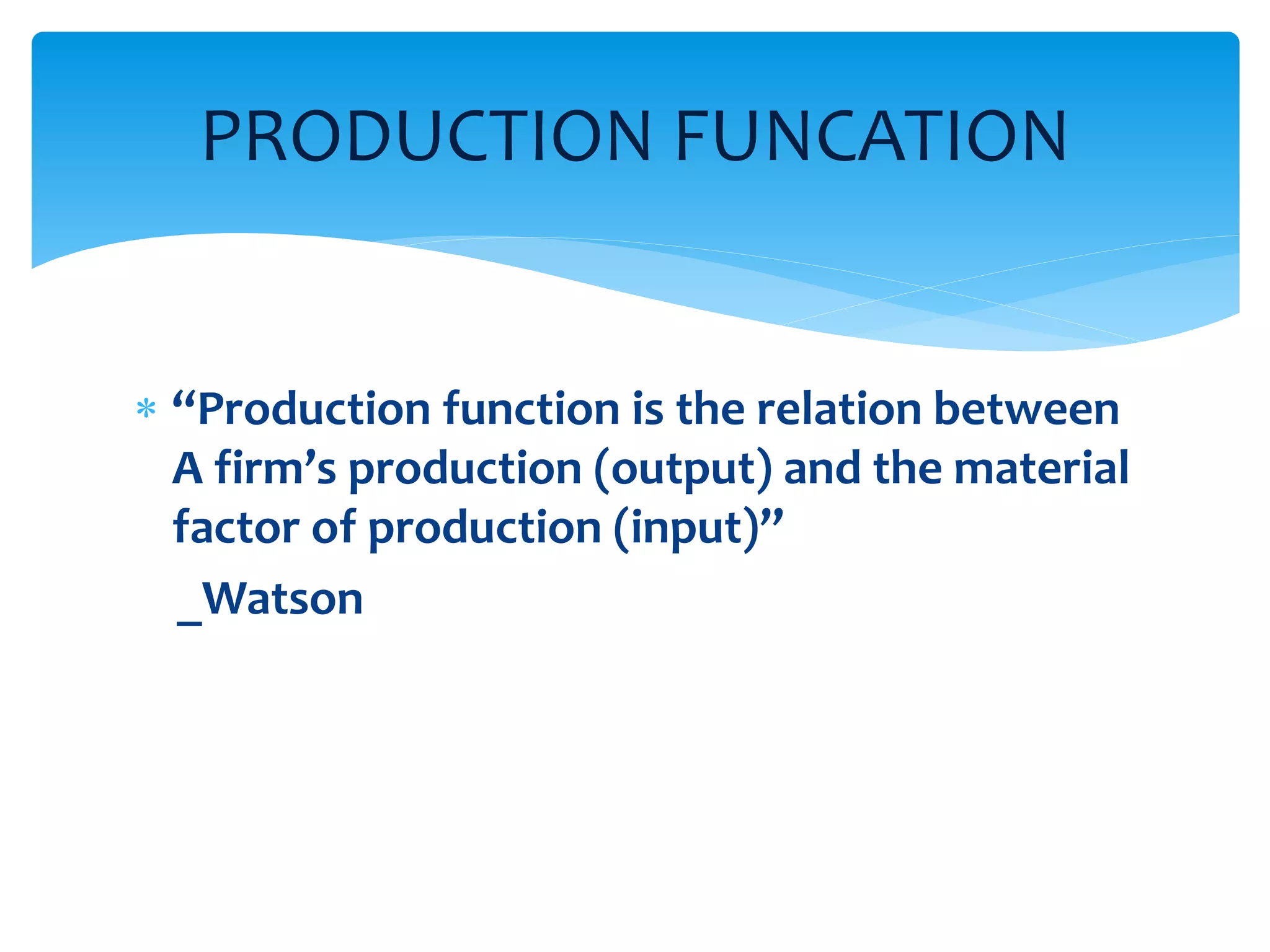
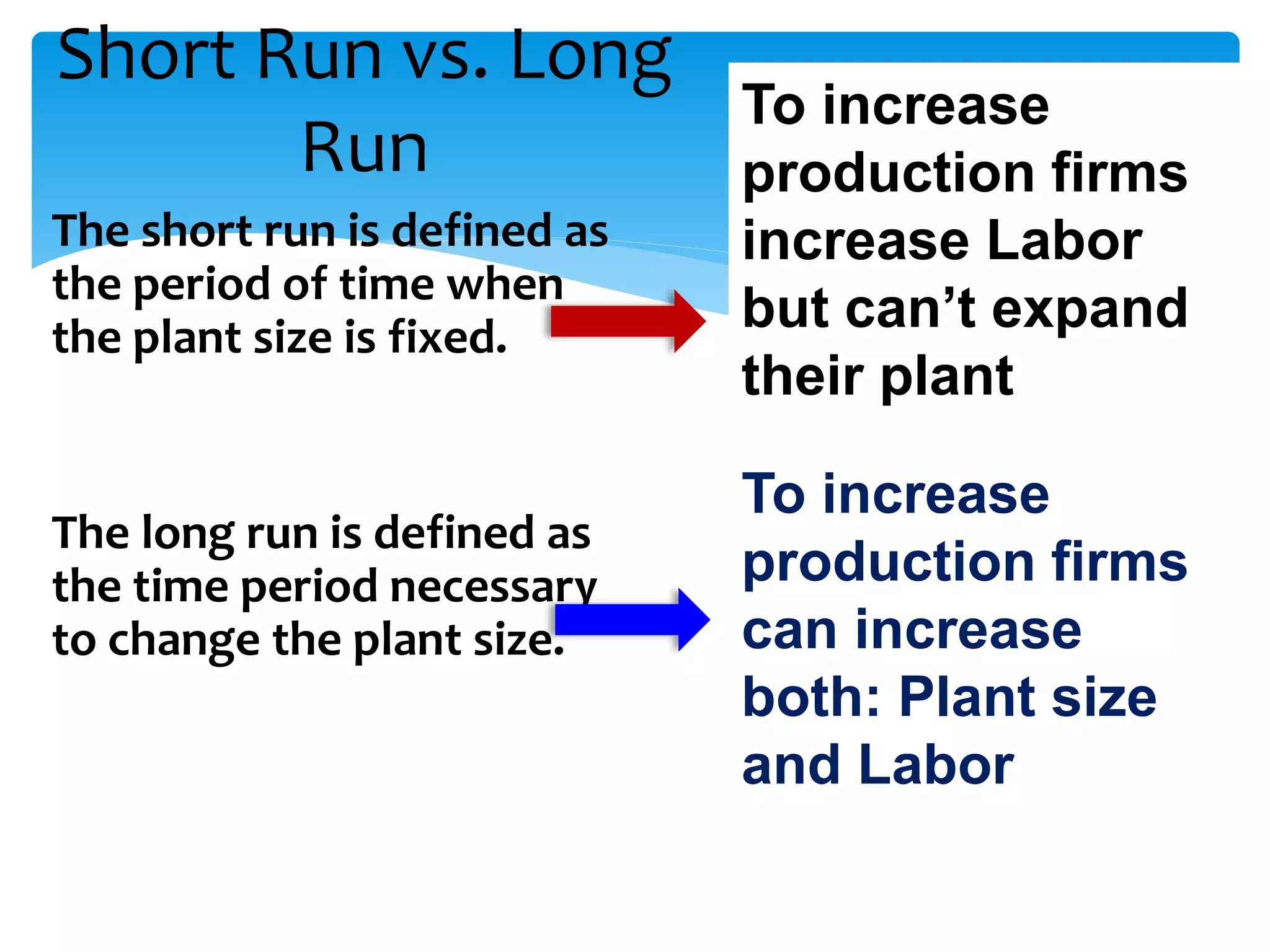
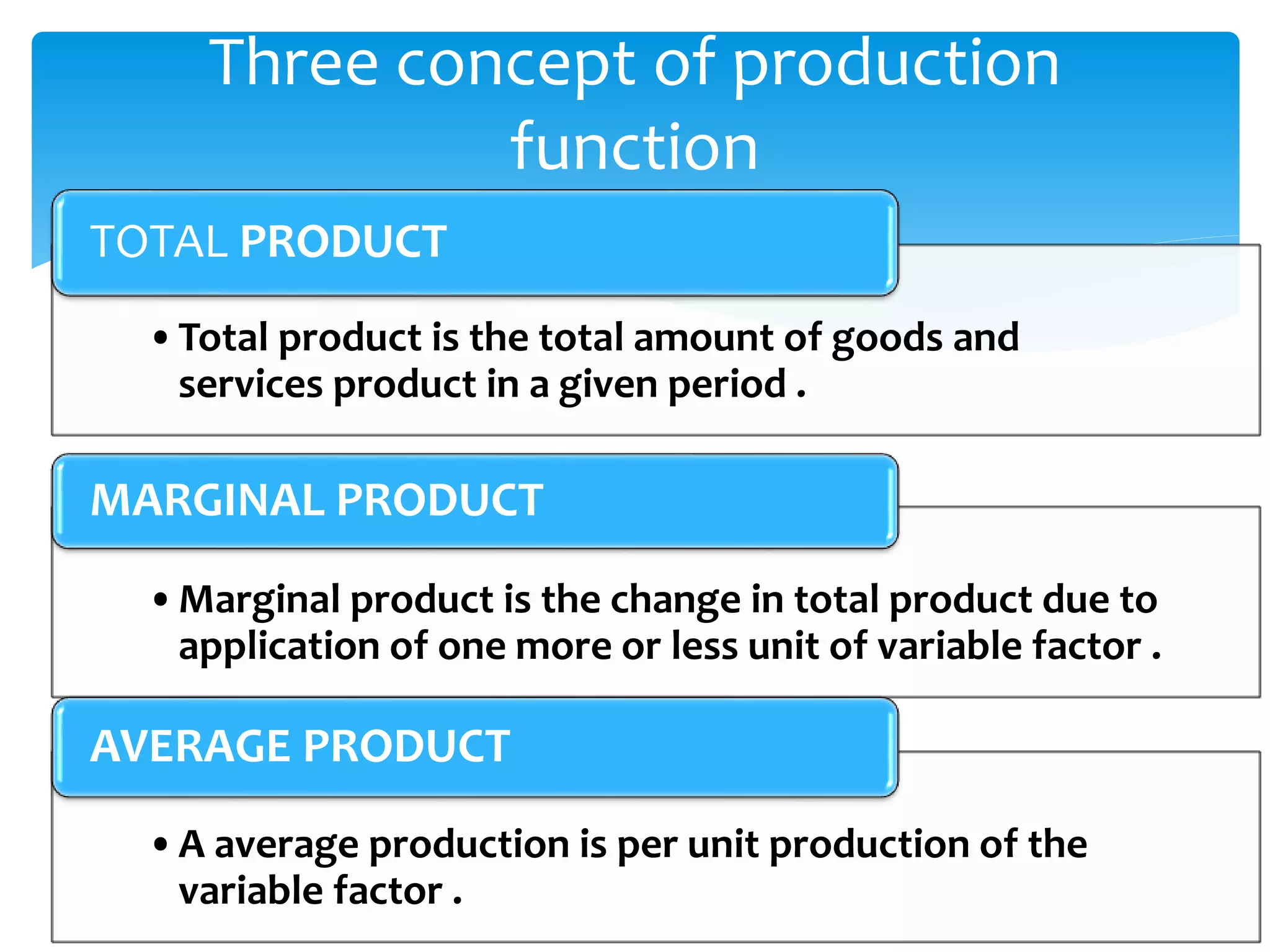
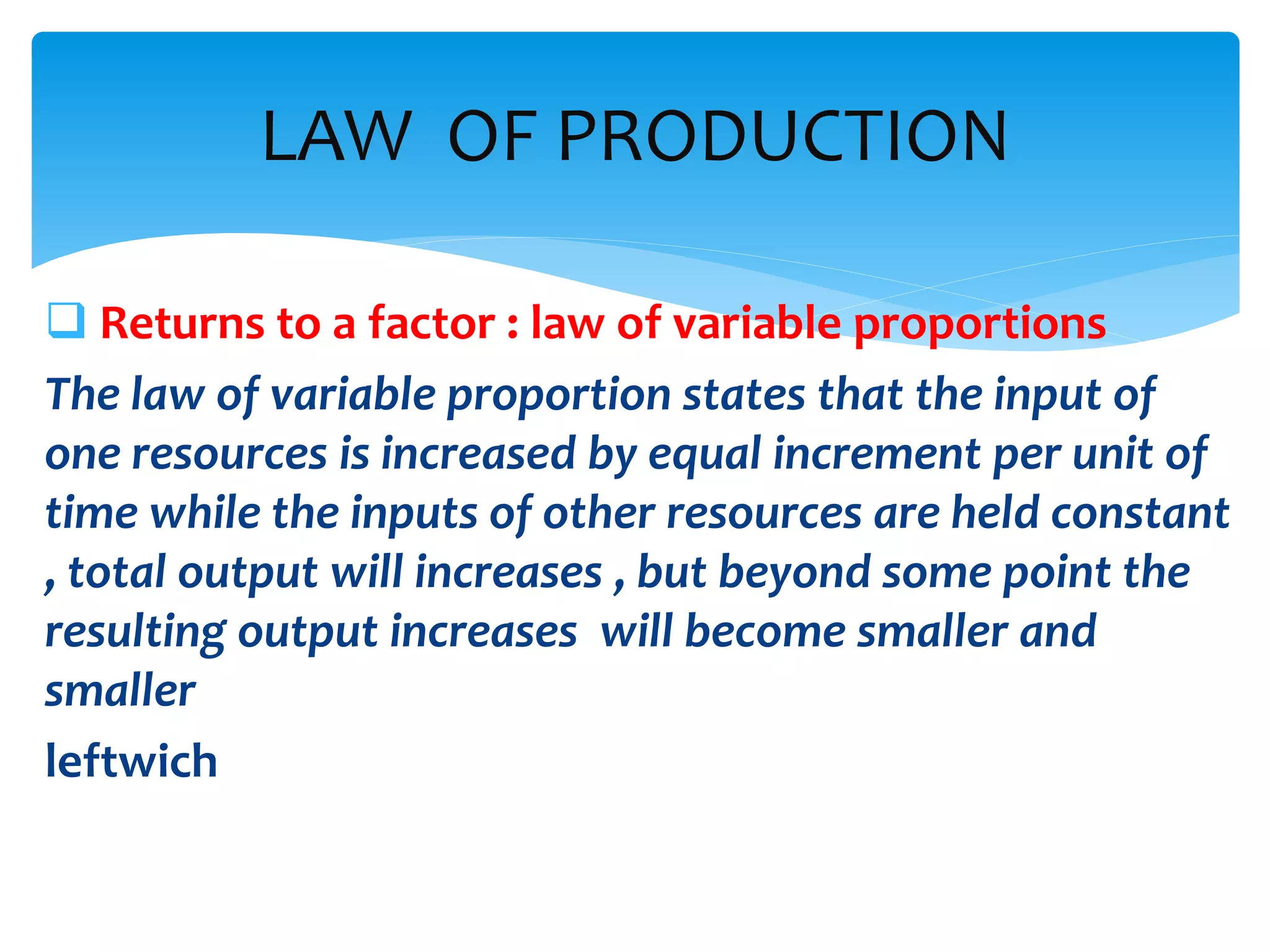
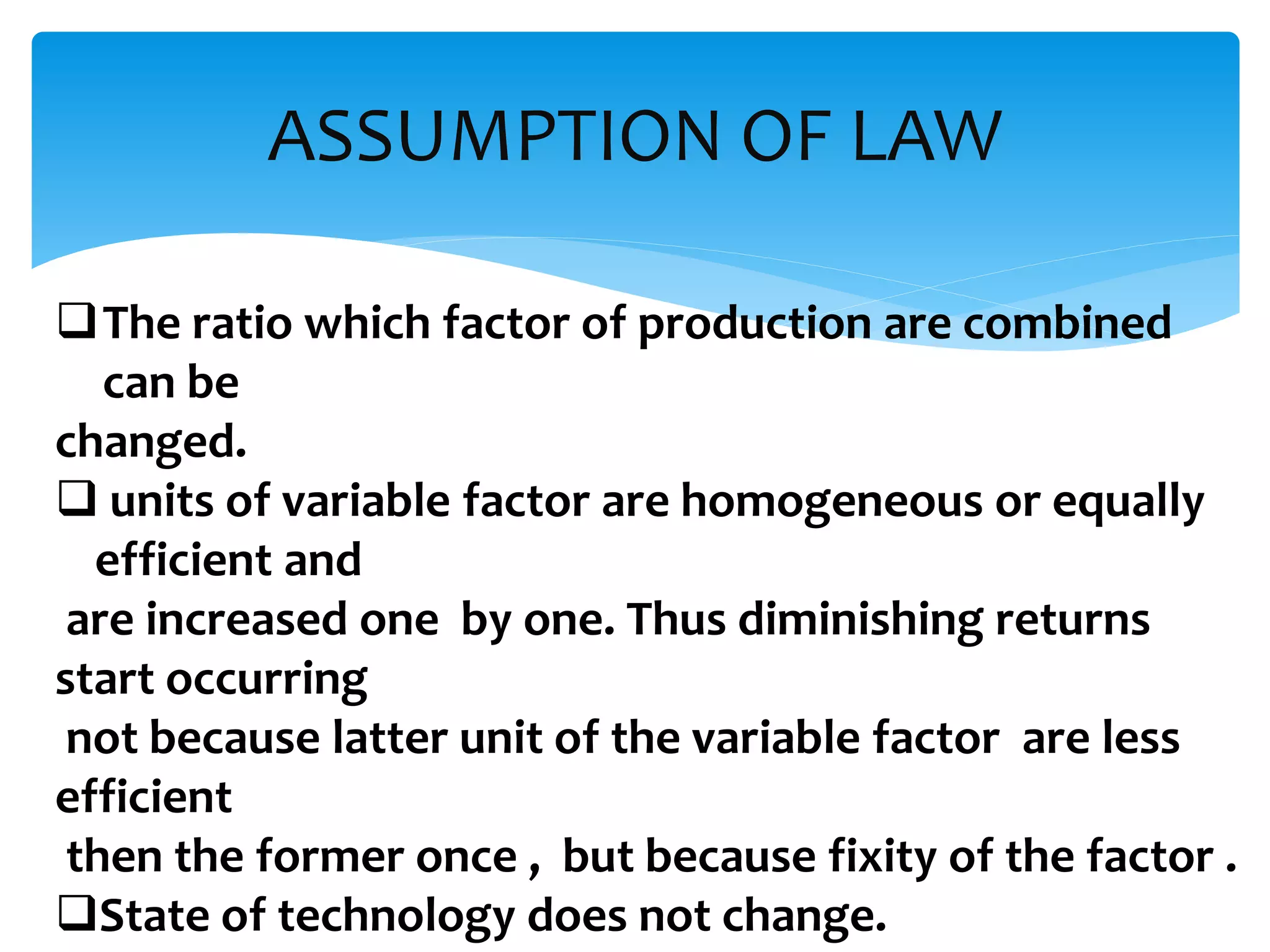
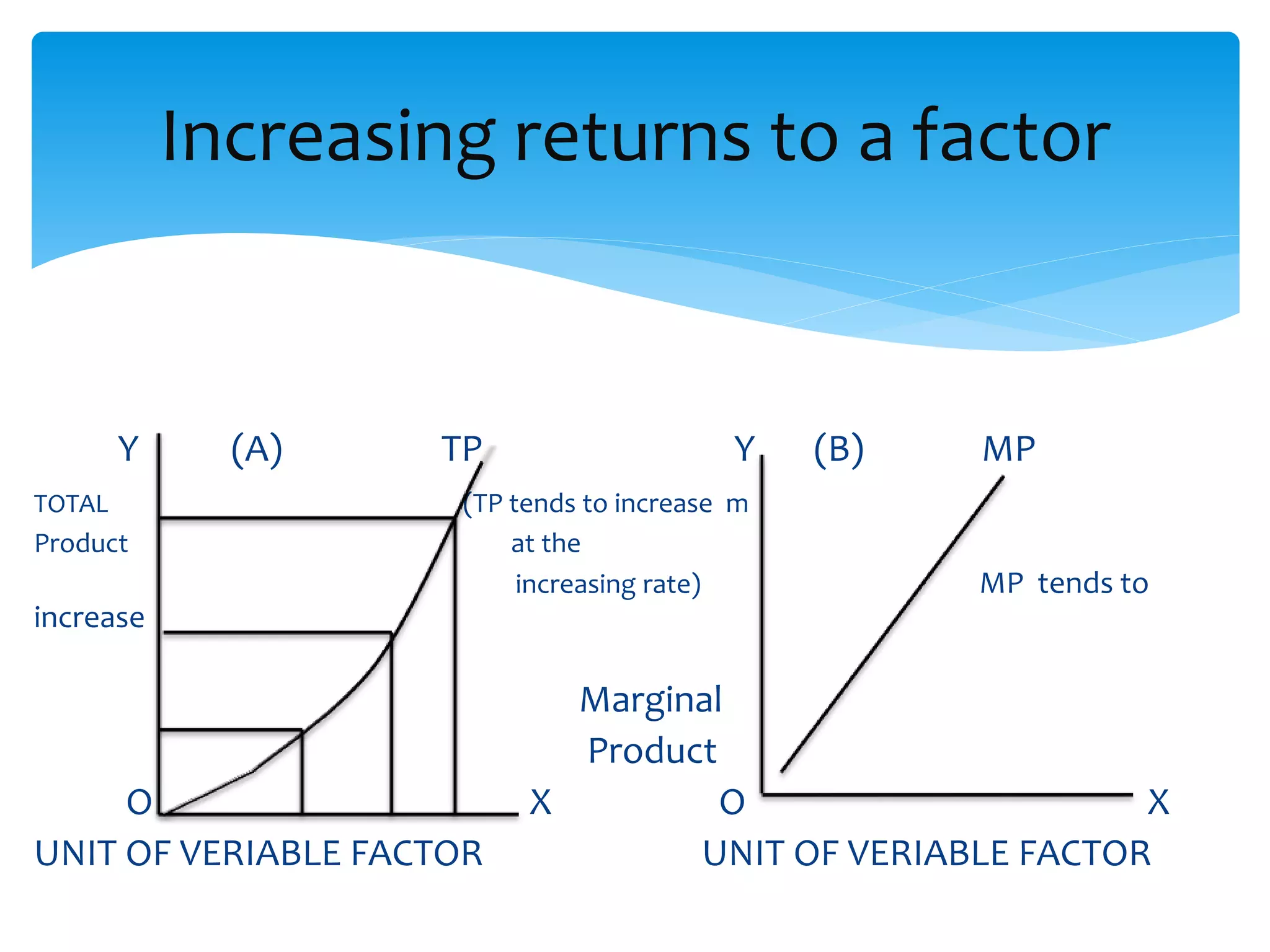
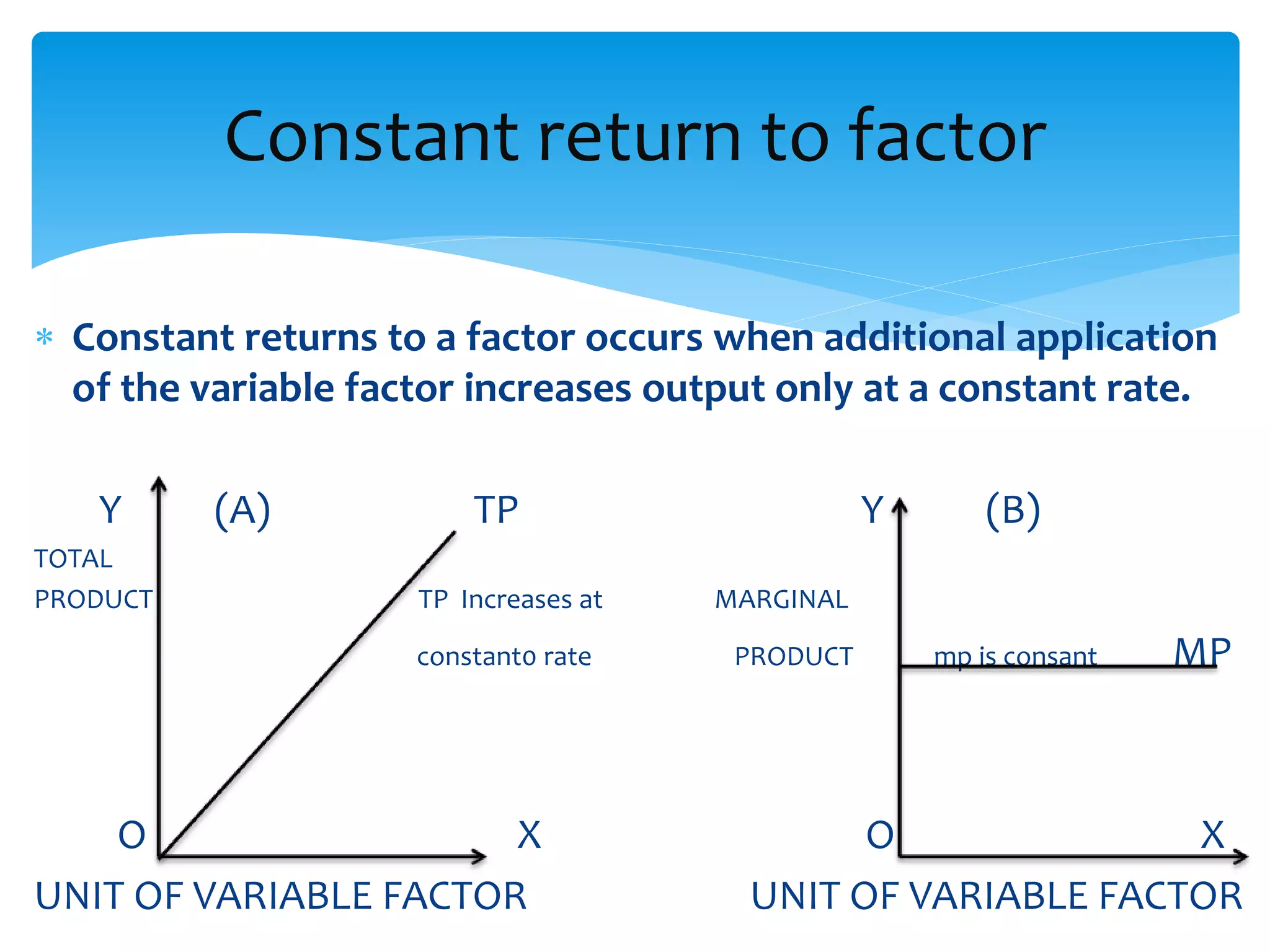
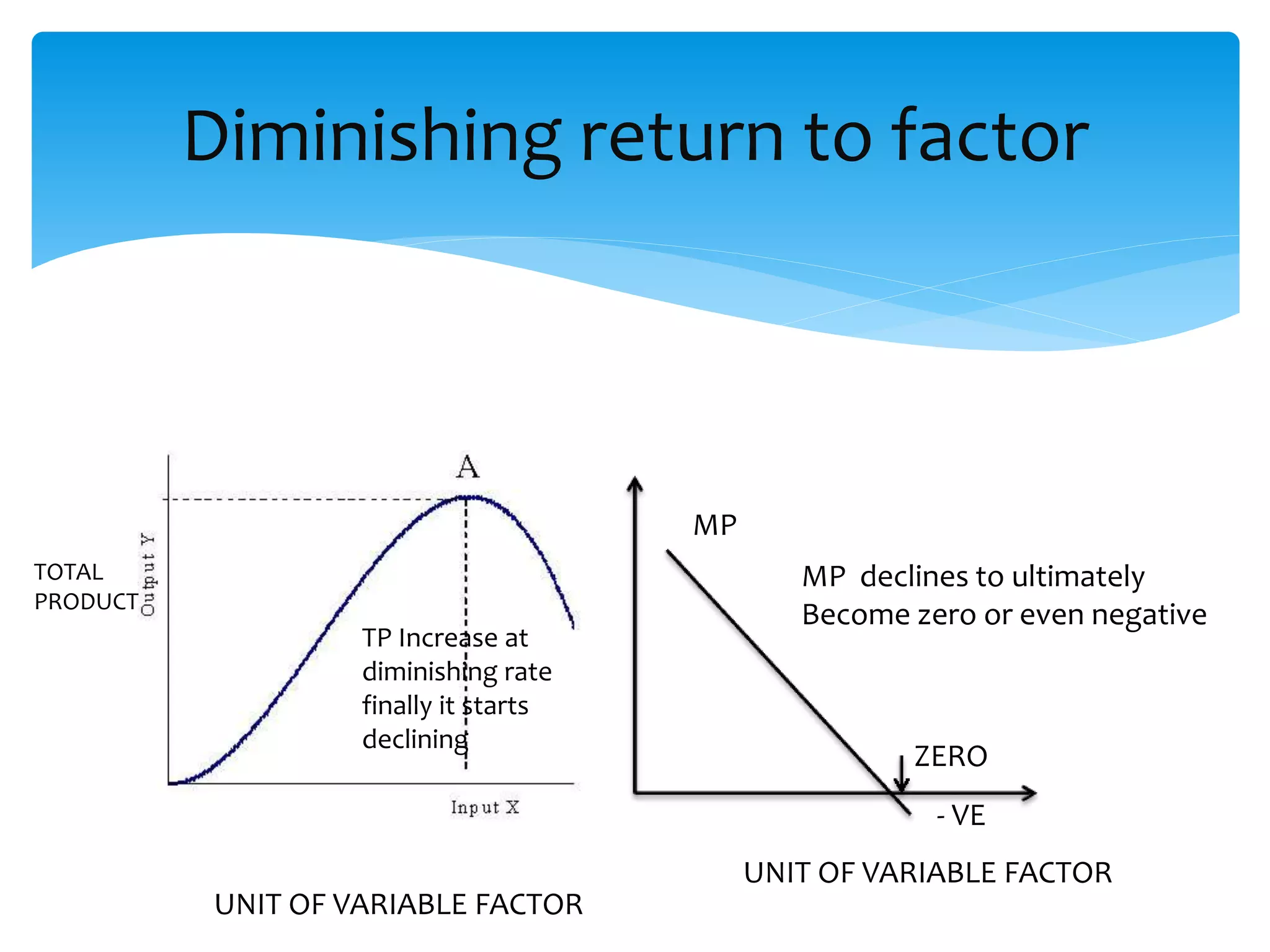
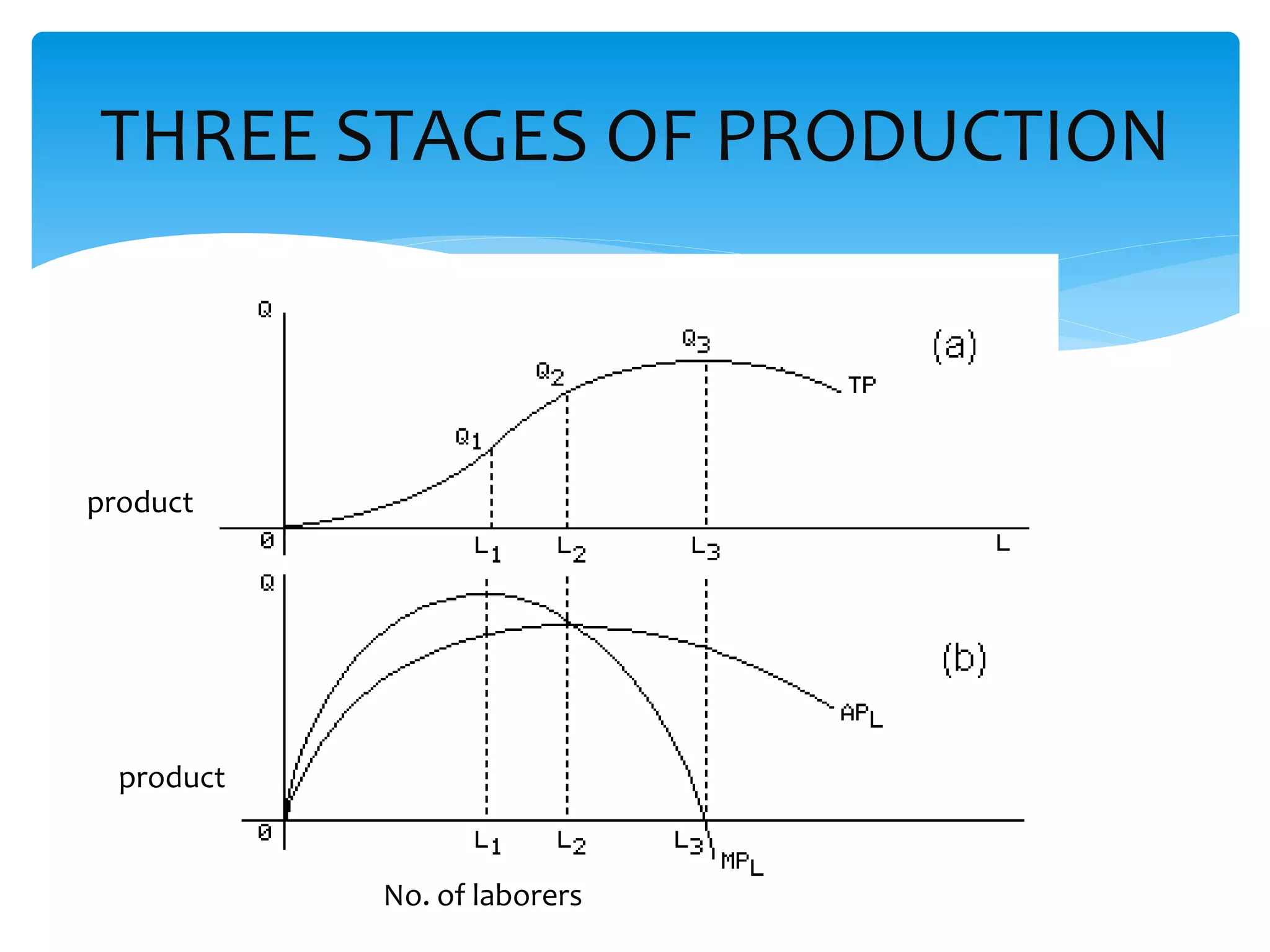
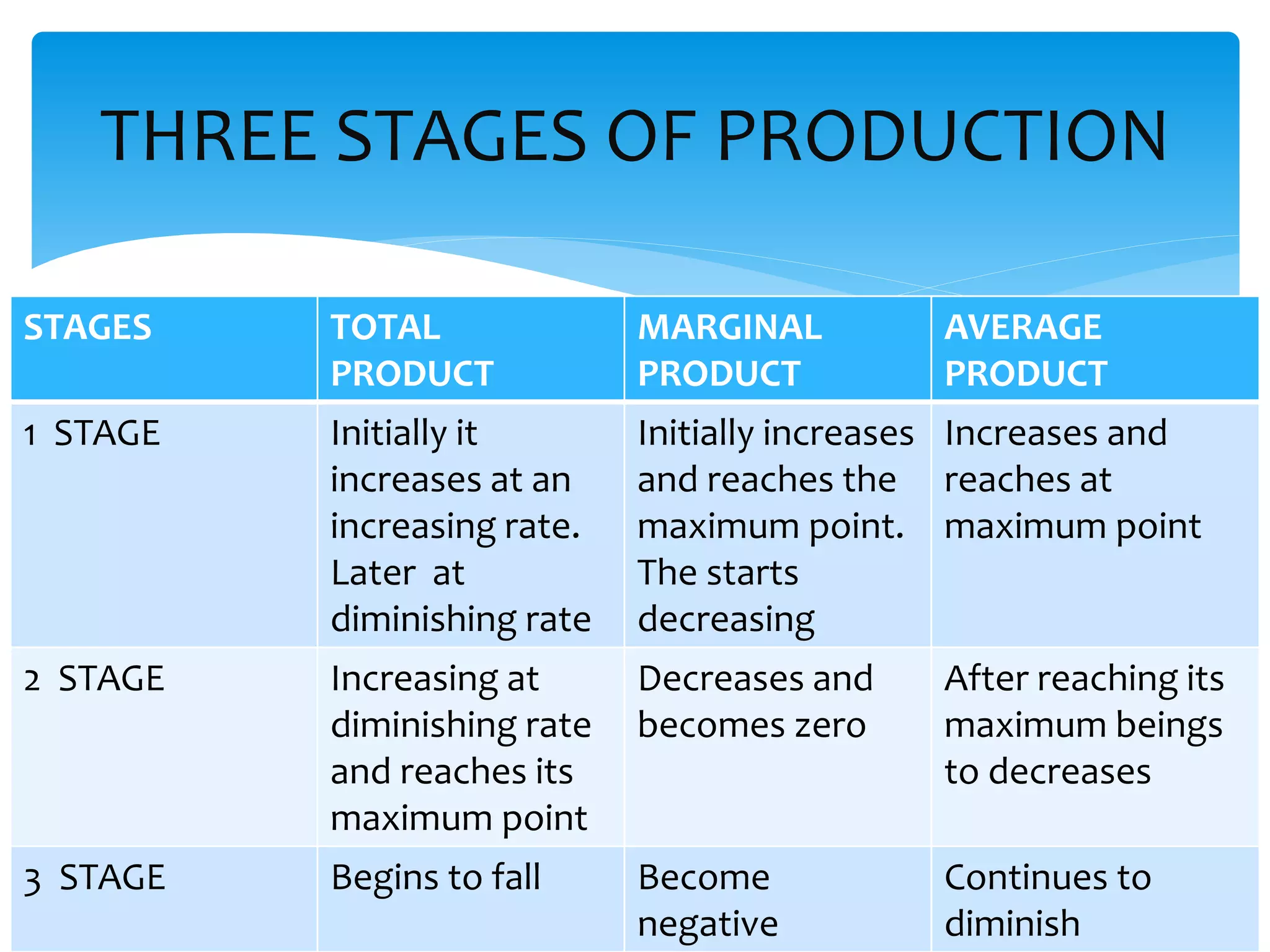
This document discusses production functions and the concept of returns to scale. It defines a production function as the relationship between a firm's output and inputs. It describes the concepts of total product, average product and marginal product. It explains the short run and long run, and the assumptions of the law of variable proportions. It discusses increasing, decreasing and constant returns to scale, and the causes of each. It also covers internal and external economies of scale, and potential diseconomies of large scale production.







![ “The term return to scale refer to the change
in output as all factor change by the same
proportion ”
RETURN TO SCALE
P = f[L,K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gurujambheshwersciencetechnologyuniversityhissar-151129042922-lva1-app6891/75/production-funcation-21-2048.jpg)