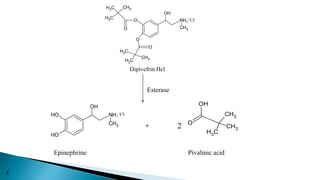
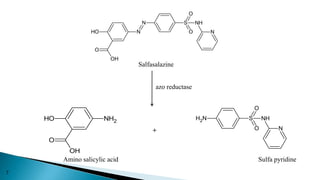
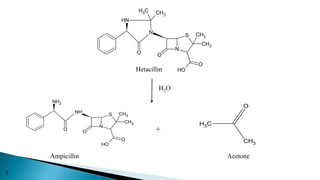
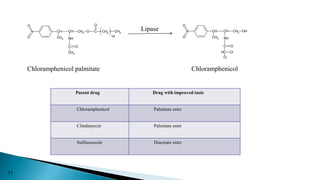
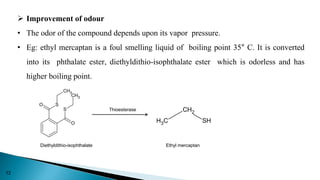
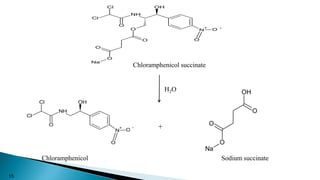
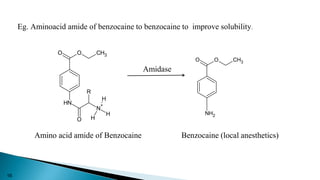
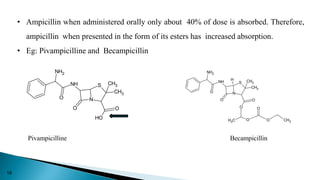
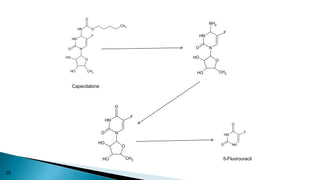
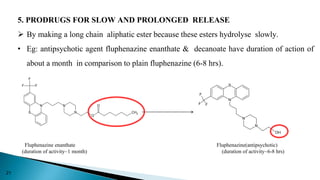
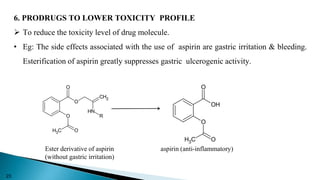
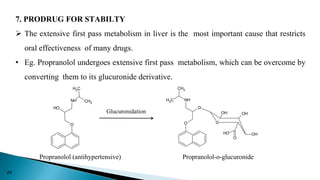
This document discusses prodrugs, which are pharmacologically inactive derivatives of active drugs that are designed to improve drug properties like solubility, absorption, and site-specific delivery. Prodrugs are converted to the active drug within the body through enzymatic or non-enzymatic reactions. The document classifies prodrugs according to their functional groups and provides examples like ester prodrugs that are hydrolyzed by esterases. It also discusses the pharmaceutical applications of prodrug design like improving patient acceptance, increasing solubility and absorption, targeting specific sites, and providing slow and prolonged drug release.