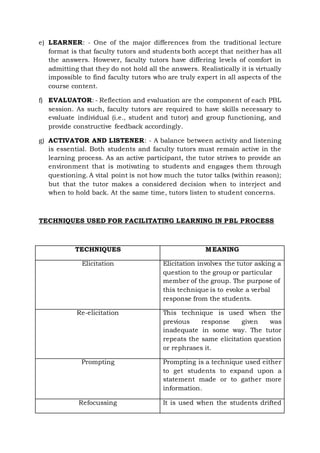
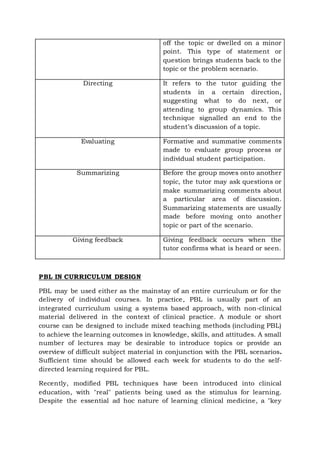
Problem-based learning (PBL) is a student-centered instructional strategy where students collaboratively solve problems and reflect on their experiences. It shifts the focus from teachers to students and encourages students to take responsibility for their own learning. PBL can be used to enhance content knowledge and develop skills like communication, problem-solving, and self-directed learning. In PBL, students work in small groups with a tutor to identify learning needs from real-world problems and independently research the issues to find solutions. Assessment focuses on higher-order thinking versus factual recall alone. While PBL has advantages like active learning and motivation, it also has disadvantages such as resource intensive nature and information overload for students.