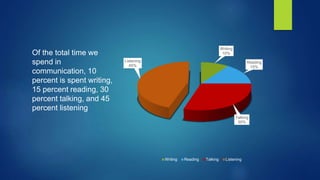
Listening is an important yet undervalued part of communication that involves hearing, attending to, interpreting, and responding to messages. There are different types of listening like discriminative, comprehensive, critical, and empathetic listening suited to various situations. Effective listening techniques include making eye contact, keeping an open mind, not interrupting, and responding with body language. Barriers to listening can be environmental distractions, physical impairments, linguistic challenges, psychological factors, and uninteresting content.