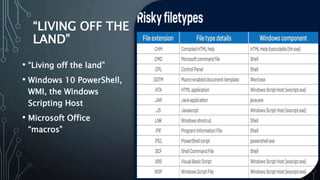
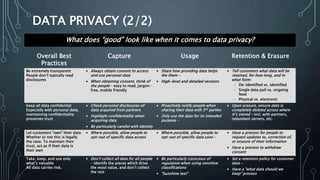
The document outlines key strategies and best practices for cybersecurity, emphasizing the importance of data privacy and accountability within organizations. It stresses the necessity of utilizing established frameworks, such as NIST and CIS, for effective risk management and the need for continuous training and communication regarding data security. It also highlights the significance of a robust data protection culture, regular assessments, and proactive incident response planning.