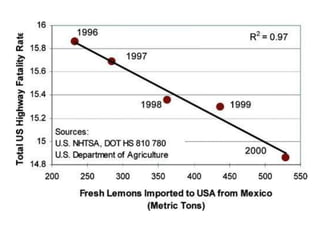
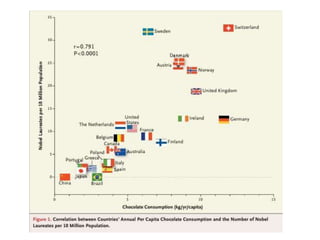
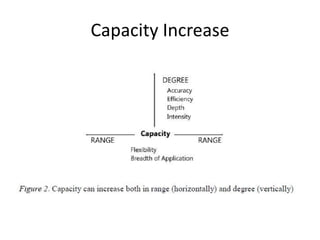
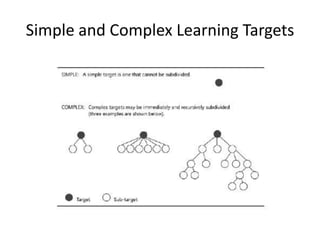
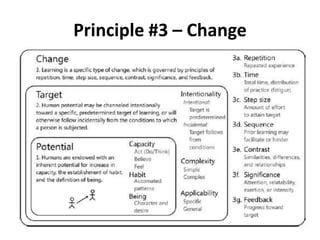
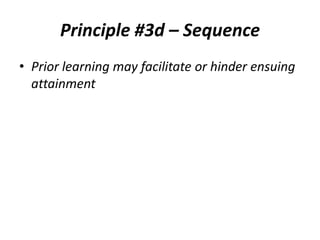
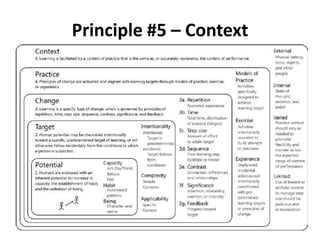
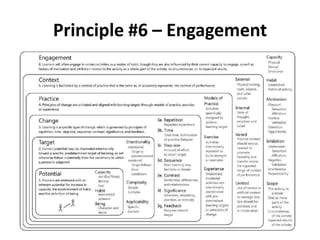
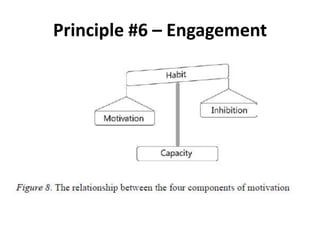
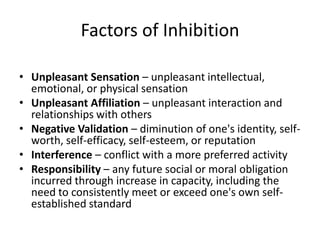
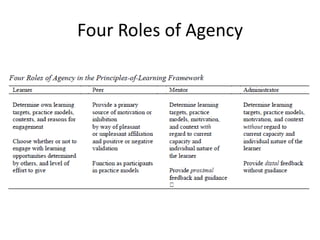
The document discusses the principles of learning as articulated by Dr. Christian Weibell, emphasizing the relationships between variables in learning methods and the shift toward principle-based approaches in education. It outlines multiple theories and approaches to studying learning, including behavioral, cognitive, constructive, human, and social perspectives, while also identifying ten key principles relevant to effective learning. The text advocates for the application of these principles in practical settings, aiming to enhance the development and evaluation of instructional products and methods.