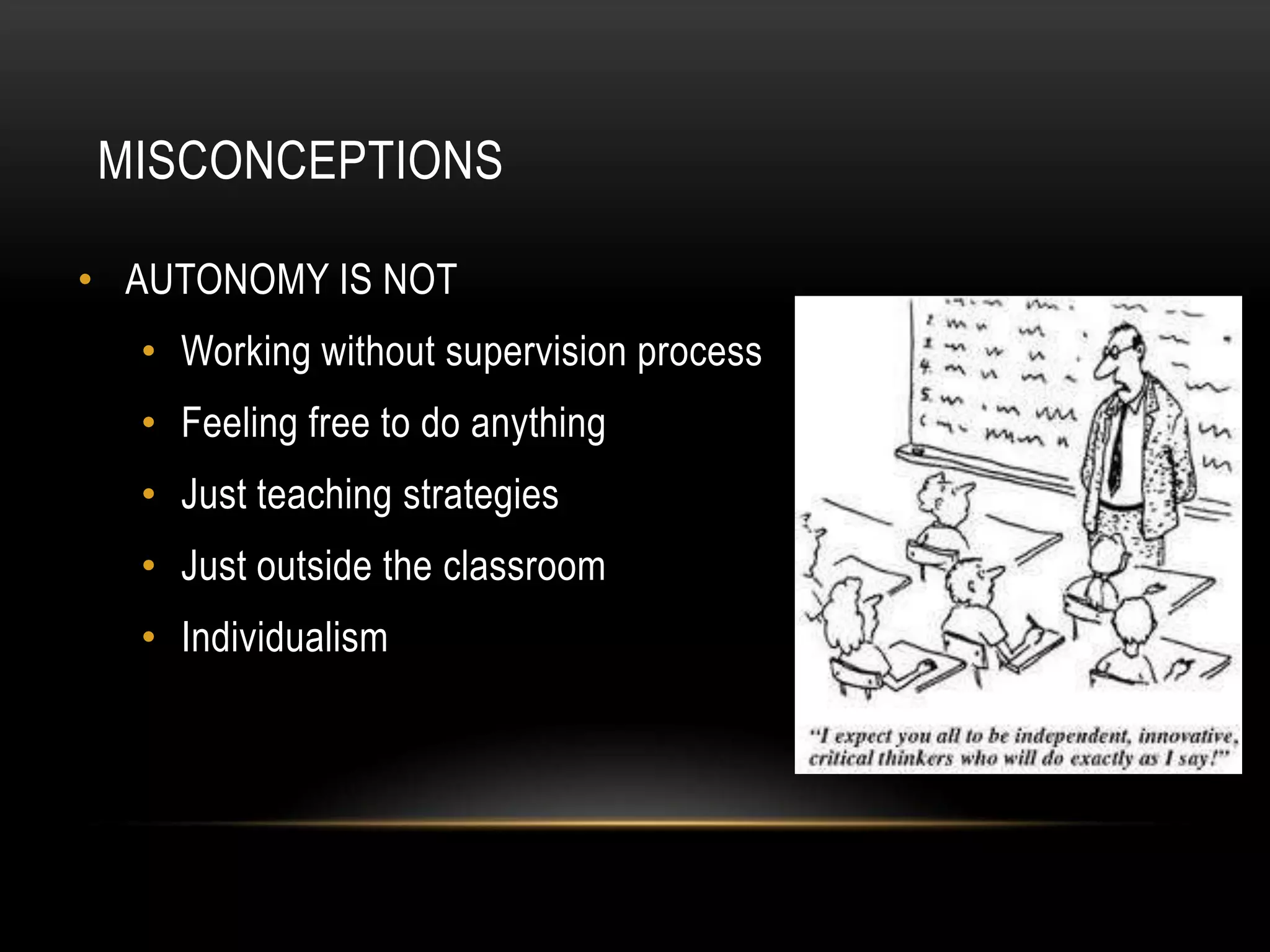
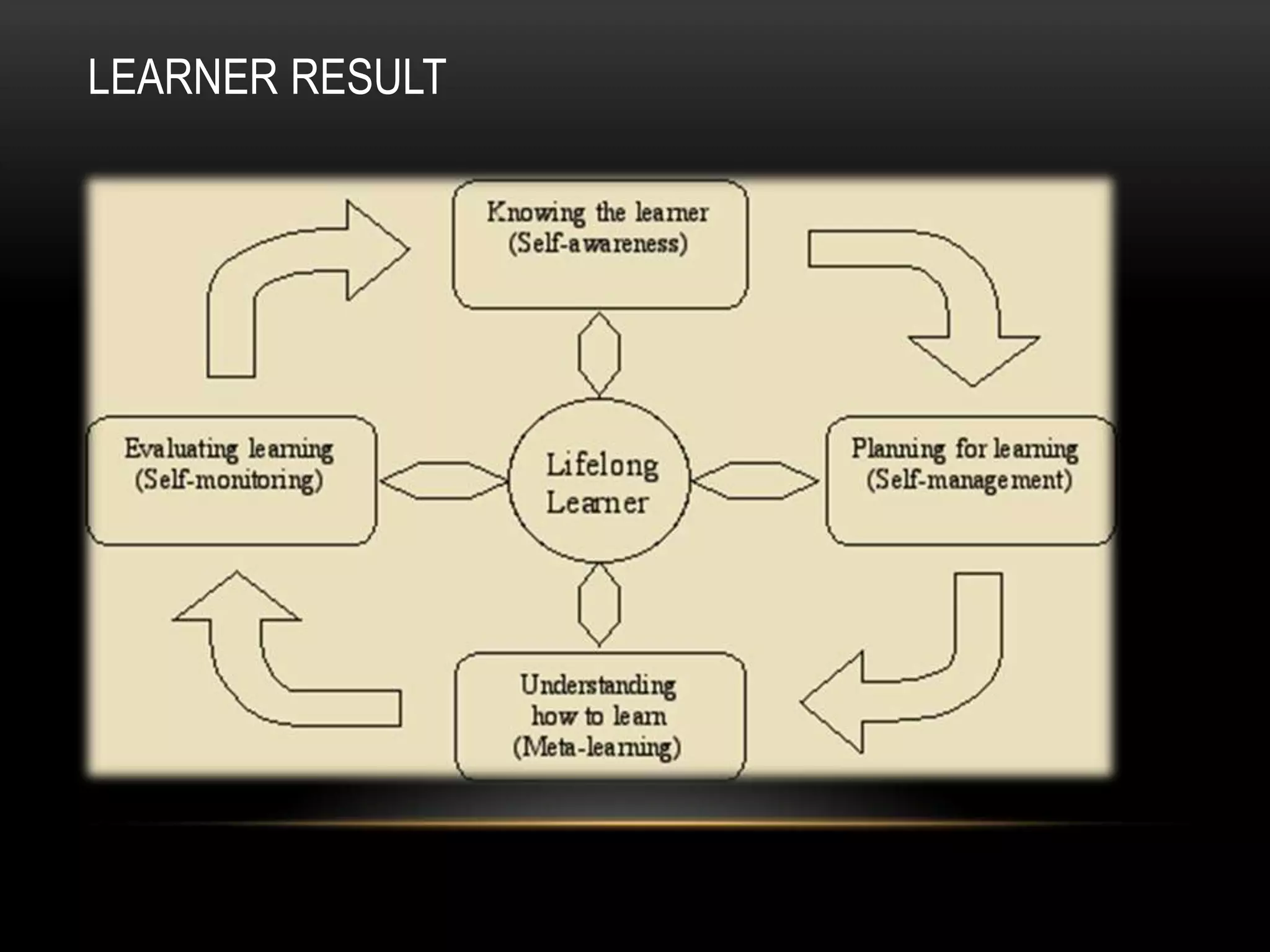
Autonomous learning involves learners taking charge of their own learning by determining objectives, contents, methods, monitoring progress, and evaluating results. It is not the same as working alone without guidance. Autonomous learning involves developing the capacity and responsibility for one's own learning process through constant reflection and decision making. When learners have more autonomy in their learning, they have more control over the discipline, techniques, process, and contents of their education.