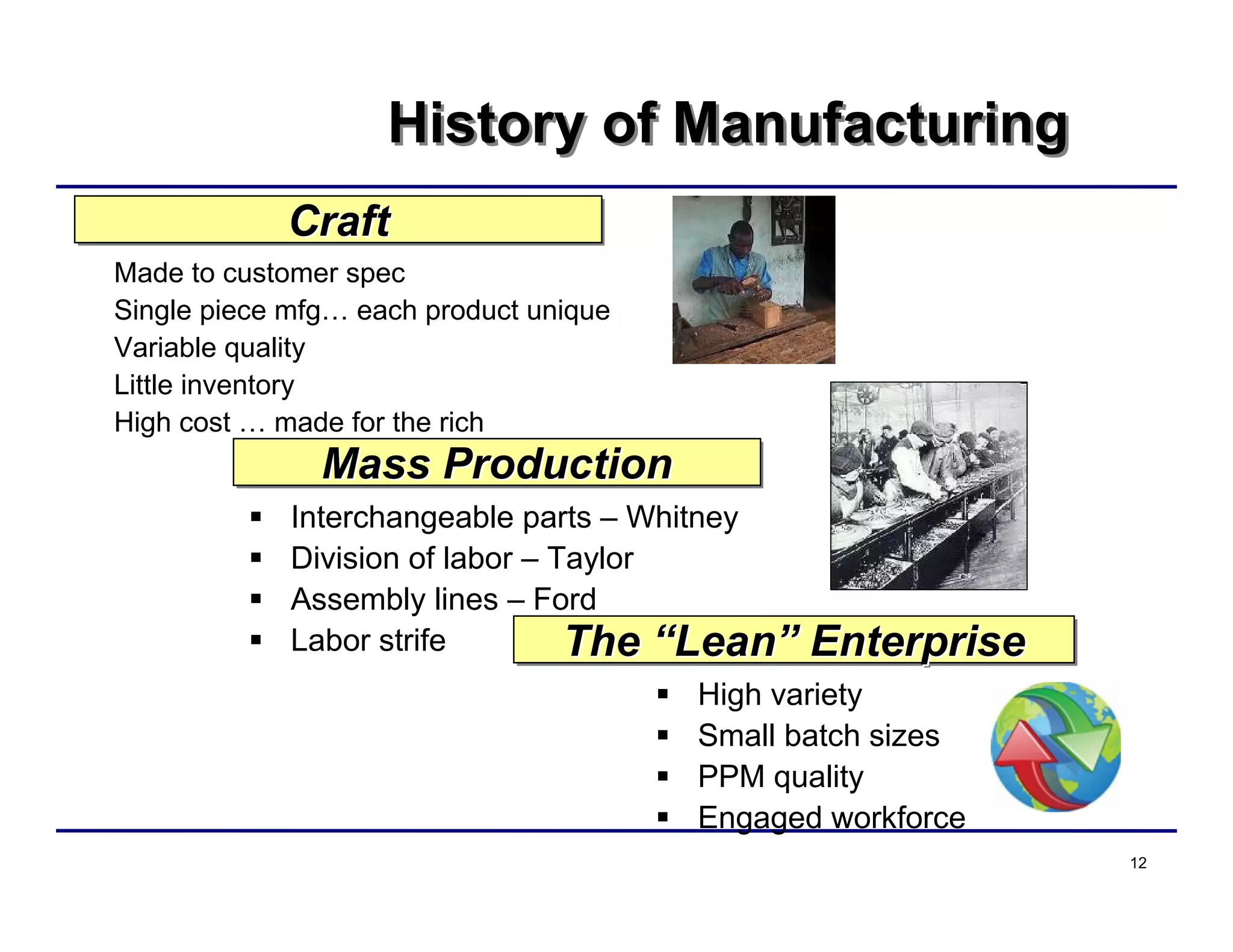
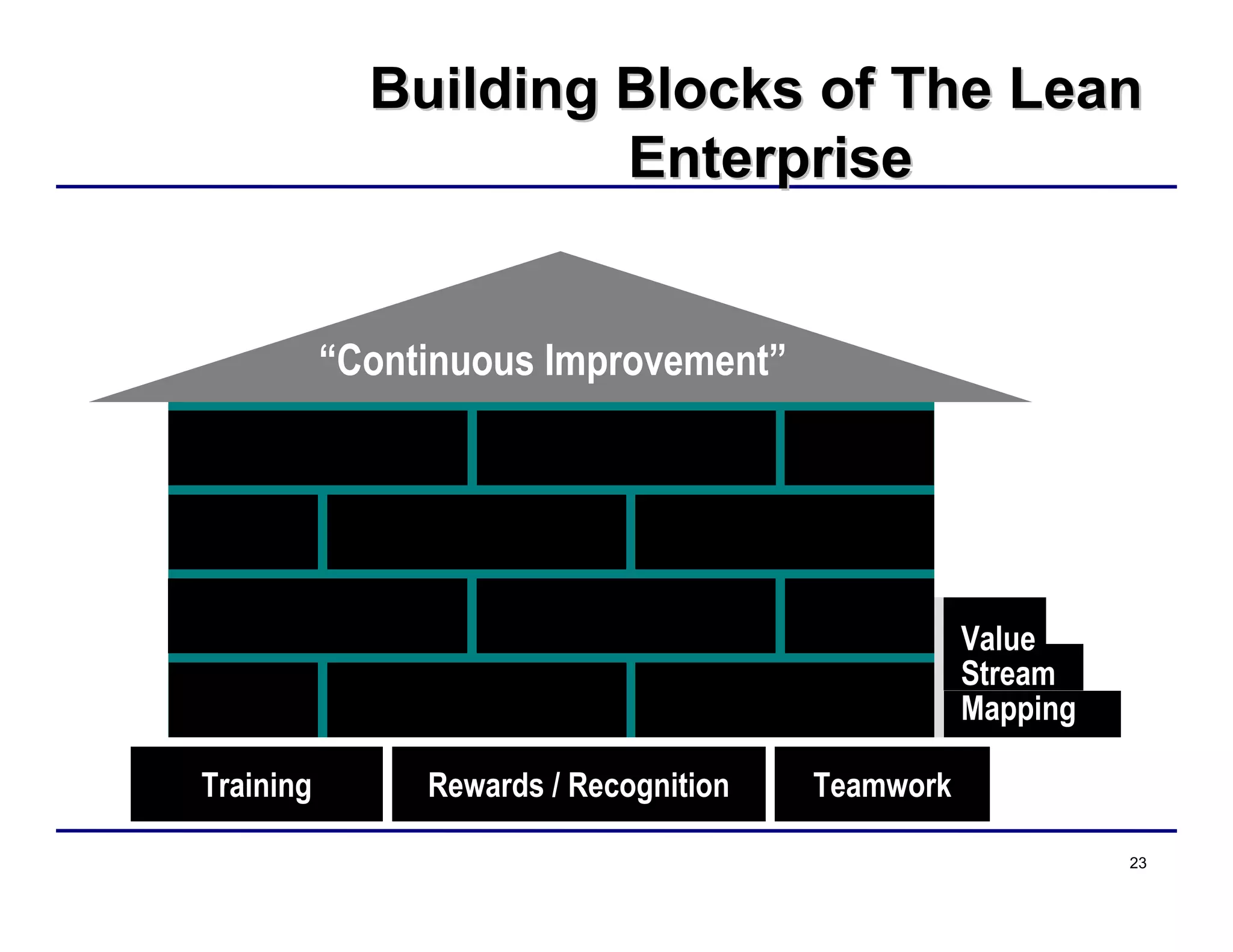
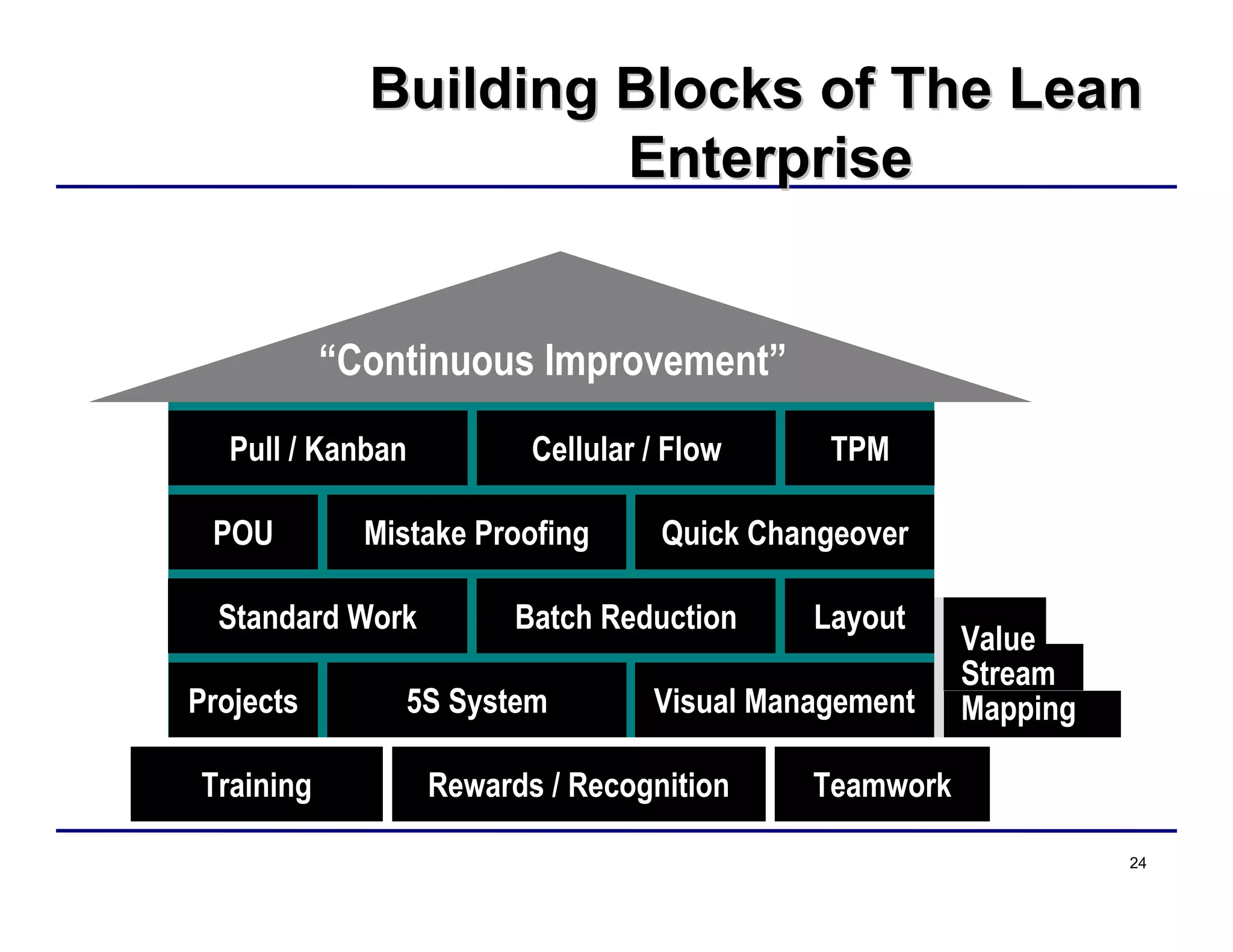
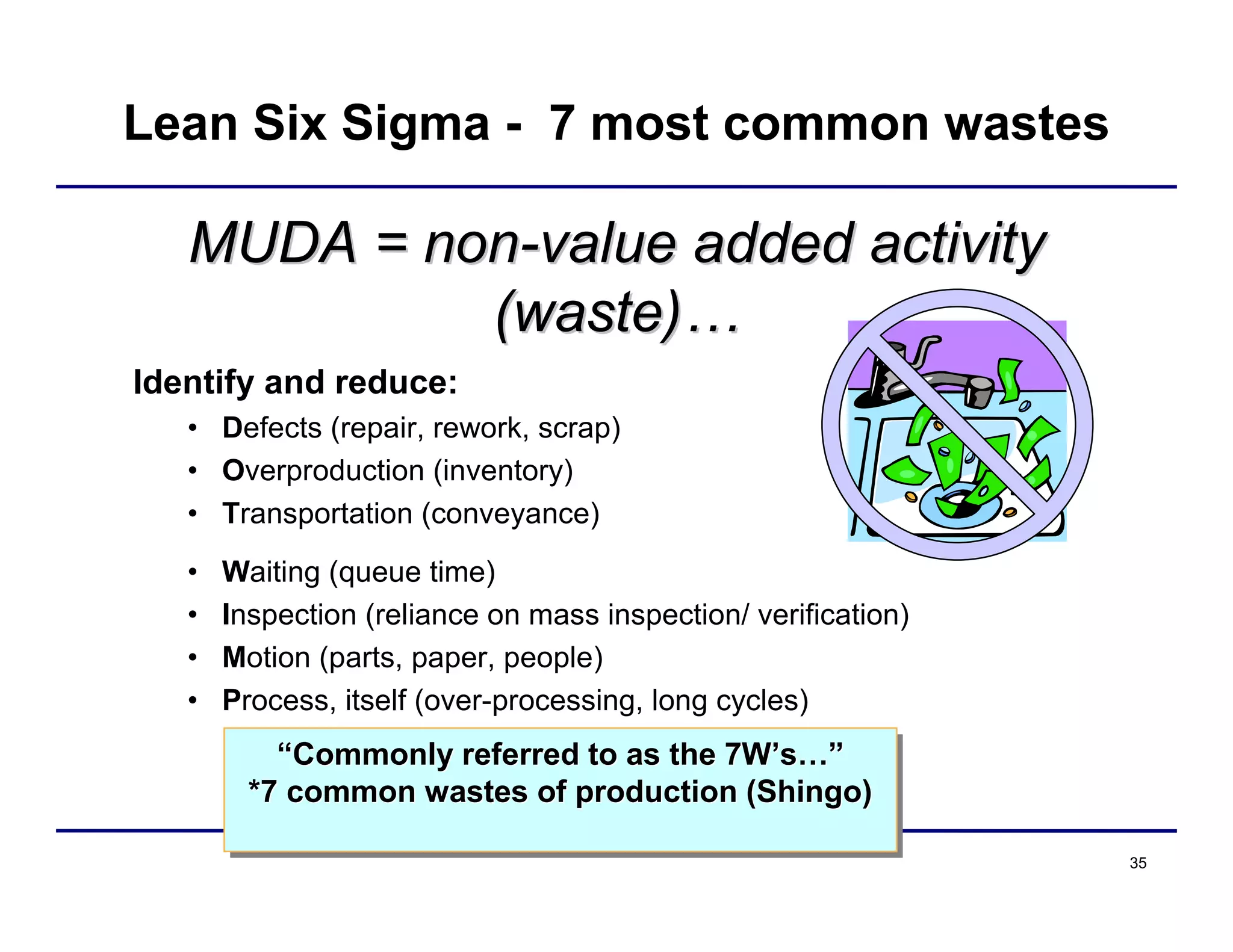
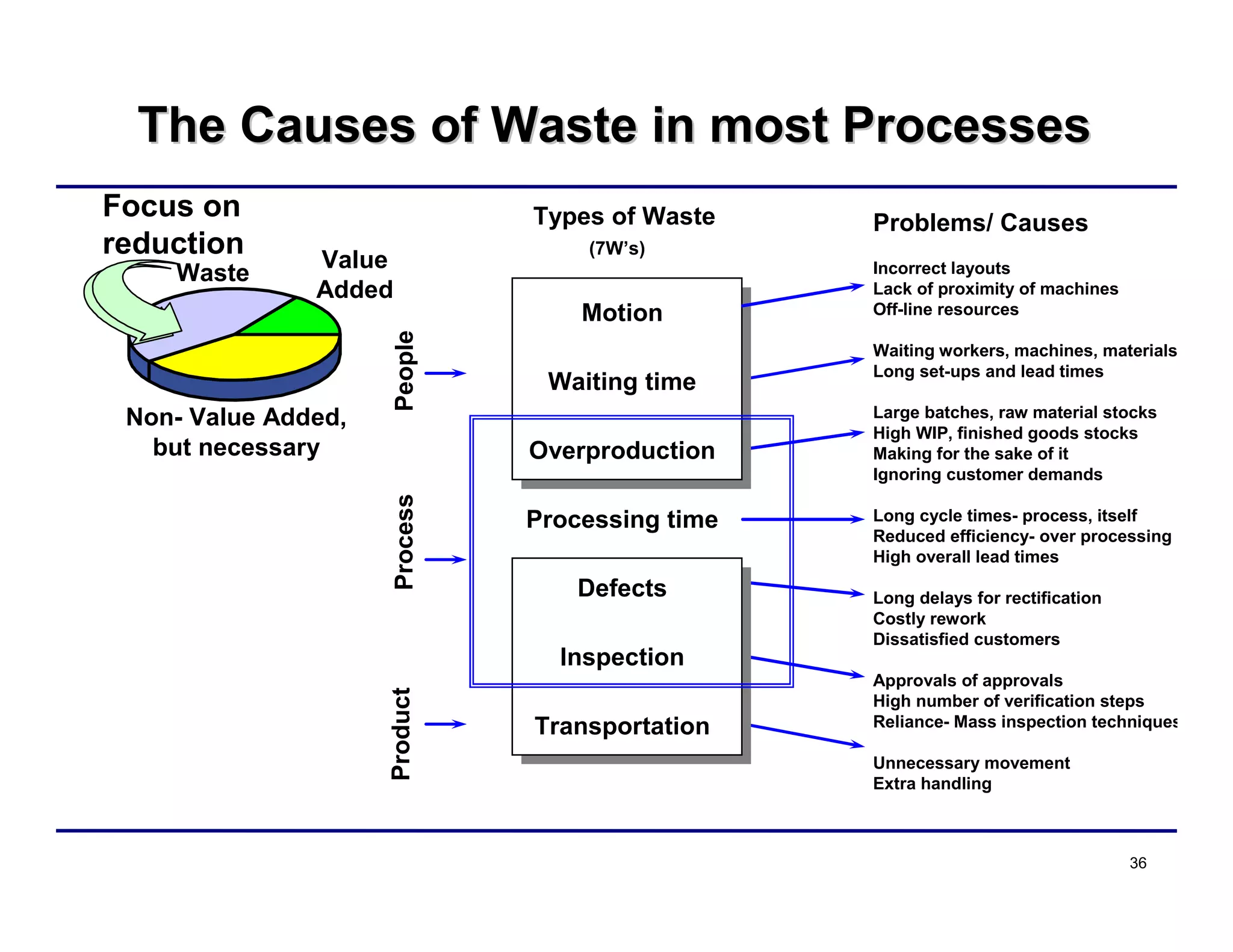
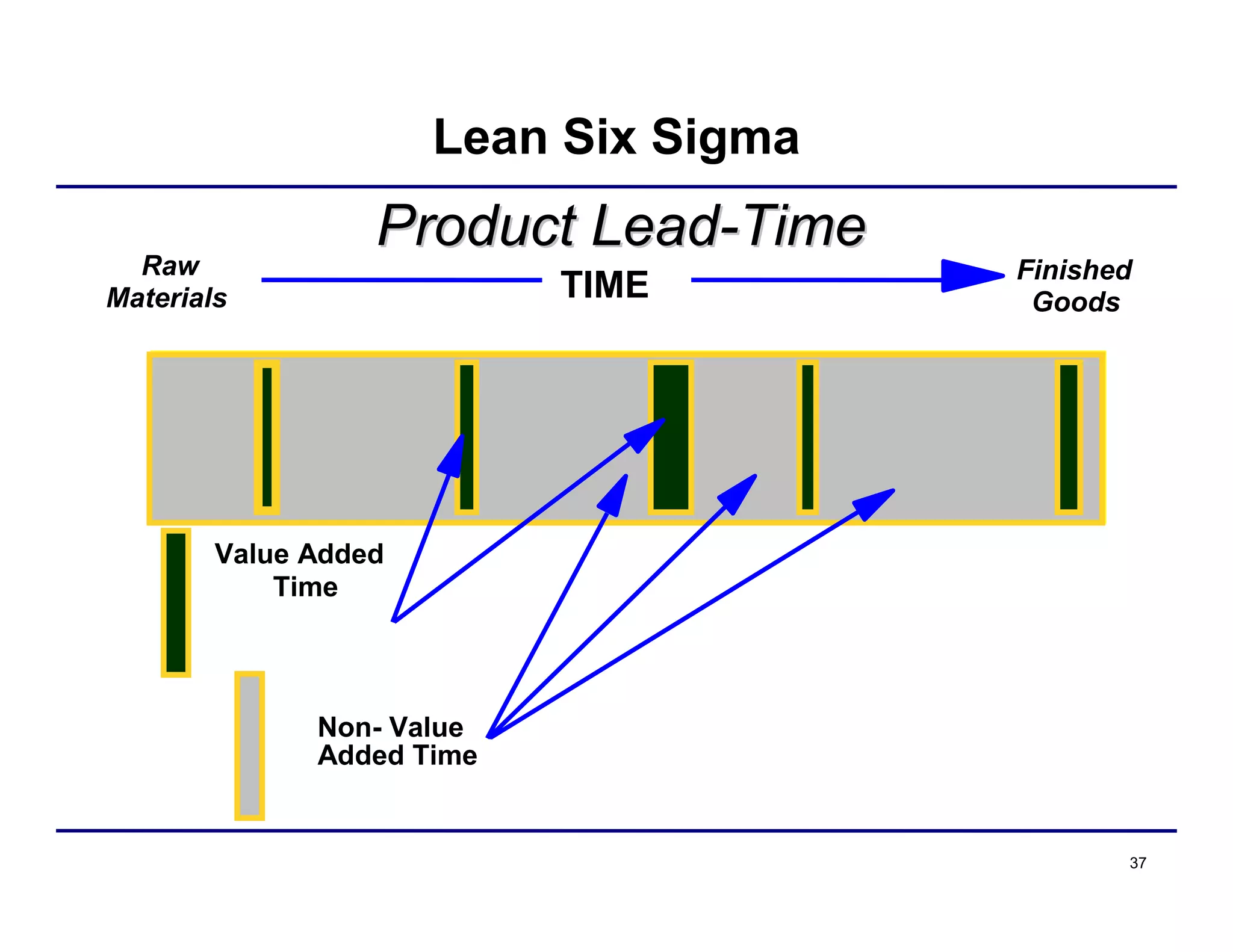
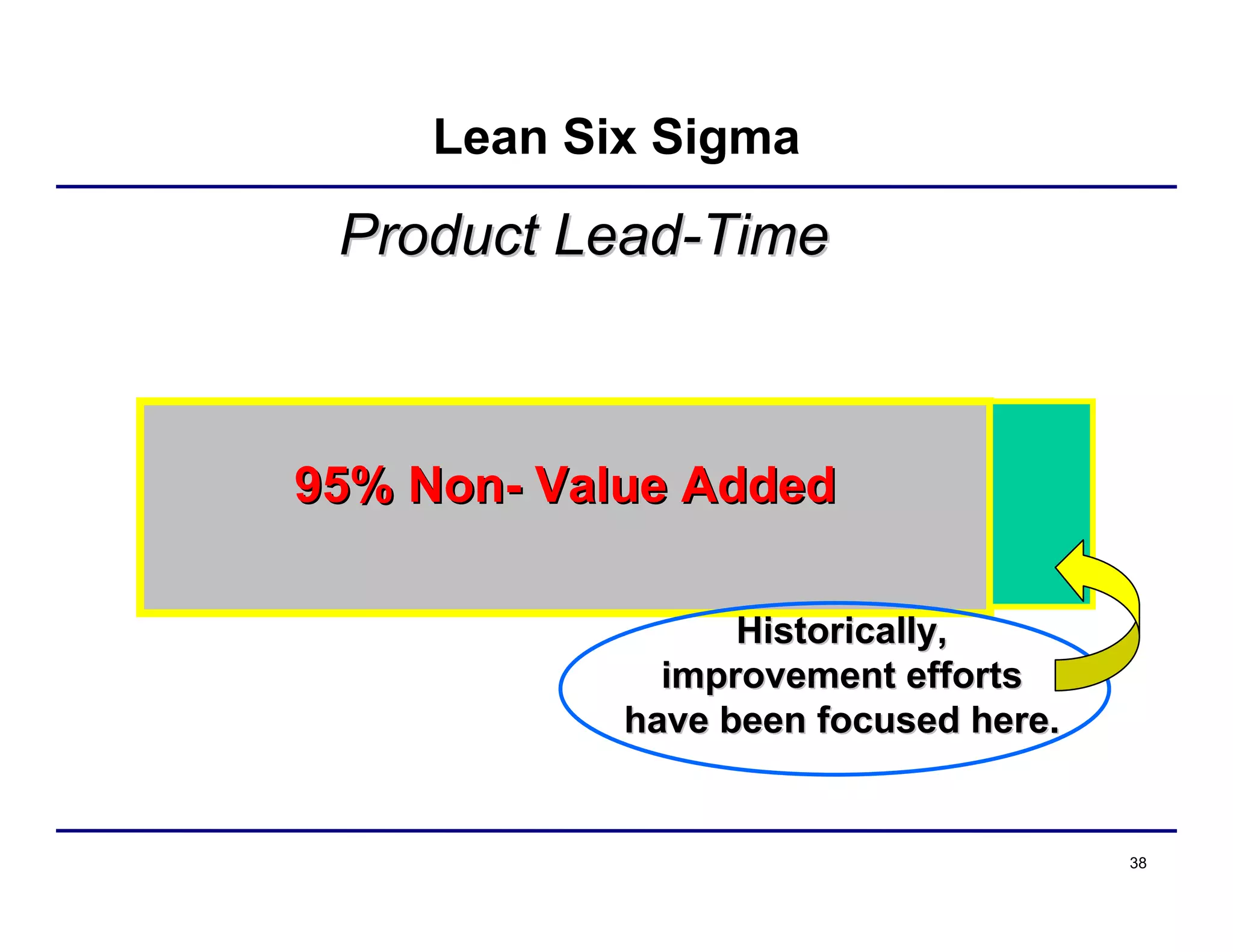
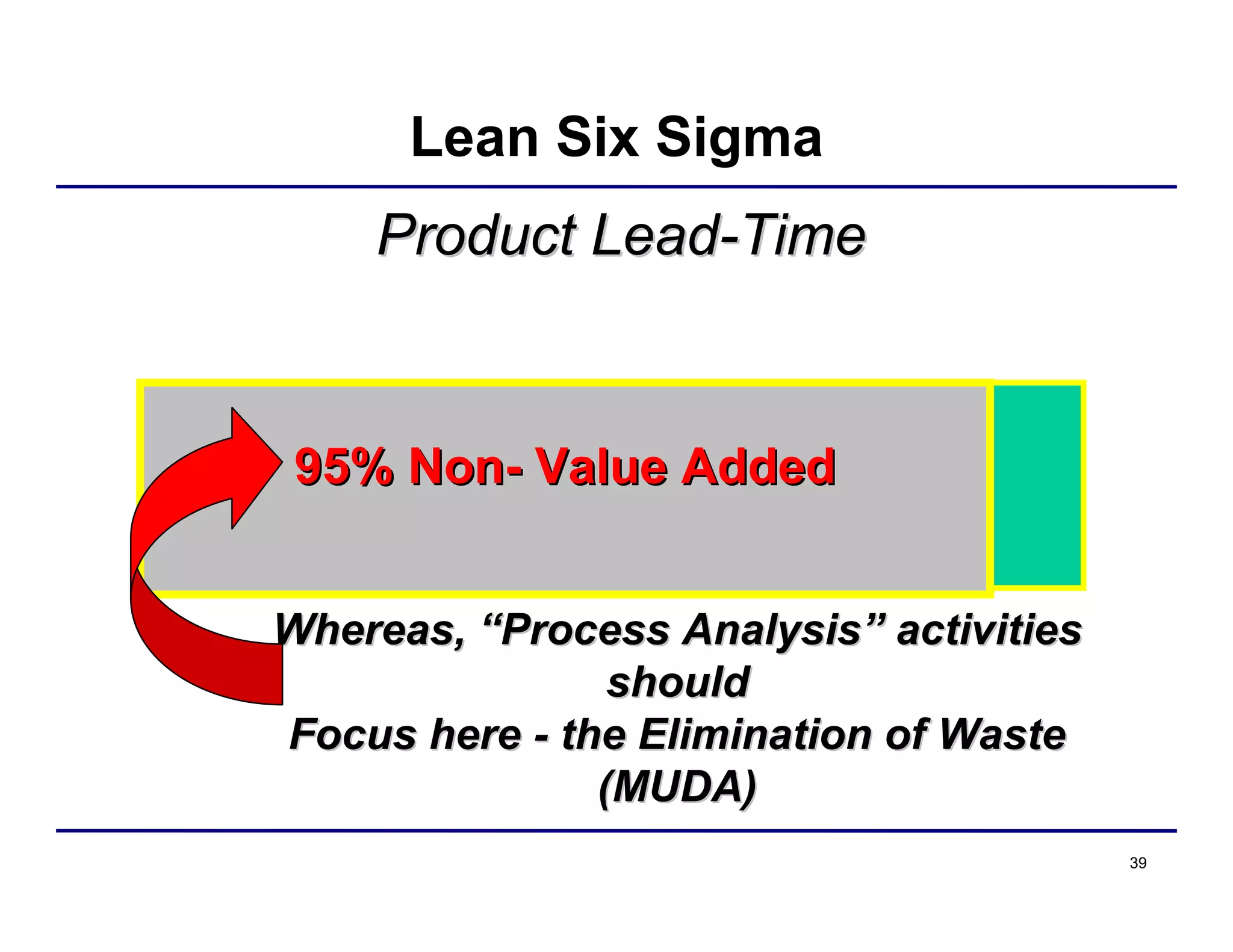
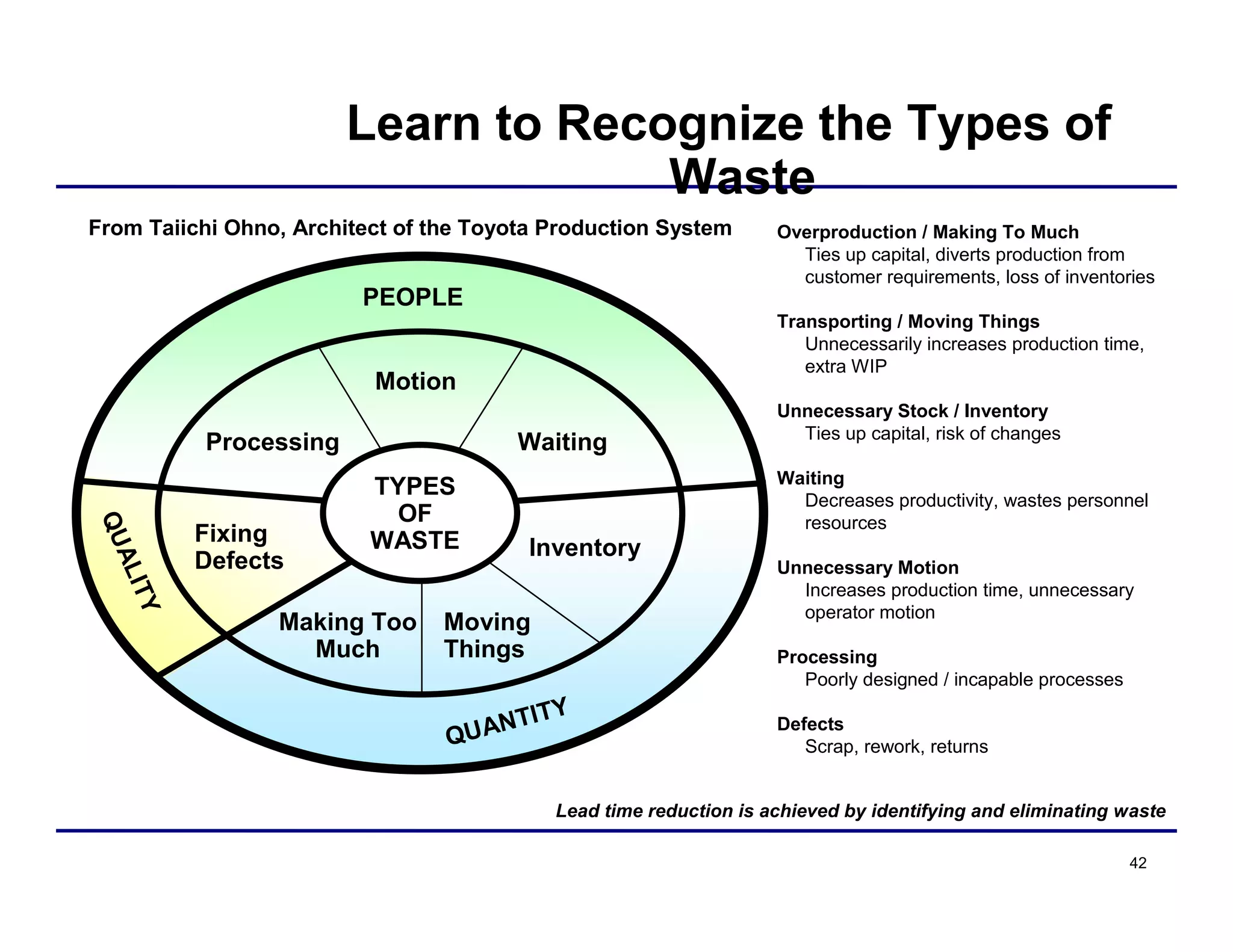
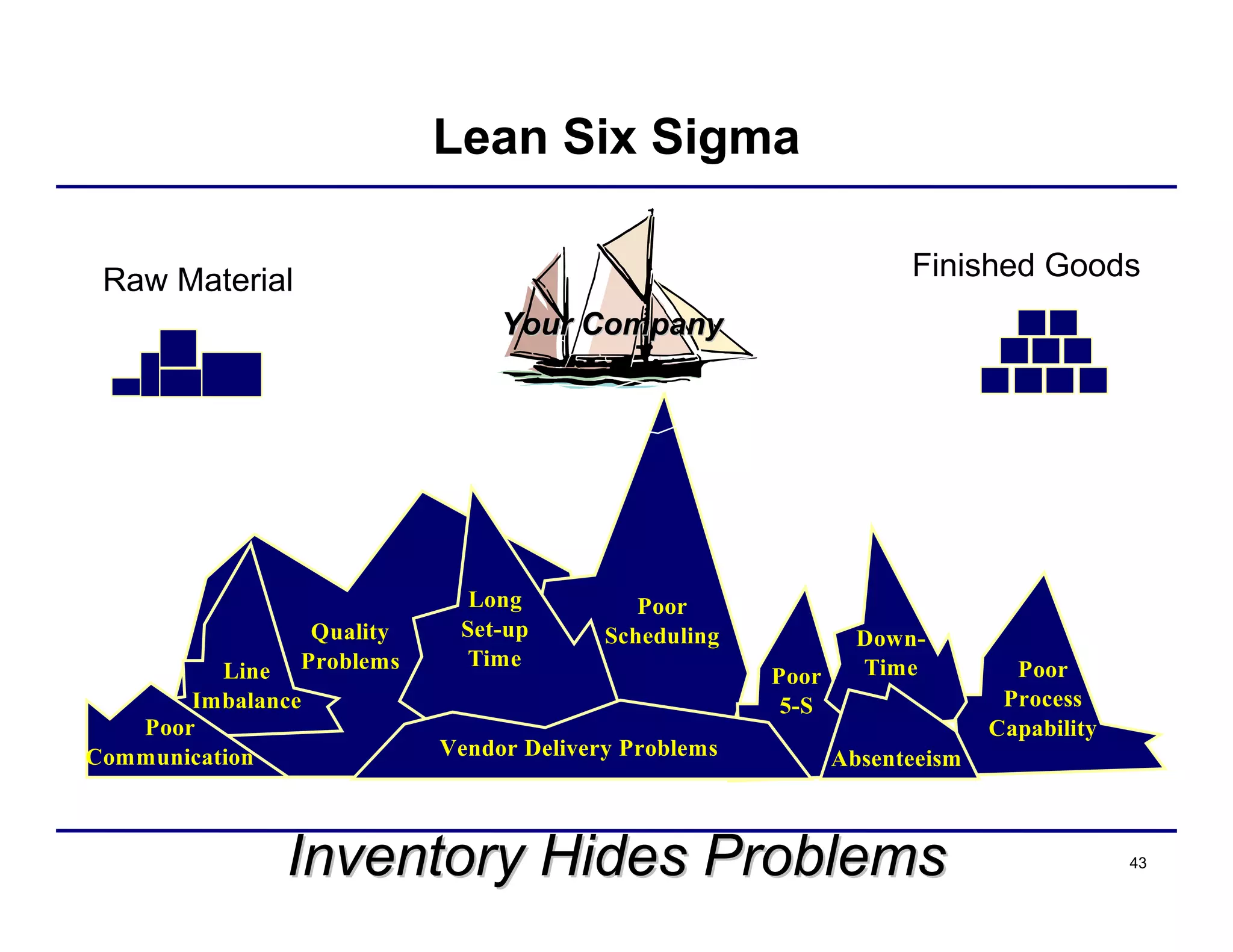
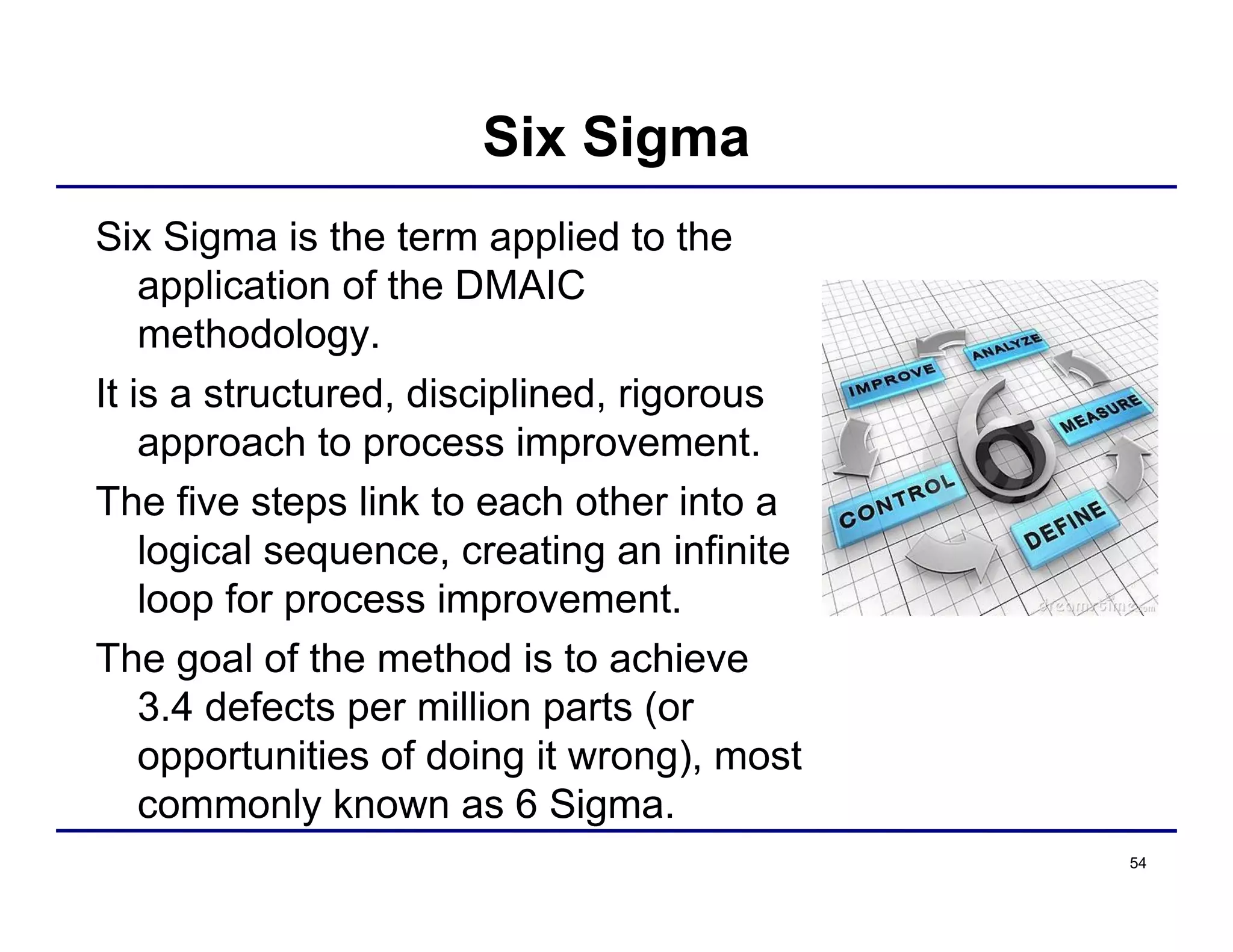
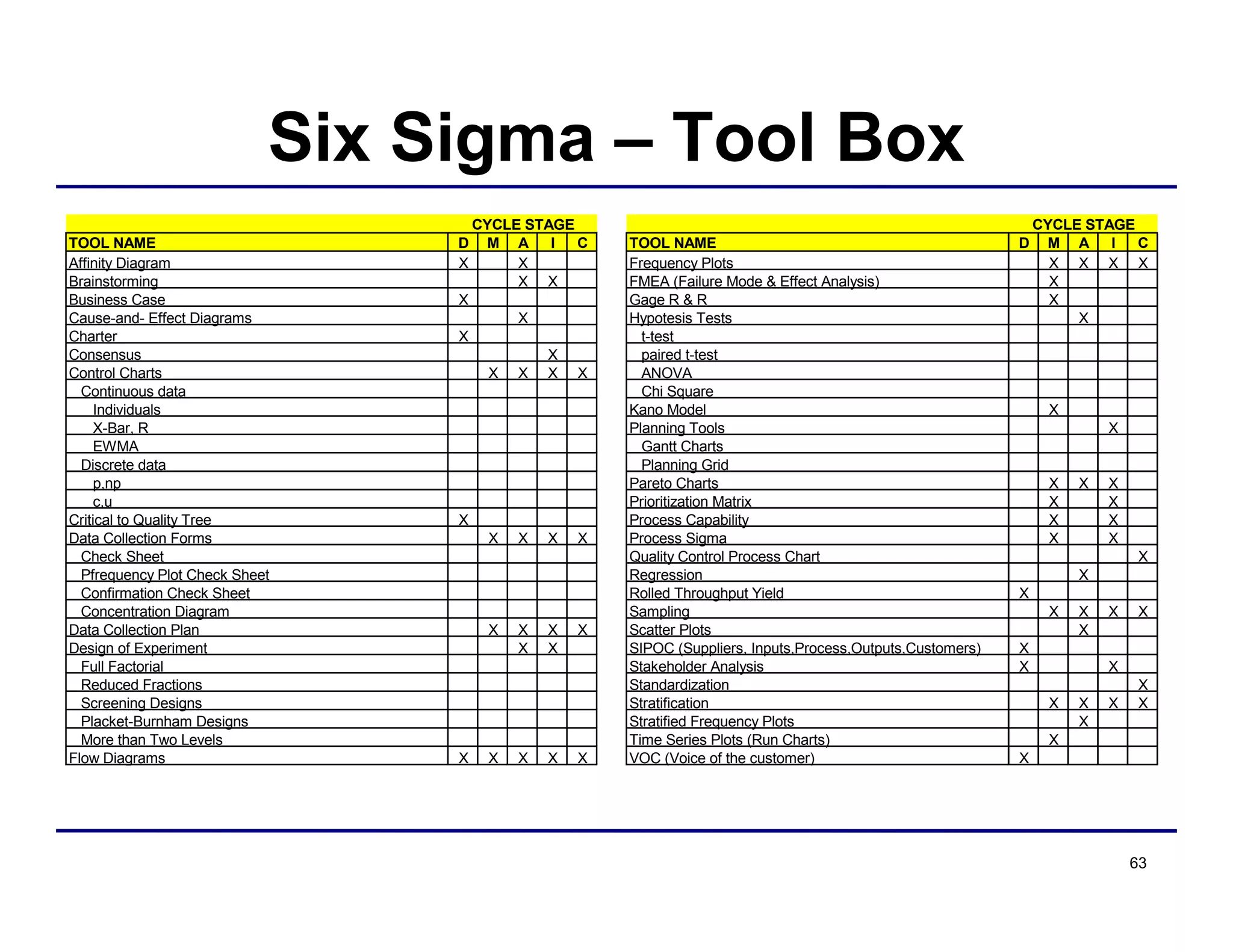
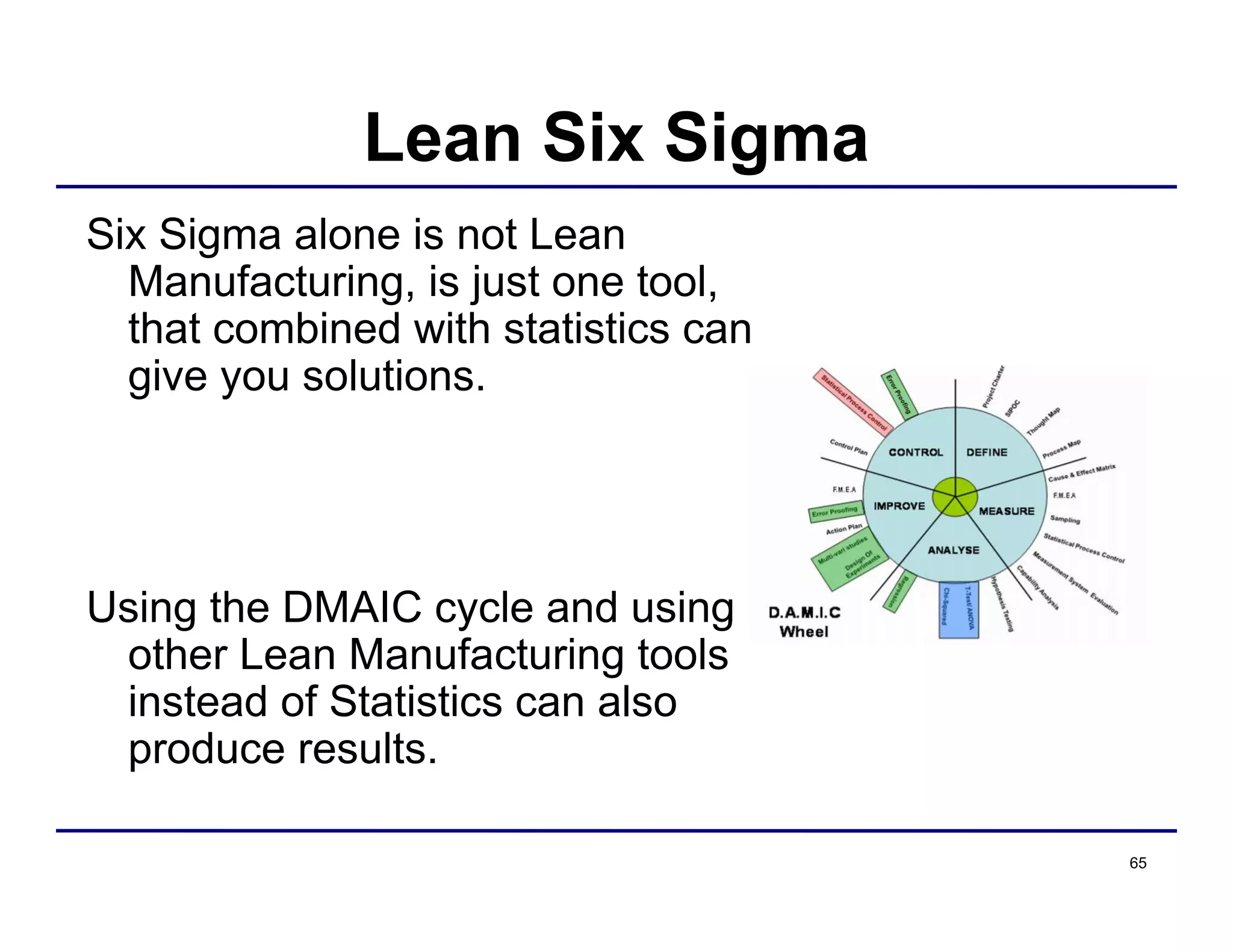
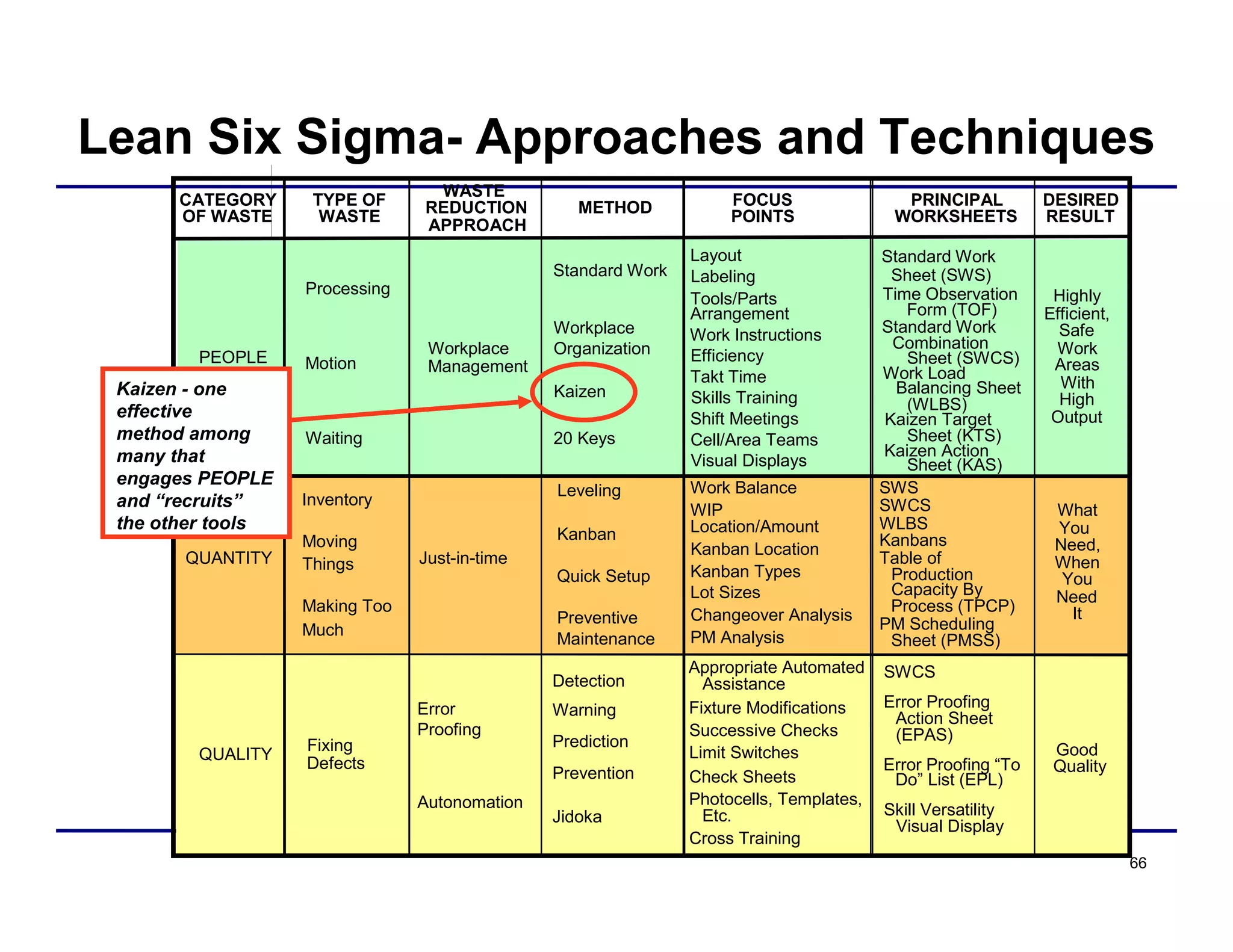
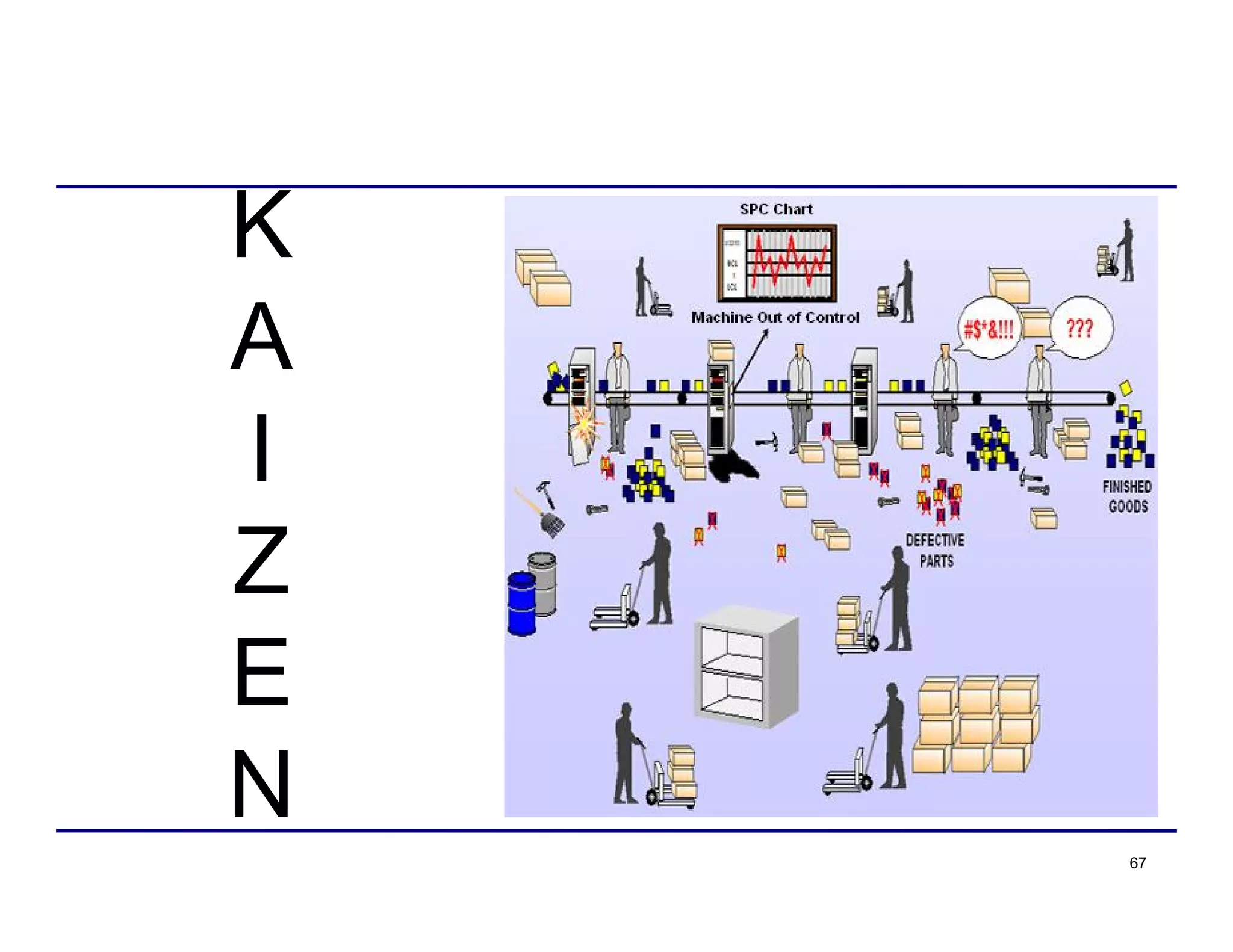
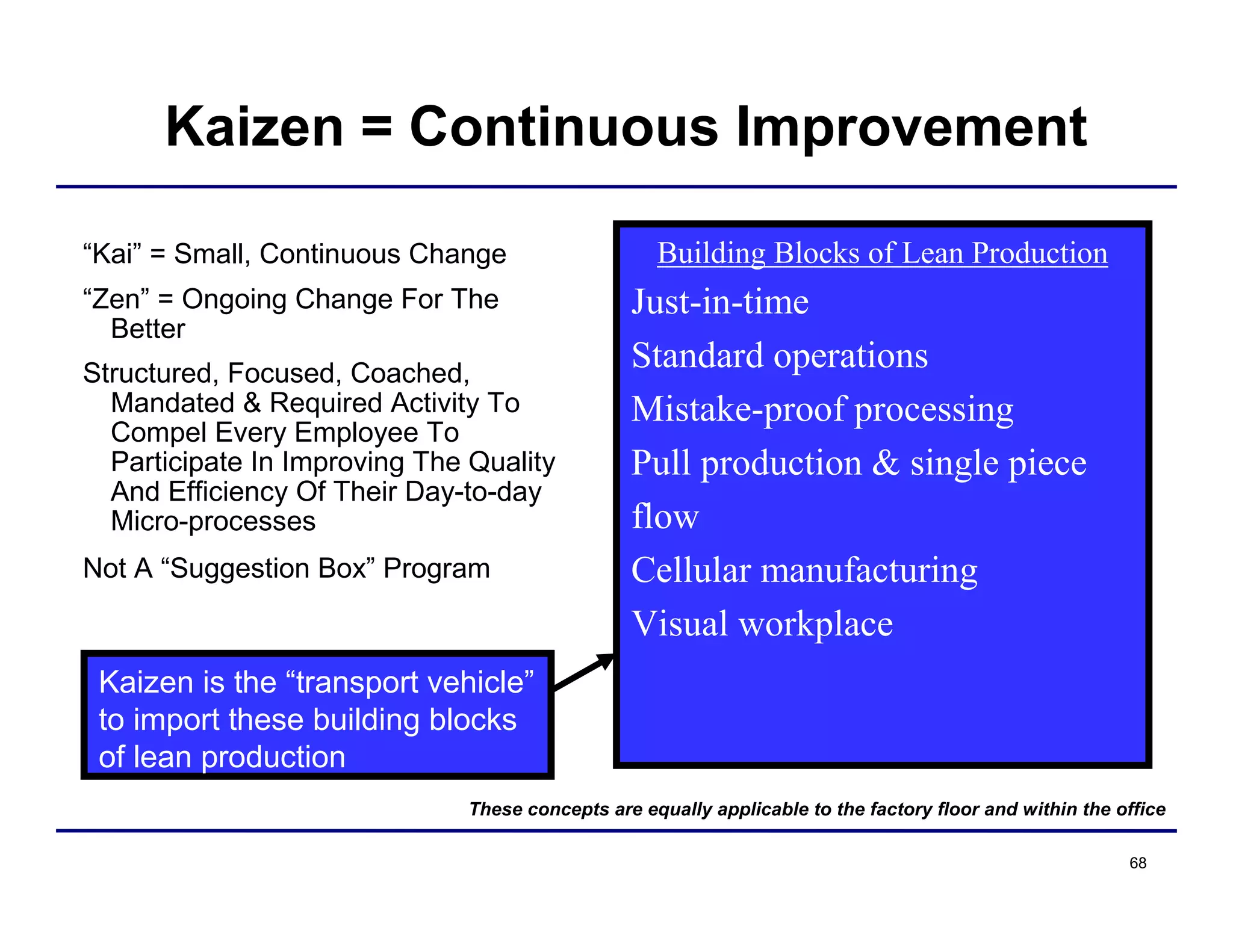
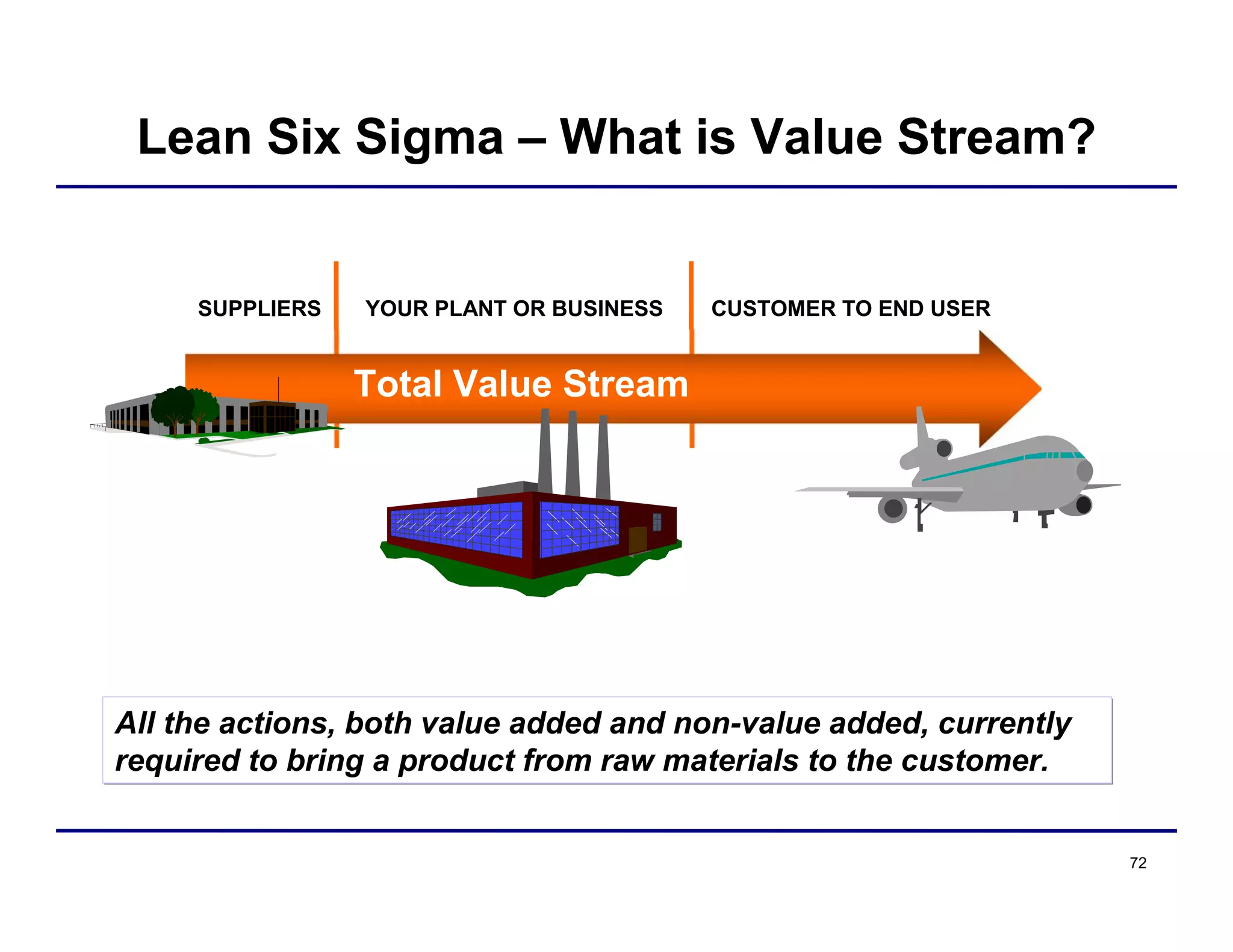
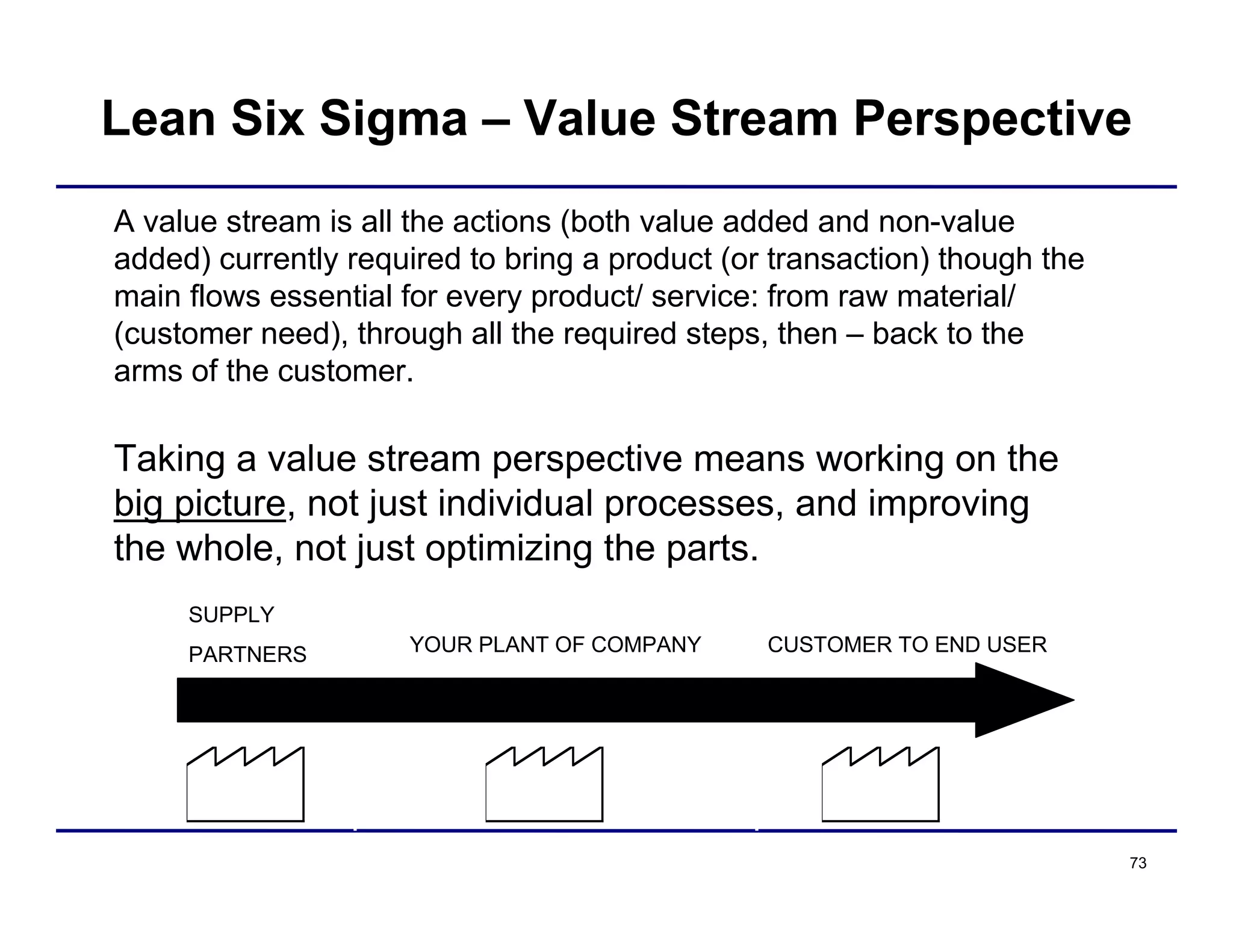
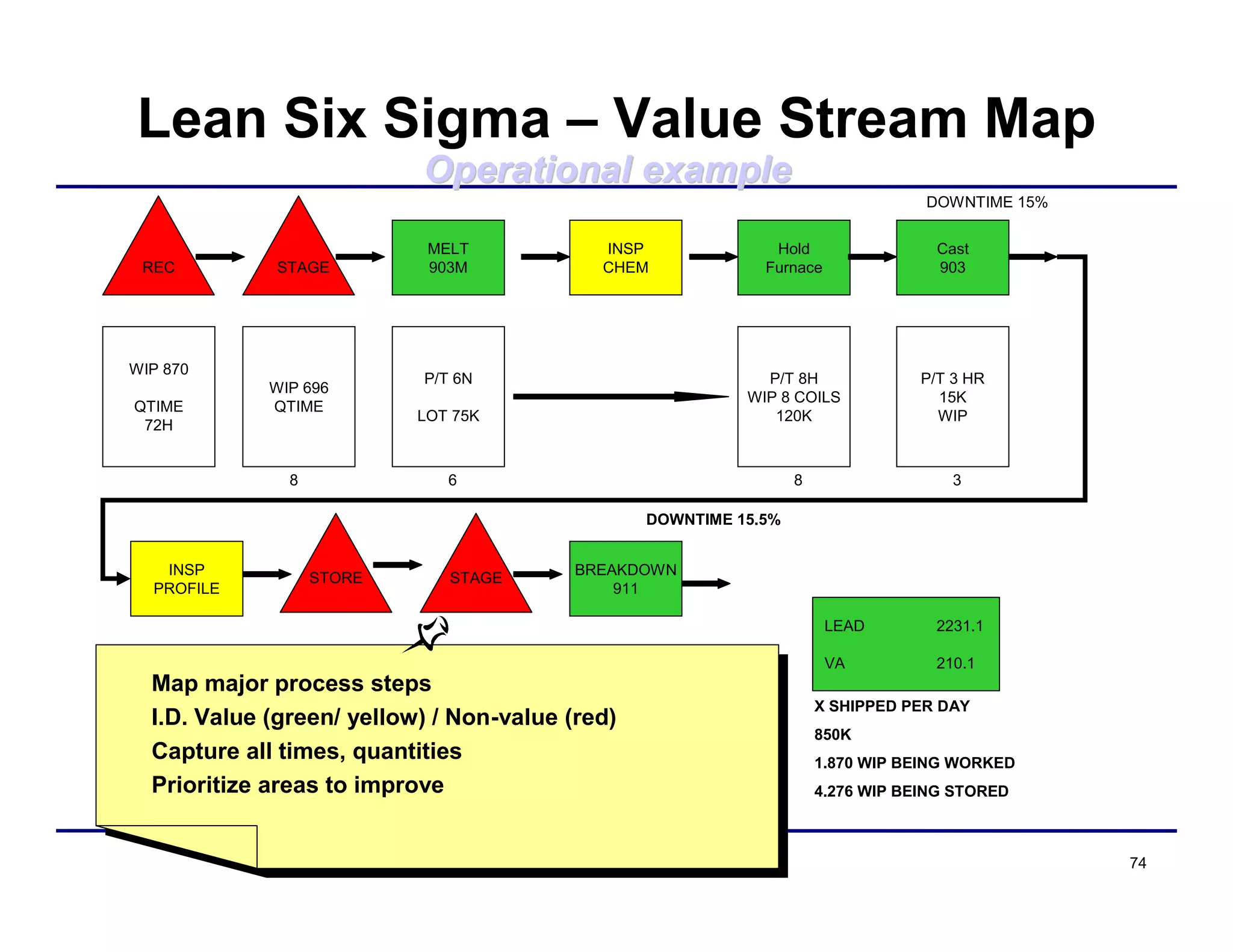
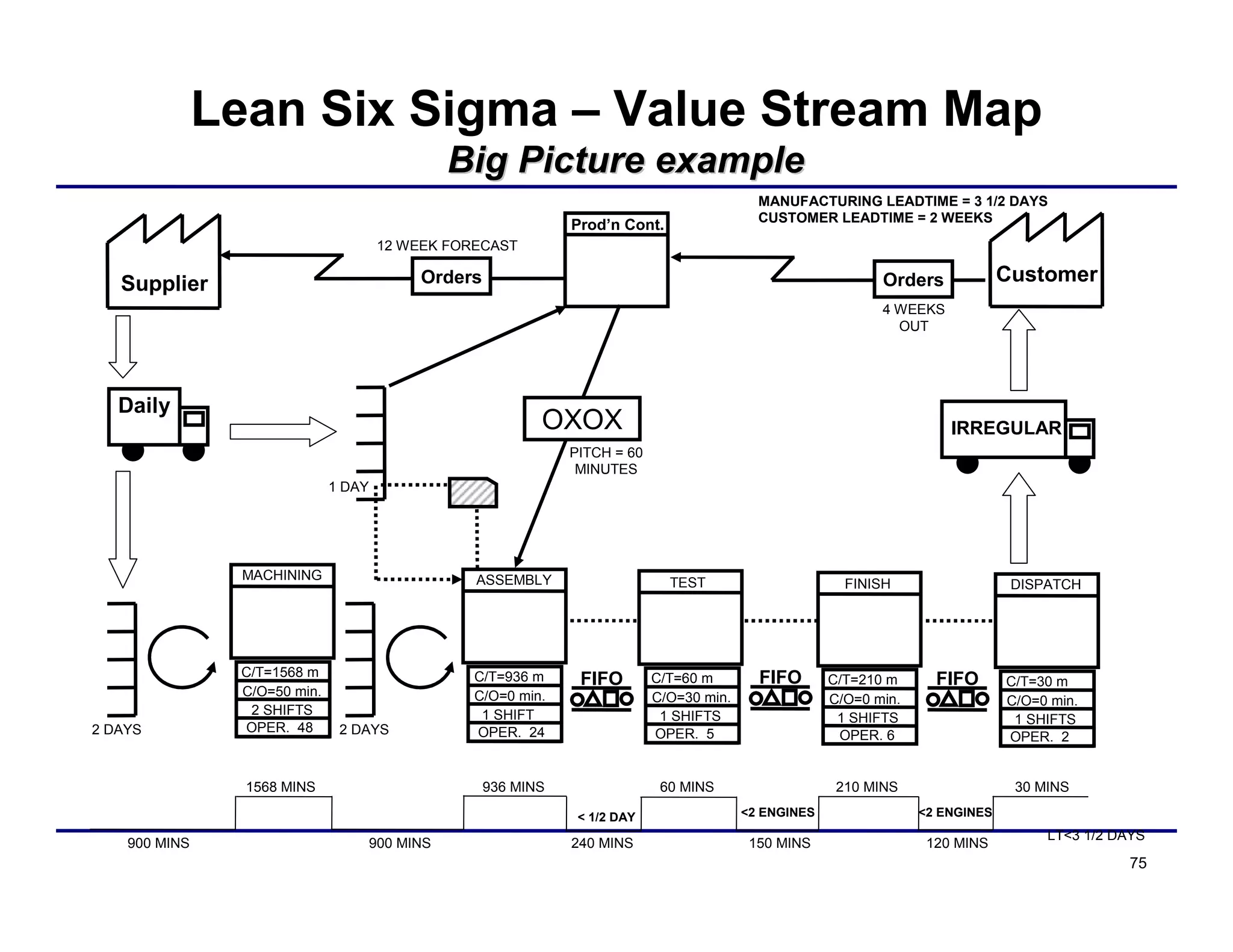
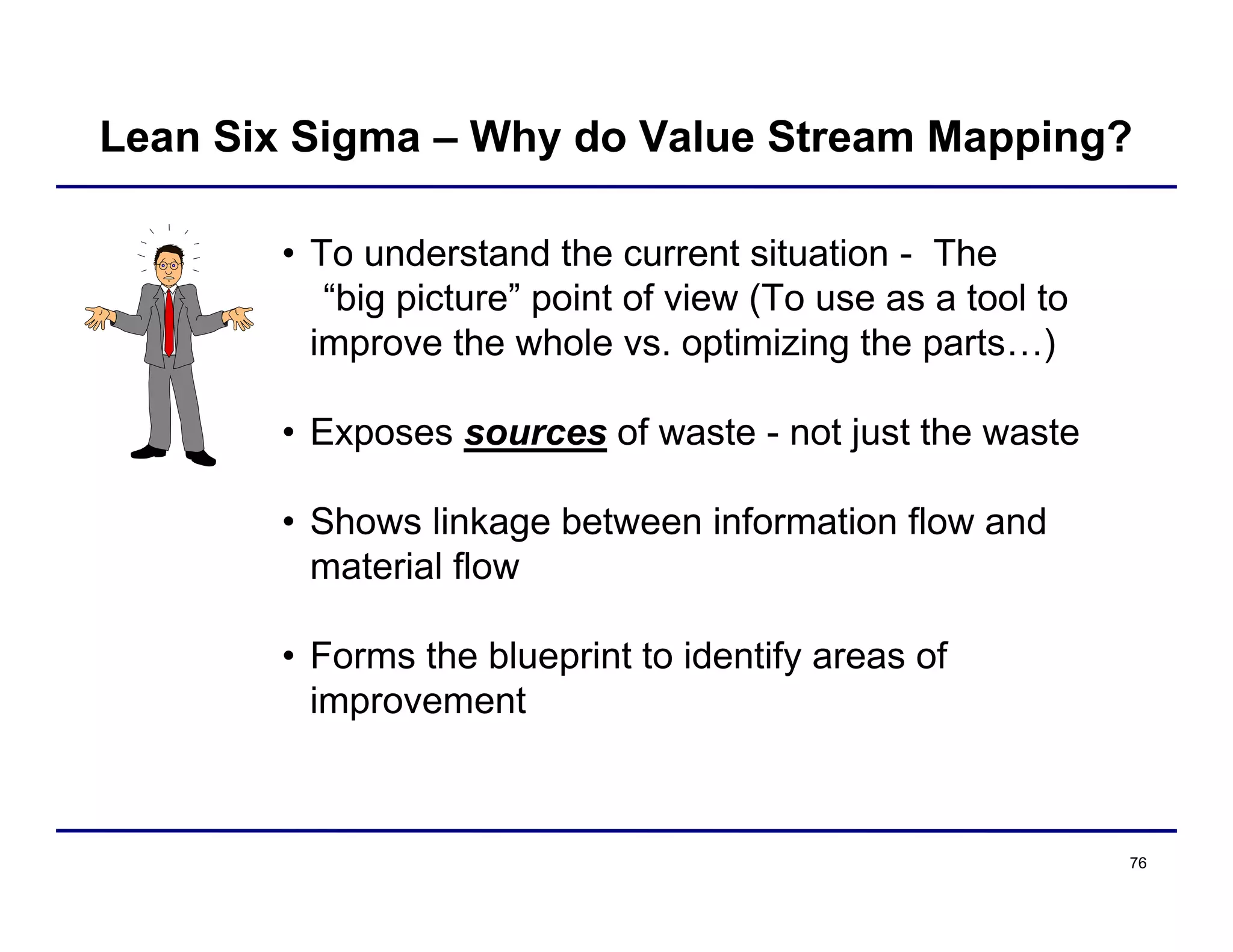
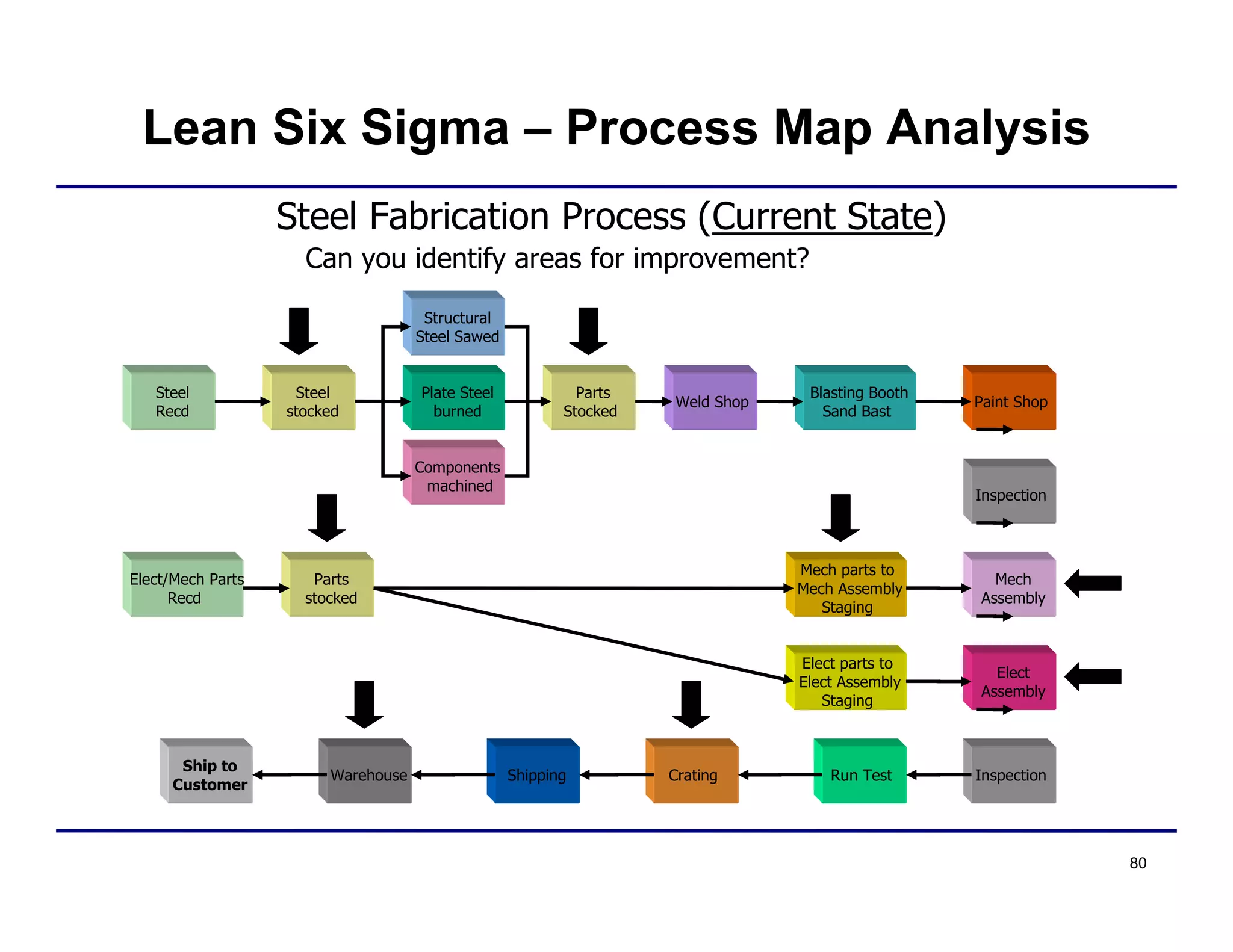
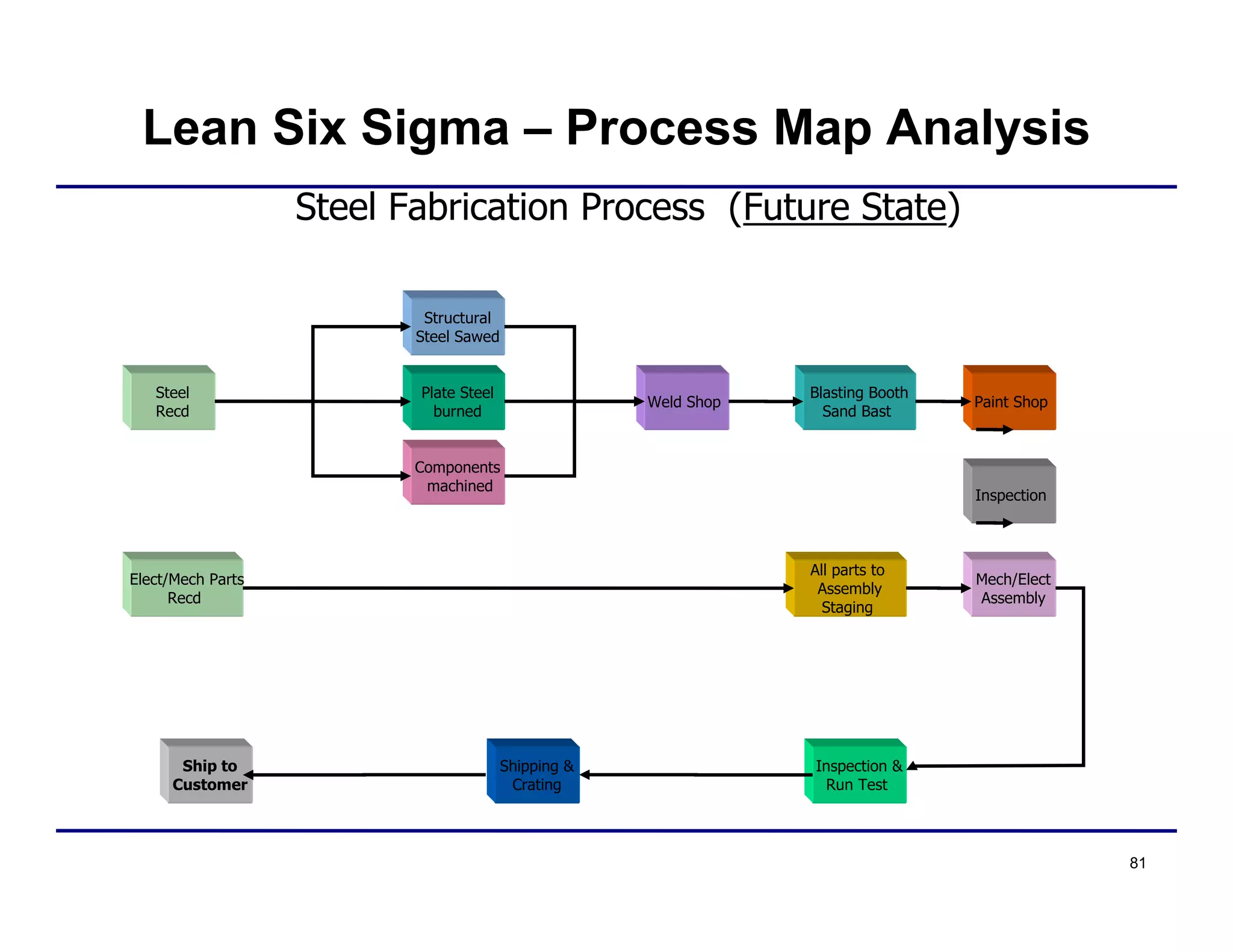
This document provides an overview and agenda for principles of Lean Six Sigma and CAPA. It discusses Lean Six Sigma strategies for improving quality, eliminating waste, reducing lead time and costs. The document defines value-added vs. non-value added activities and the seven most common types of waste. It explains how identifying and reducing waste can help reduce lead times and costs. The expected results of Lean Six Sigma implementation may include reductions in safety incidents, scrap, cycle times within 12 months. The document emphasizes analyzing processes to identify the three major contributors to waste: overburden/overdoing, unevenness and process methods.