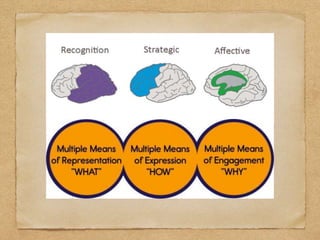
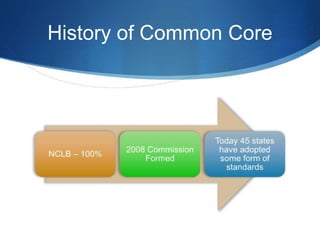
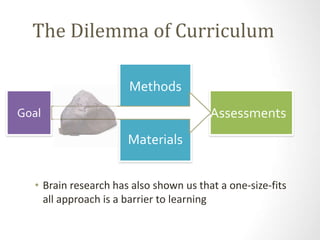
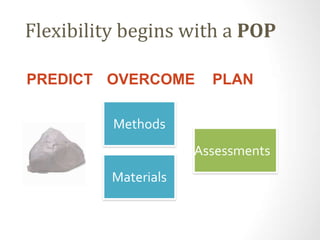
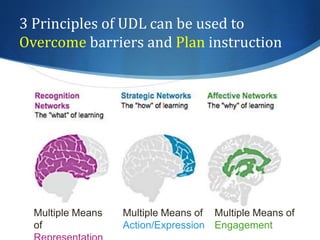
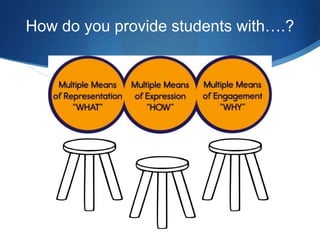
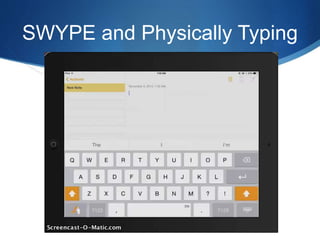
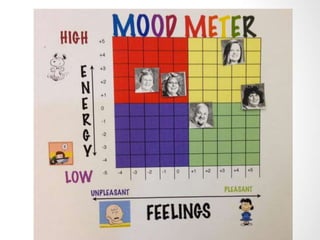
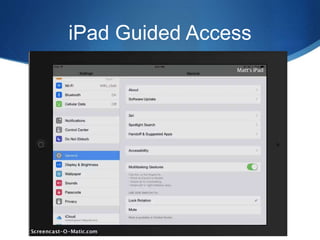
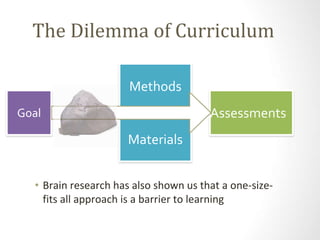
This document discusses utilizing the Universal Design for Learning (UDL) framework to impact student learning and expression. It provides an overview of the goals and agenda for a session on UDL, which includes understanding the three UDL principles, analyzing how UDL supports meeting standards, and identifying UDL-aligned resources. The overall goal is to build awareness of UDL strategies to create flexible learning environments that address learner variability and reduce barriers to access the curriculum.