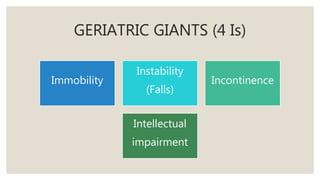
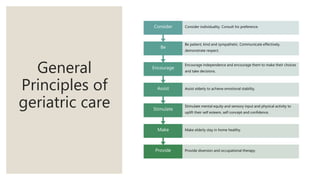
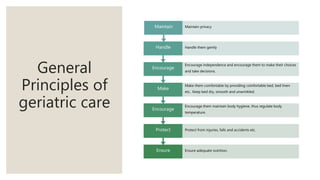
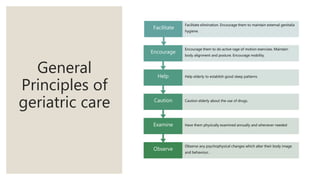
This document discusses geriatric care and nursing. It begins by defining geriatrics as focusing on healthcare for elderly patients. Geriatric nursing involves nursing care for older adults in various settings like homes, hospitals, and nursing homes. The document then covers aging processes and changes that commonly occur in body systems with age like sensory, cardiovascular, respiratory and musculoskeletal changes. It discusses theories of aging and factors affecting aging. Key principles of geriatric care are maintaining health, early disease detection, prevention, and independence. A comprehensive geriatric assessment evaluates areas like health history, physical and mental status, social support, safety, and integrated functioning.