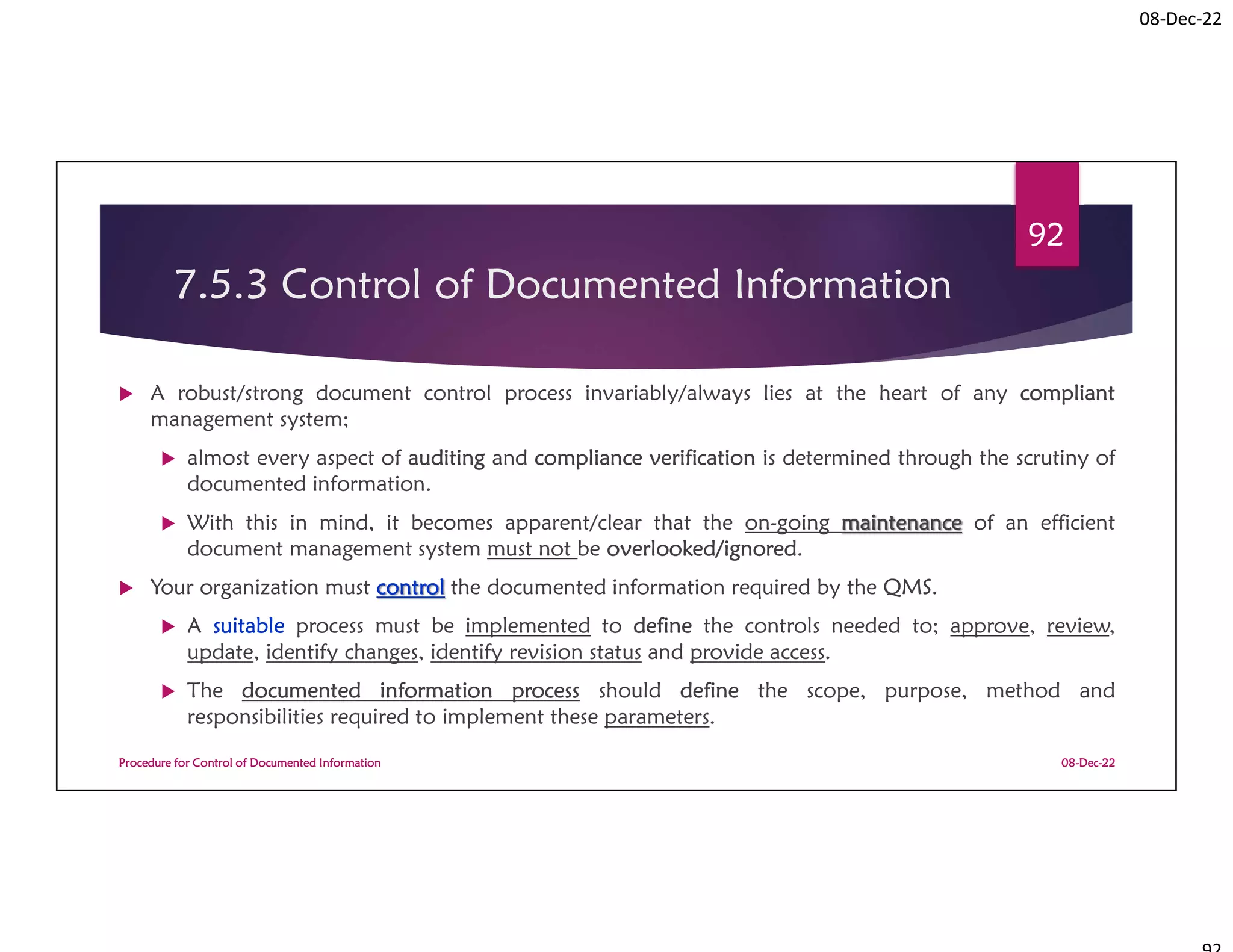
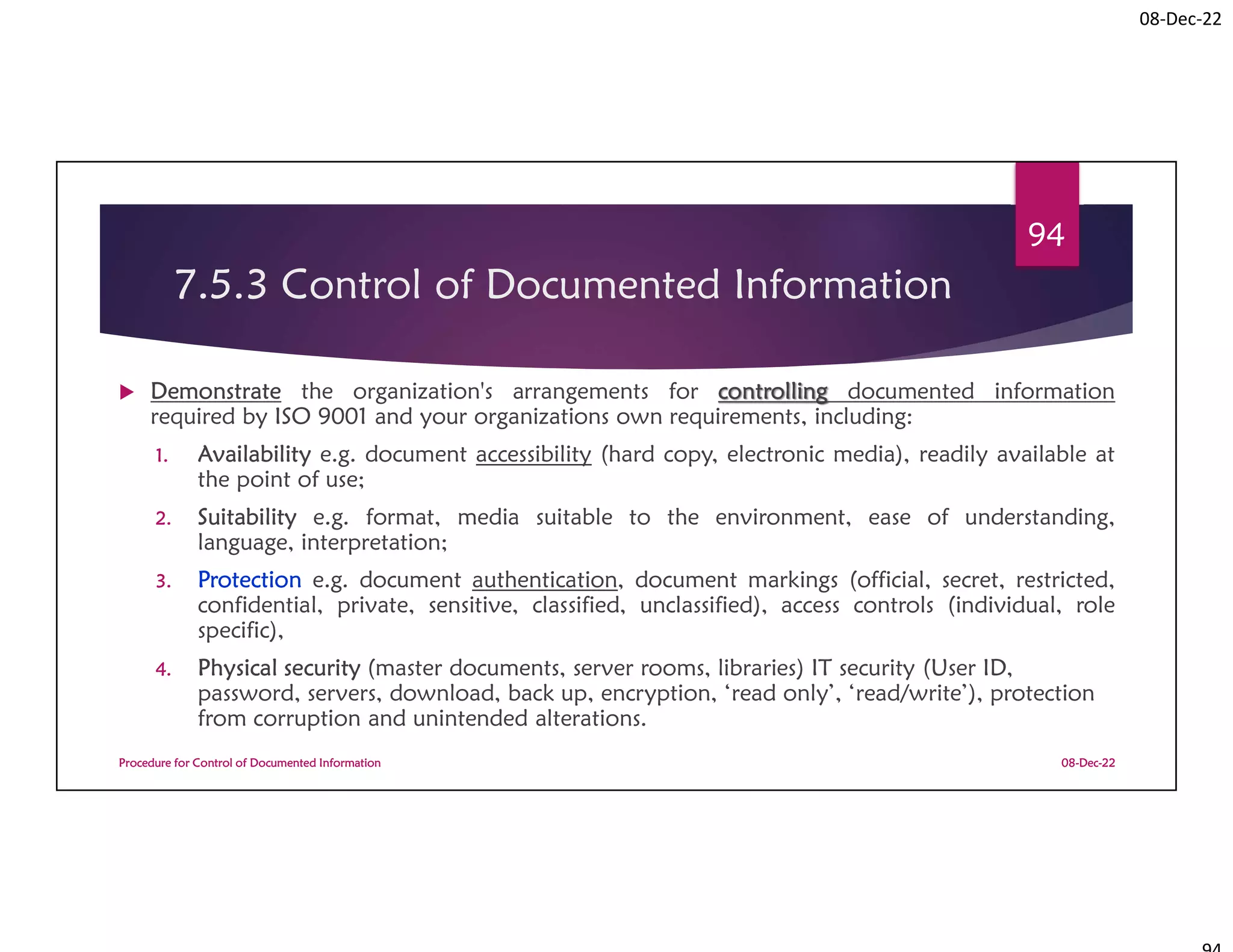
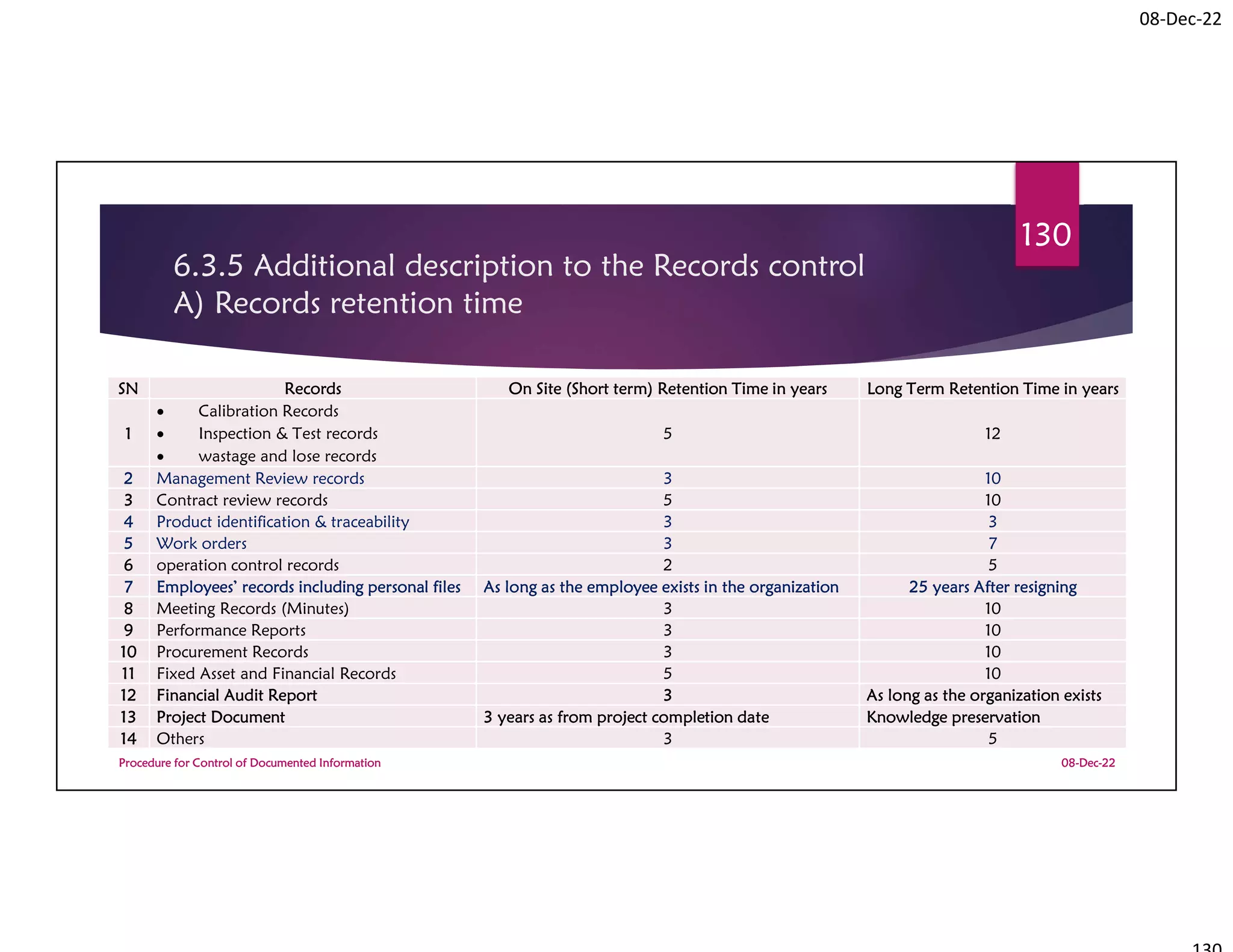
This document summarizes a workshop on ISO 9001:2015 quality management system documentation requirements. The workshop objectives were to improve documentation practices, brief attendees on ISO 9001 clauses and principles, and orient them on procedures for controlling documented information. It covered topics like the importance of documentation, the ISO definition of documented information, and the requirement to maintain control of documents and records. A procedure for controlling documented information was also presented.





























































![08-Dec-22
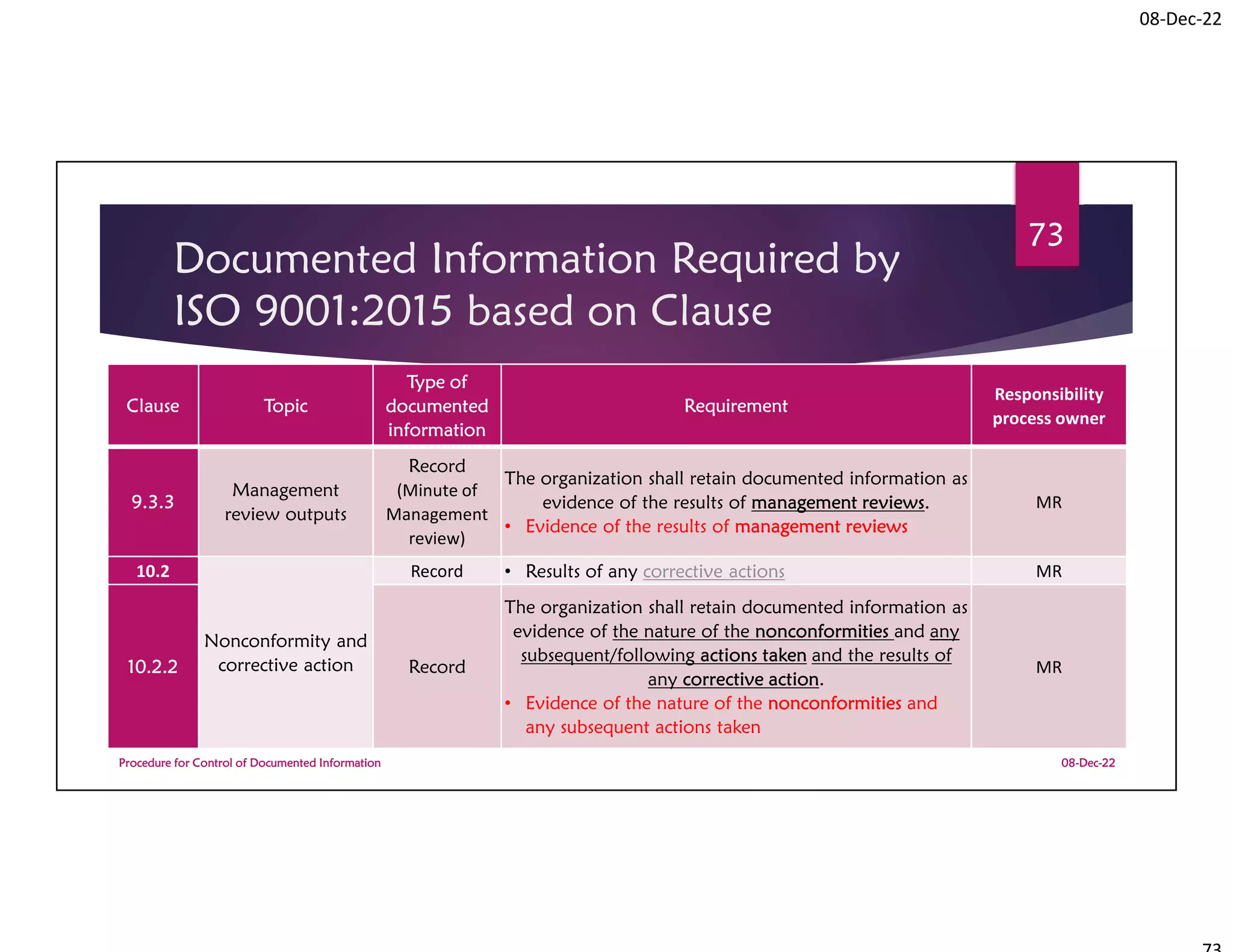
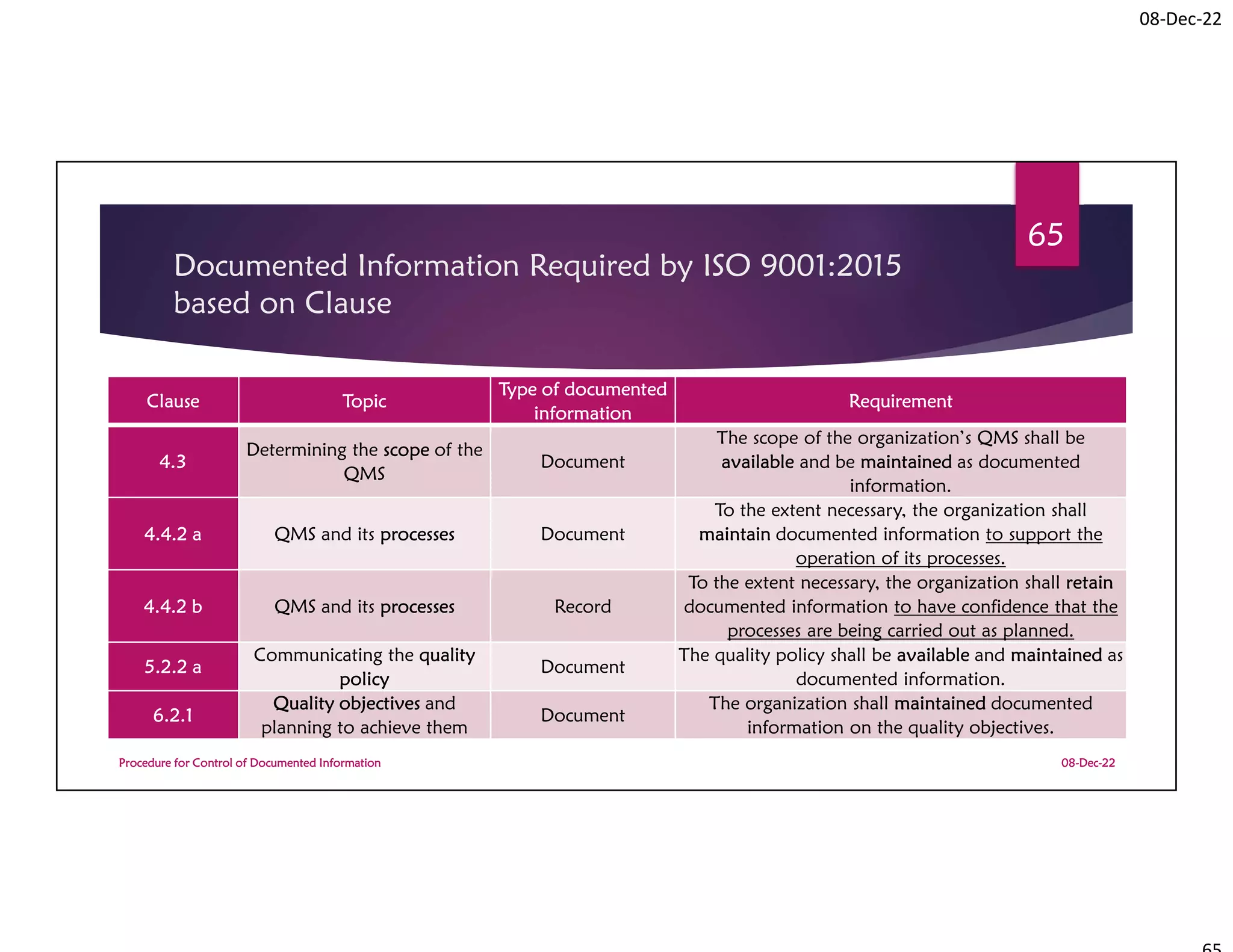
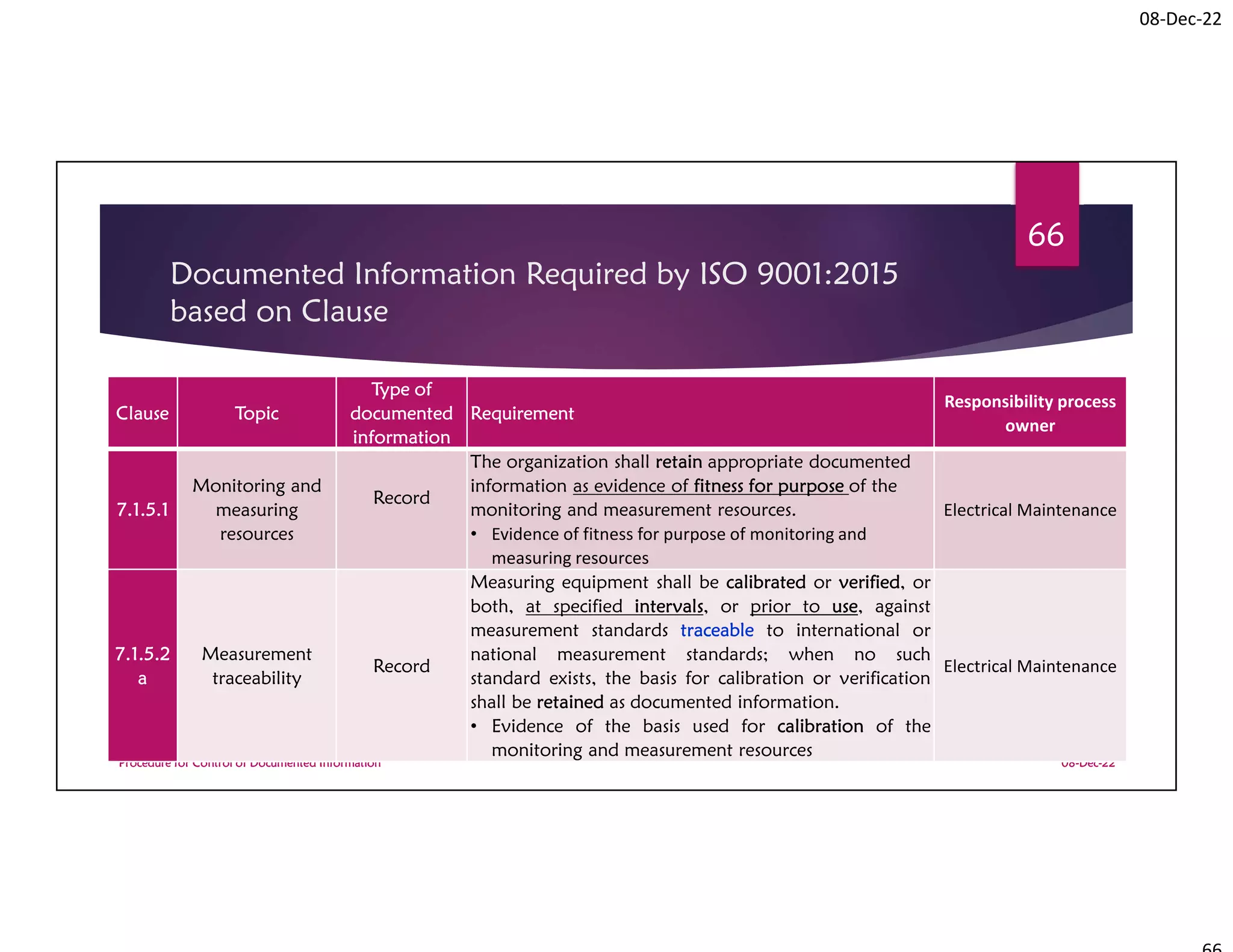
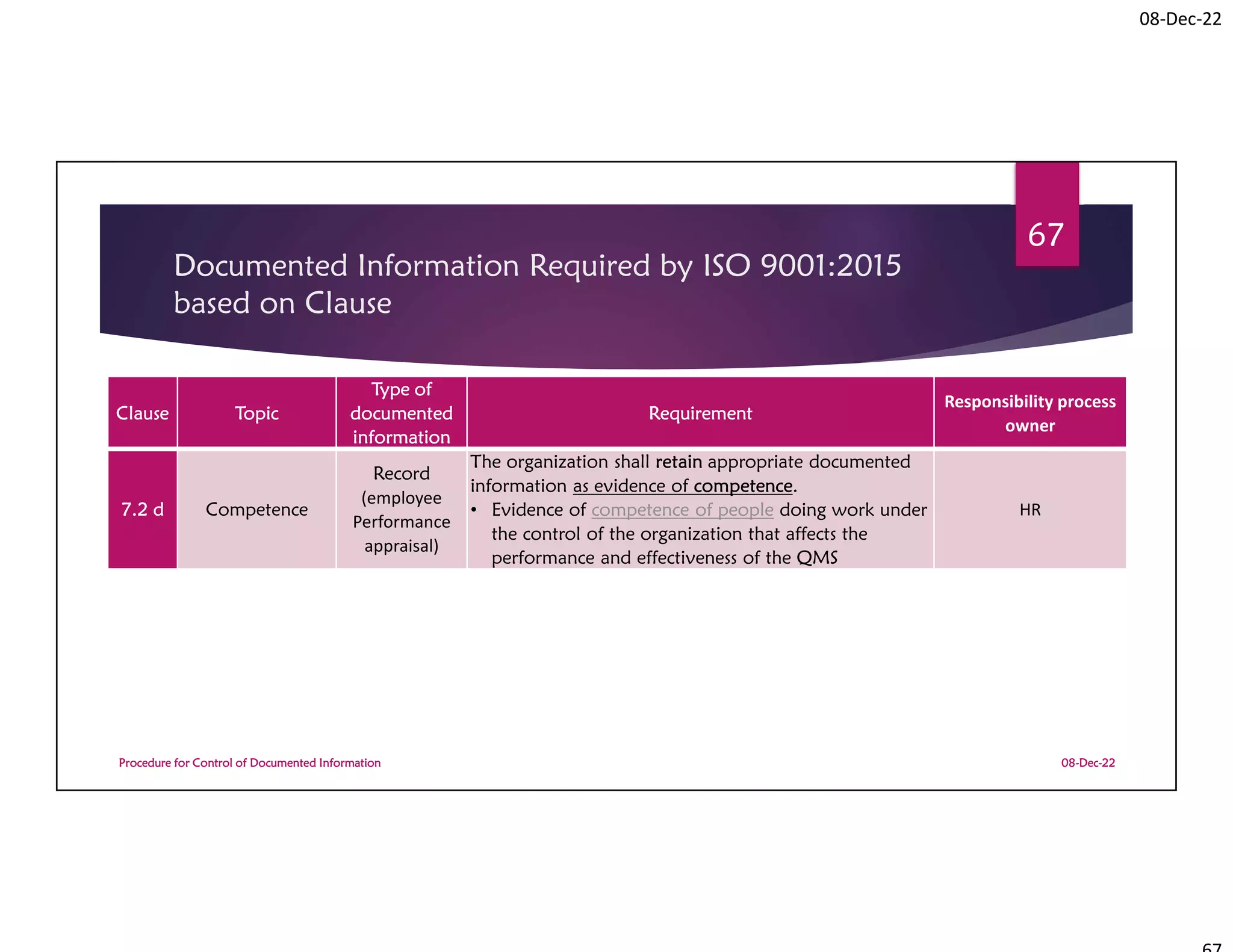
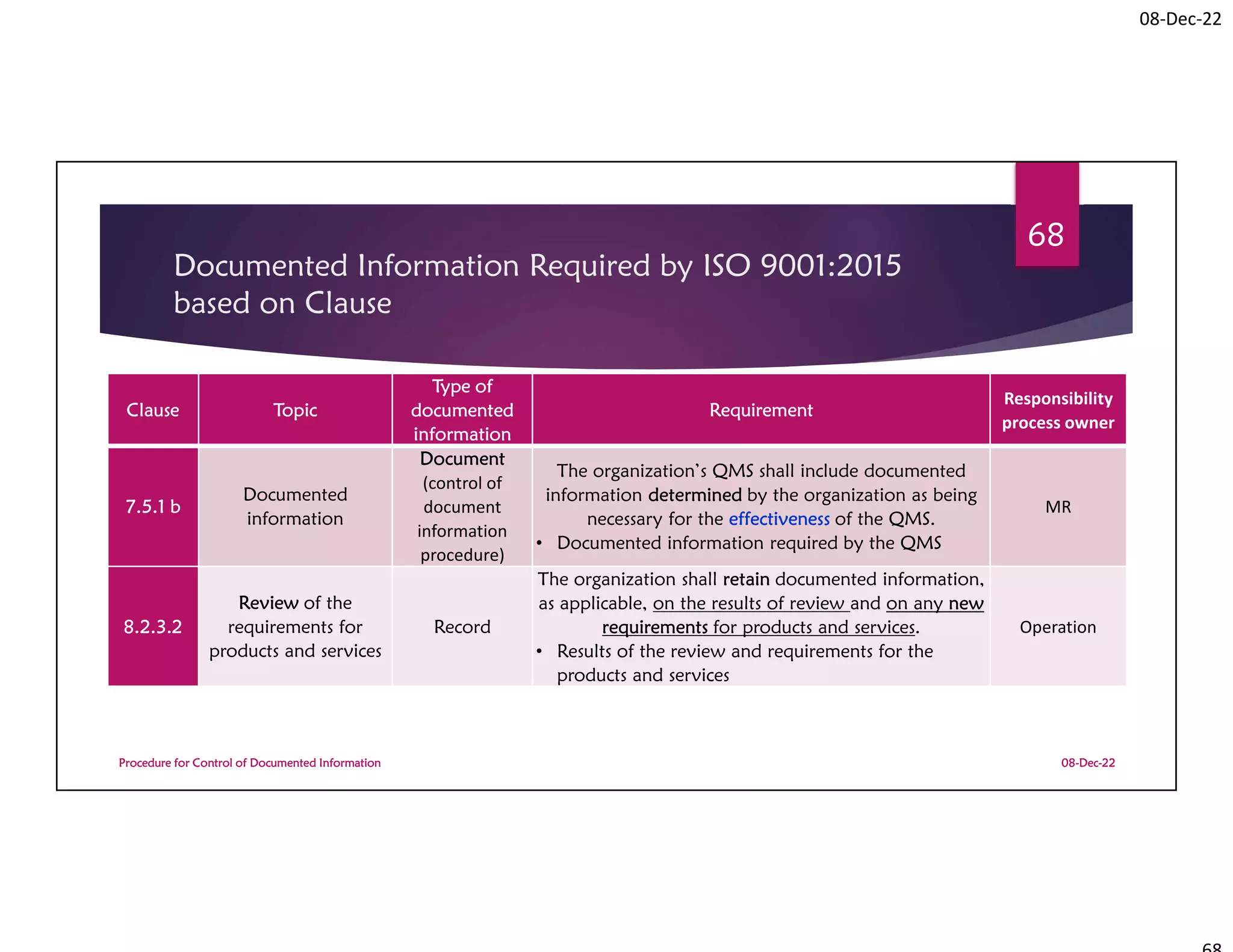
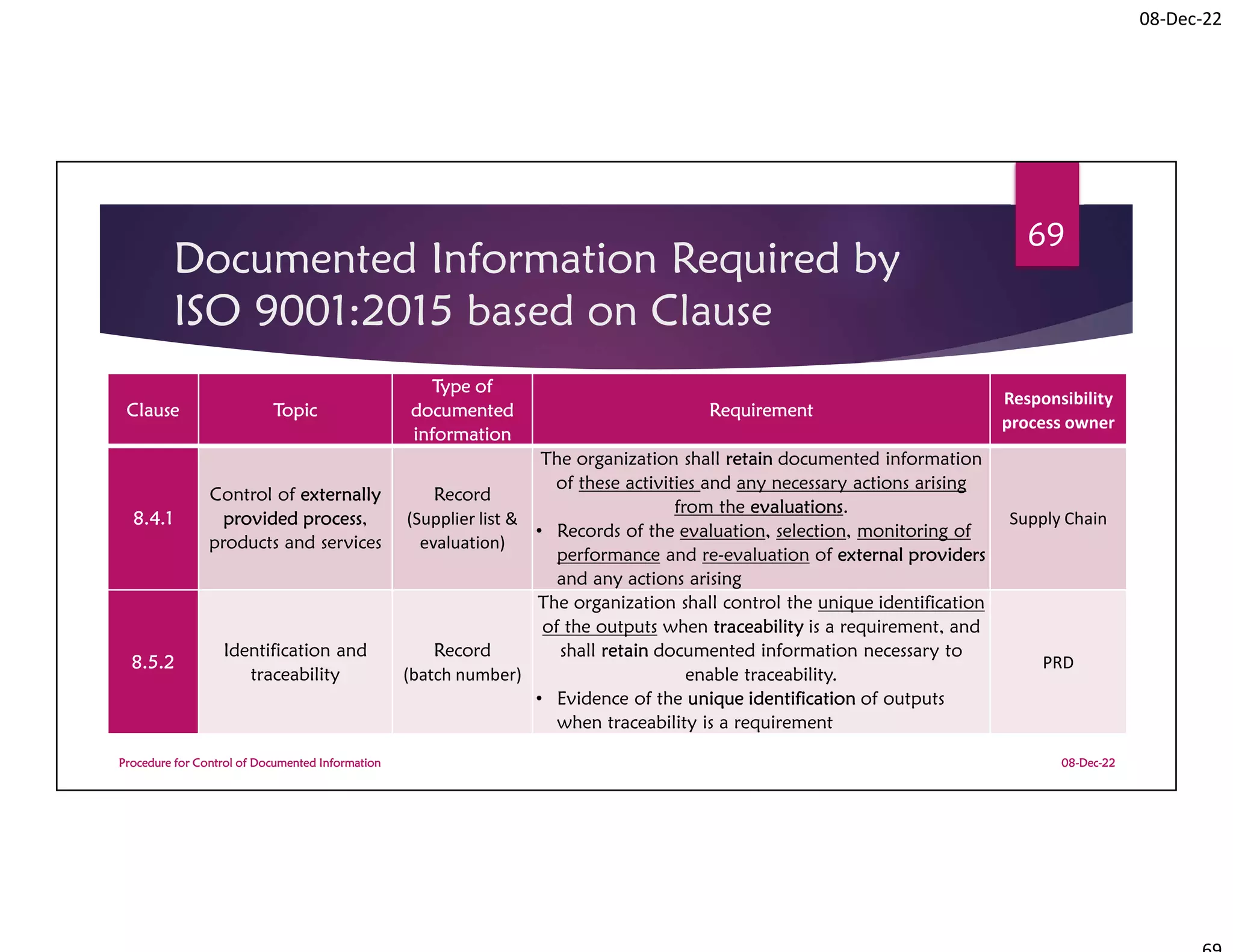
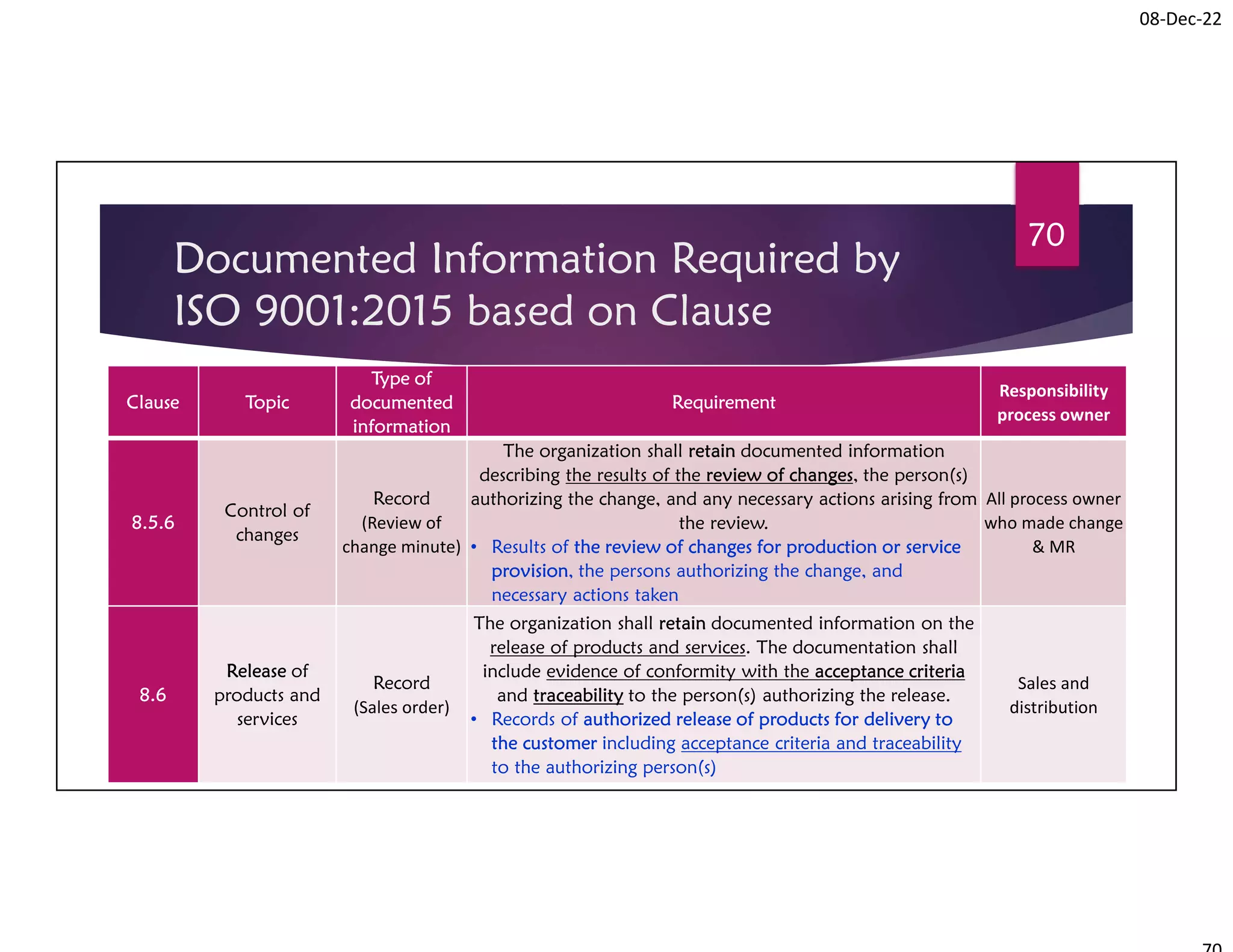
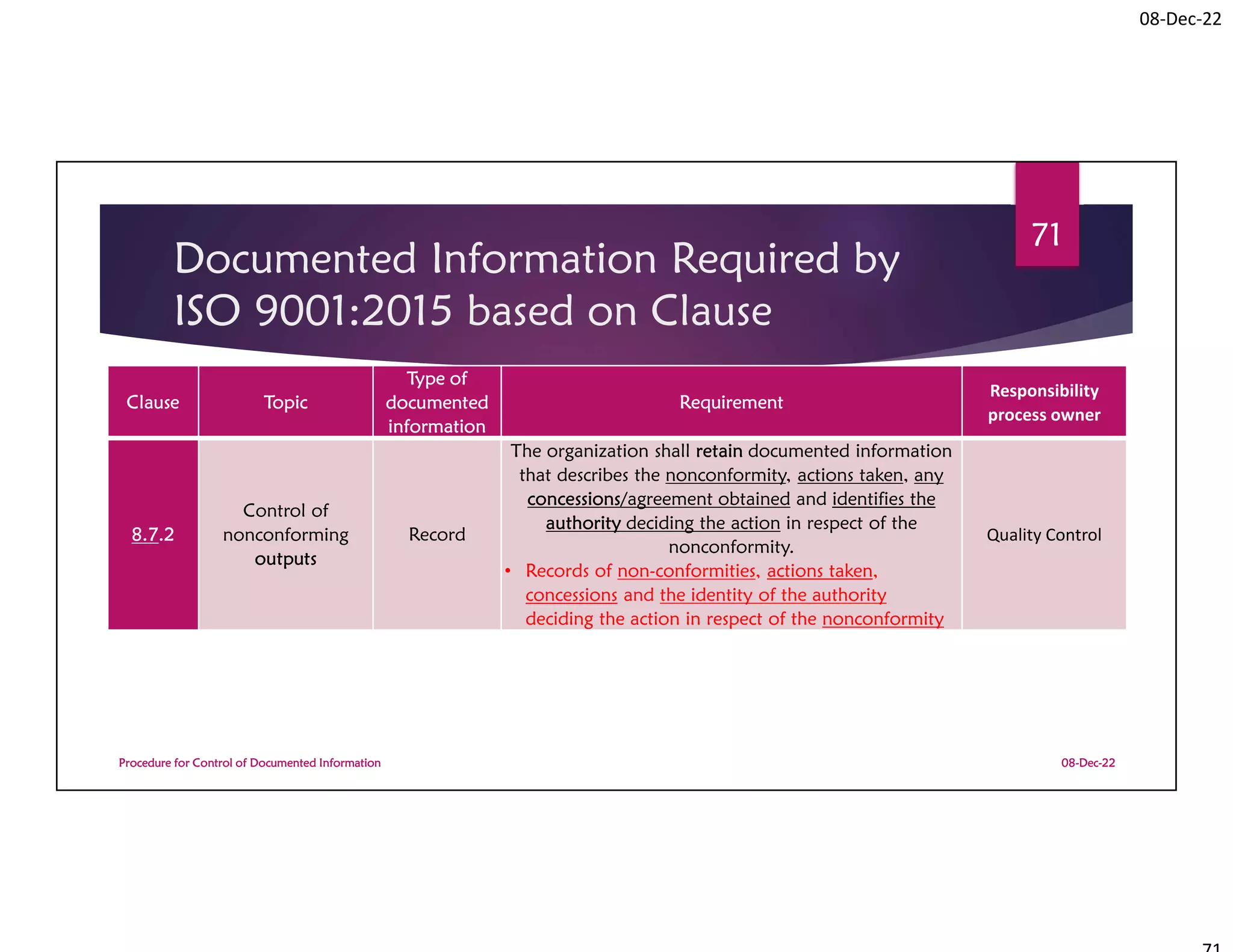
Documented Information Required by
ISO 9001:2015 based on Clause
08-Dec-22
Procedure for Control of Documented Information
72
Clause Topic
Type of
documented
information
Requirement
Responsibility
process owner
9.1.1
Monitoring,
measurement,
analysis and
evaluation
Record
(monthly and
annual
performance
report)
The organization shall retain documented information as
evidence of the results [of QMS performance
evaluation].
• Results of the evaluation of the performance and the
effectiveness of the QMS
All operational
report
9.2.2 f Internal audit
Record
(internal audit
program &
report)
The organization shall retain documented information as
evidence of the implementation of the audit program
and the audit results.
• Evidence of the implementation of the audit
programme and the audit results
MR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/procedureforcontrolofdocumentedinformationfortraniee1-230416173233-17e63101/75/Procedure-for-control-of-Documented-Information-for-traniee-1-pdf-72-2048.jpg)