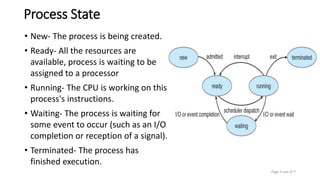
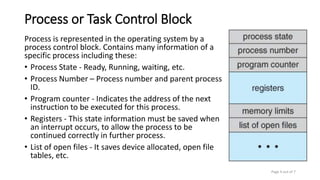
A process contains the program code, stack, data section, and heap. It is represented in the operating system by a process control block that stores information like the process state, number, program counter, registers, and open files. The operating system uses a scheduler to select processes from memory and choose among ready processes, switching between them through context switching that saves the current process control block and loads the next one.