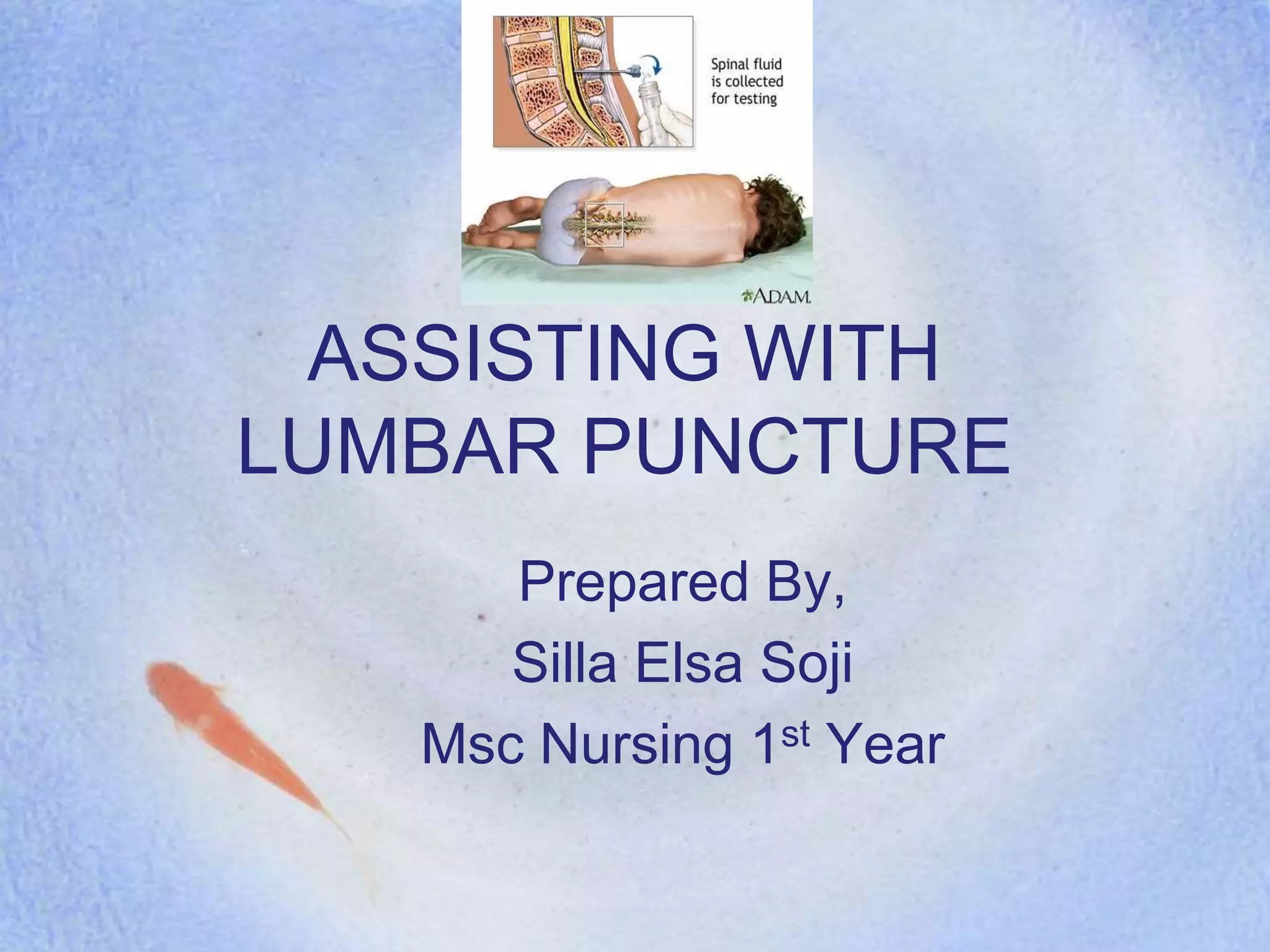
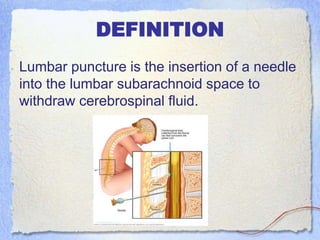
The document outlines the procedure and indications for performing a lumbar puncture, which involves inserting a needle into the lumbar subarachnoid space to withdraw cerebrospinal fluid. It details the necessary materials, patient preparation, and monitoring, as well as contraindications and potential complications such as CSF leakage and infection. The document also emphasizes the importance of post-procedure care, including keeping the patient flat for a specified time and monitoring for any adverse effects.