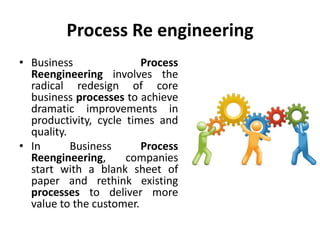
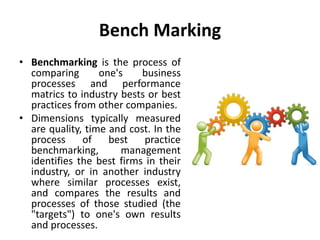
The document discusses various methodologies for process improvement, including Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), Business Process Reengineering (BPR), and Benchmarking. It highlights the shift from traditional organizational structures to more empowered team-based approaches, emphasizing the importance of customer value and effective performance measures. Additionally, it touches on Sociotechnical Systems, which focus on the interaction between people and technology in the workplace.