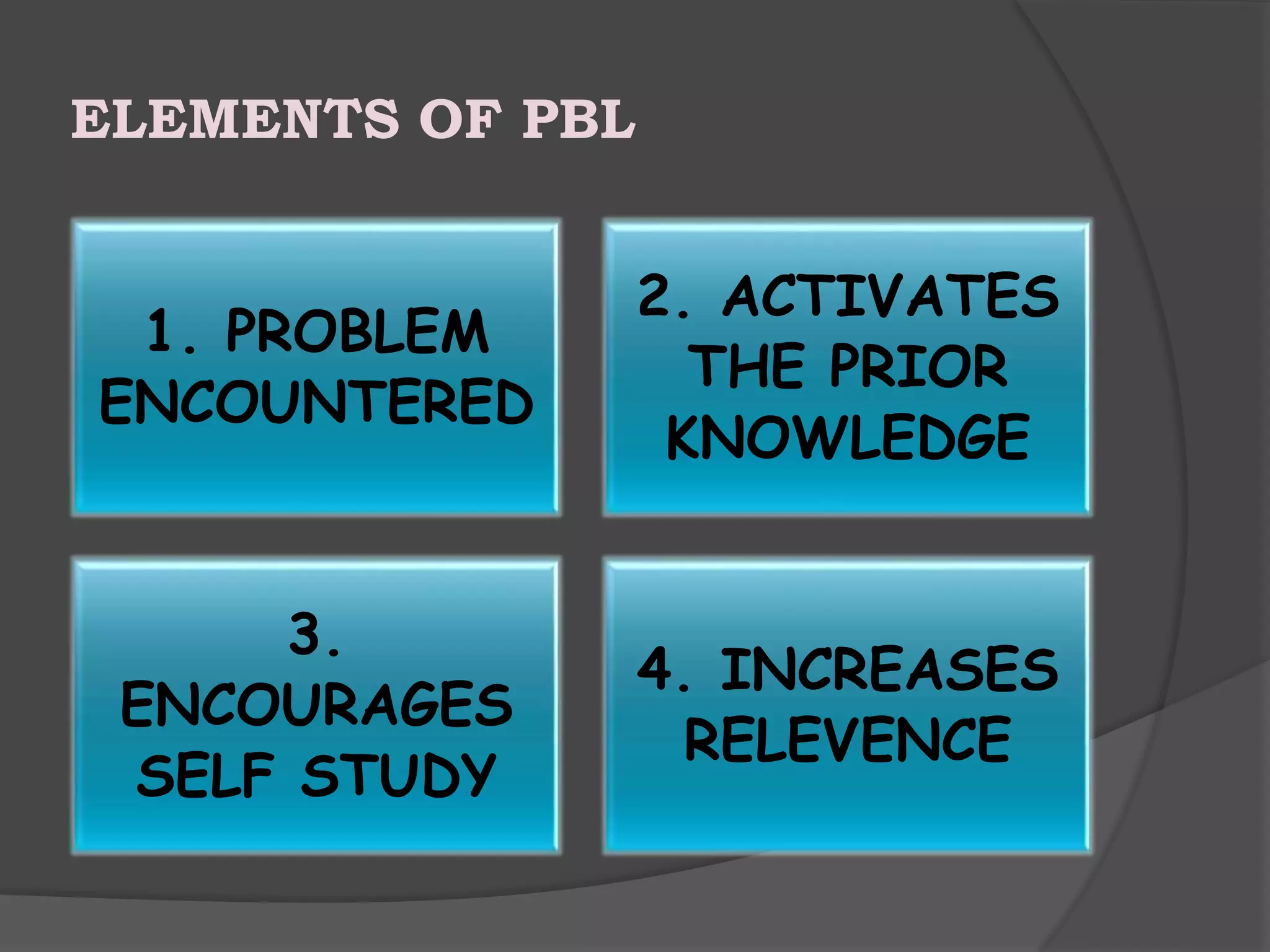
Problem-based learning (PBL) is an instructional method that presents students with real-world problems to solve. It develops critical thinking and self-directed learning skills. Key aspects of PBL include students working in small groups on an open-ended problem, with teachers acting as facilitators rather than lecturers. PBL aims to develop problem-solving, self-directed learning, collaboration, and integration of knowledge across different subject areas. Groups have assigned roles like leader, scribe, and members to keep discussions organized and on track. While PBL enhances skills like communication and lifelong learning, it also requires significant time and effort from both students and teachers.