This document discusses key concepts in probability and information theory, including:
- Random variables that can take on discrete or continuous states, described by probability mass functions or probability density functions.
- Common probability distributions like the Bernoulli, Gaussian, and exponential distributions.
- Information theory concepts like entropy, Kullback-Leibler divergence, and how to structure probabilistic models as directed or undirected graphs.









![Expectation(기댓값), Variance(분산) and Covariance(공분산)
Expectation
𝔼 𝑥~𝑝 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 𝑃 𝑥 𝑓(𝑥)
𝔼 𝑥~𝑝 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑝 𝑥 𝑓 𝑥 𝑑𝑥
Mean value
Variance
𝑉𝑎𝑟 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝔼 (𝑓 𝑥 − 𝔼 𝑓 𝑥 )2
Covariance
𝐶𝑜𝑣(𝑓 𝑥 , 𝑔 𝑦 ) = 𝔼 (𝑓 𝑥 − 𝔼 𝑓 𝑥 )(𝑔 𝑦 − 𝔼[𝑔(𝑦)])
𝑥, 𝑦 사이에 선형관계가 있으면 𝐶𝑜𝑣는 양 또는 음의 값을 갖음
선형관계가 존재하지 않으면 0
𝐶𝑜𝑣가 0일지라도 선형관계 외의 관계가 존재할 수 있음](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probabilityinformationtheory-170928155139/85/Probability-Information-theory-10-320.jpg)



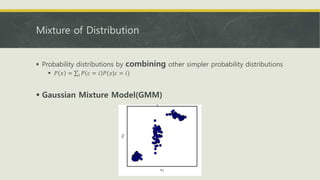



![Shannon Entropy
Can quantify the amount of uncertainty in an entire probability distribution
using the Shannon entropy
𝐻 𝑥 = 𝔼 𝑥~𝑃 𝐼 𝑥 = −𝔼 𝑥~𝑃[𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑃 𝑥 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probabilityinformationtheory-170928155139/85/Probability-Information-theory-21-320.jpg)
![Kullback-Leibler(KL) Divergence
To measure how different two distributions are
𝐷 𝐾𝐿(𝑃| 𝑄 = 𝔼 𝑥~𝑃 log
𝑃 𝑥
𝑄 𝑥
= 𝔼 𝑥~𝑃[log 𝑃 𝑥 − log 𝑄(𝑥)]
Properties
Non Negative
KL Divergence is Asymmetric
𝐷 𝐾𝐿(𝑃||𝑄) ≠ 𝐷 𝐾𝐿(𝑄||𝑃)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/probabilityinformationtheory-170928155139/85/Probability-Information-theory-22-320.jpg)