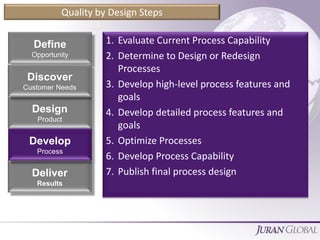
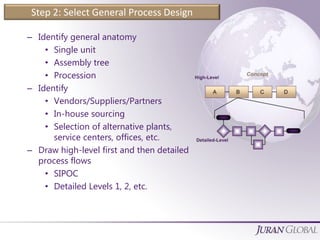
The document outlines a systematic approach to process innovation consisting of four steps: planning, transferring, operational management, and quality by design. It emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs, establishing process capabilities, and optimizing processes to ensure effectiveness, efficiency, and timeliness. Additionally, it provides a detailed guide on identifying process features and goals, setting performance targets, and involving cross-functional teams in the design process.