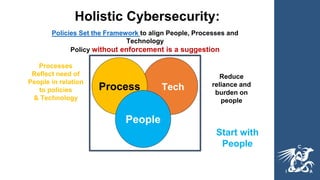
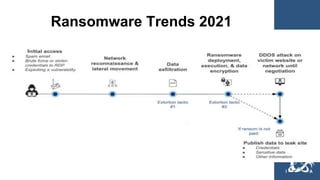
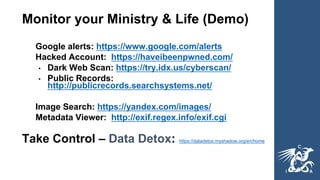
This document provides guidance on cybersecurity best practices for organizations. It notes that no network is completely secure and individuals often enable hacking through mistakes. It recommends establishing an incident response plan, purchasing cyber insurance, developing security policies and procedures, considering outsourcing security monitoring, regularly backing up data in multiple secure locations, and using a password manager. The document also warns against common pitfalls like not sustaining long-term security resources and provides links to additional cybersecurity resources.