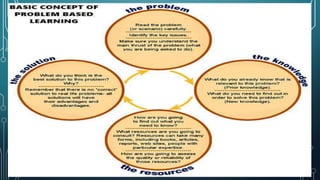
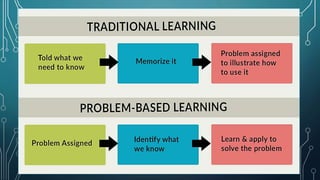
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) is an educational approach that encourages students to work in groups to solve real-world issues while developing self-directed learning skills. Established by Howard Barrows in 1986, PBL emphasizes a learner-centered environment with collaborative work, where teachers act as facilitators, and has principles focusing on independence, group learning, and the use of diverse materials. While PBL enhances problem-solving and communication skills, it can pose challenges like information overload and difficulties in assessment.