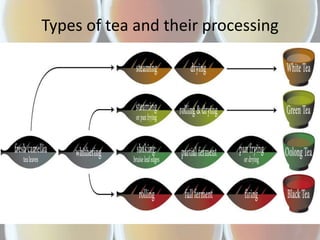
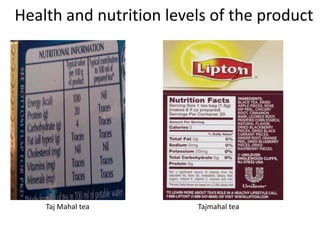
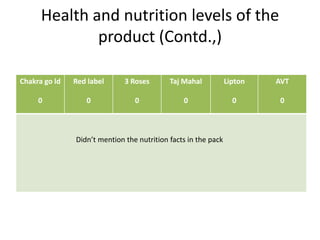
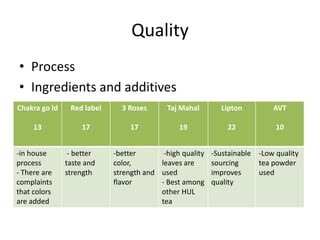
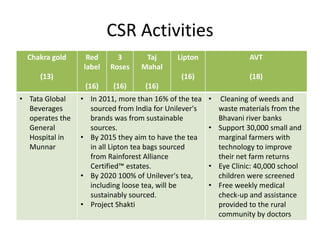
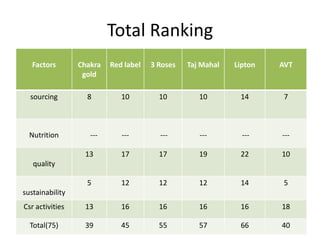
The document summarizes the processing methods and health benefits of tea. It discusses two main tea processing methods - CTC (Crush, Tear and Curl) used for tea bags, and the Orthodox method which includes withering, drying, rolling, and drying steps. It then describes each step in Orthodox tea processing including plucking, withering, disruption, oxidation, fixation, yellowing, rolling, and drying. The document also discusses the composition of tea, health benefits of tea, some risks of drinking tea, and compares milk tea to plain tea. It provides details on common tea adulterants and grading criteria for popular Indian tea brands.