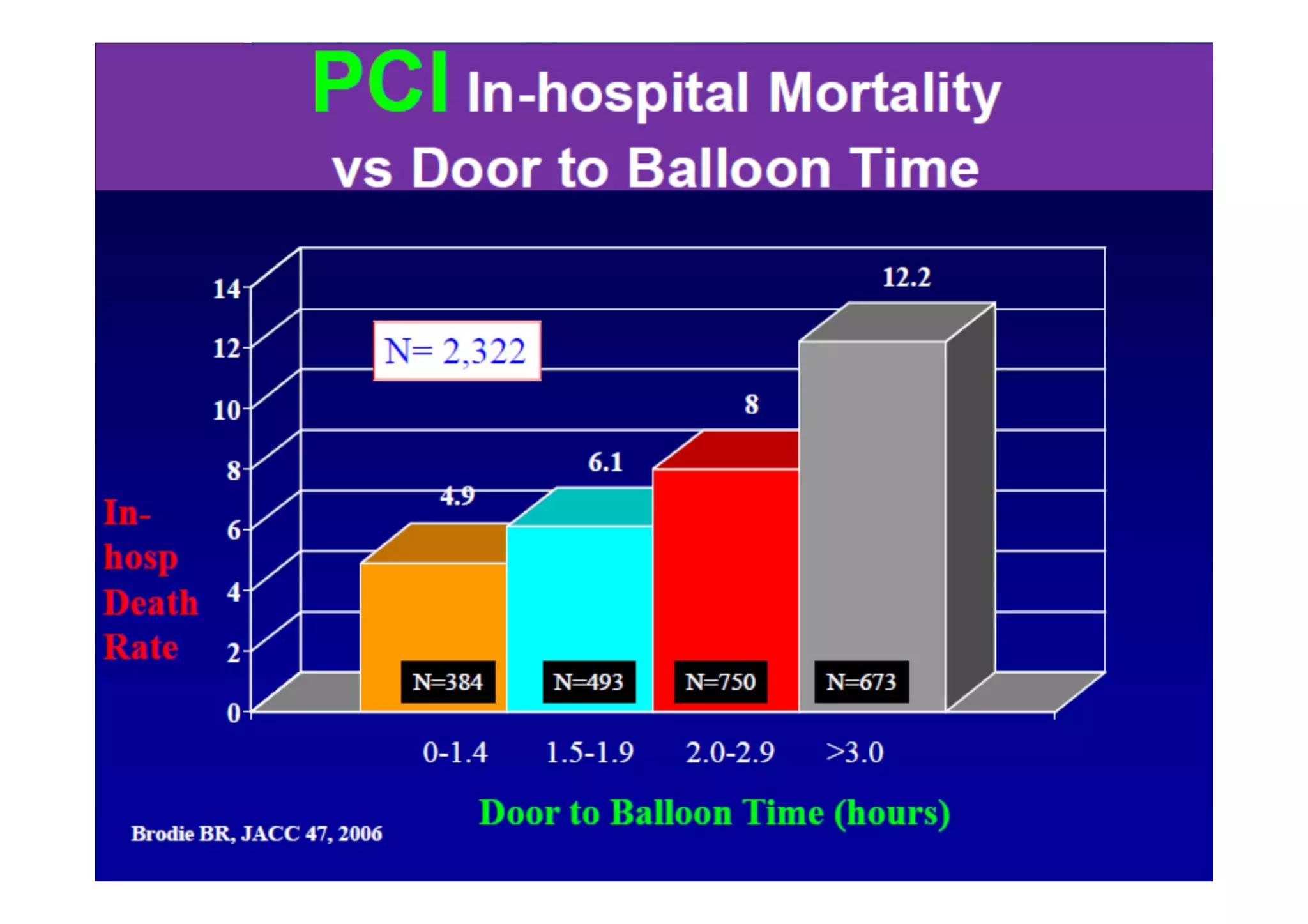
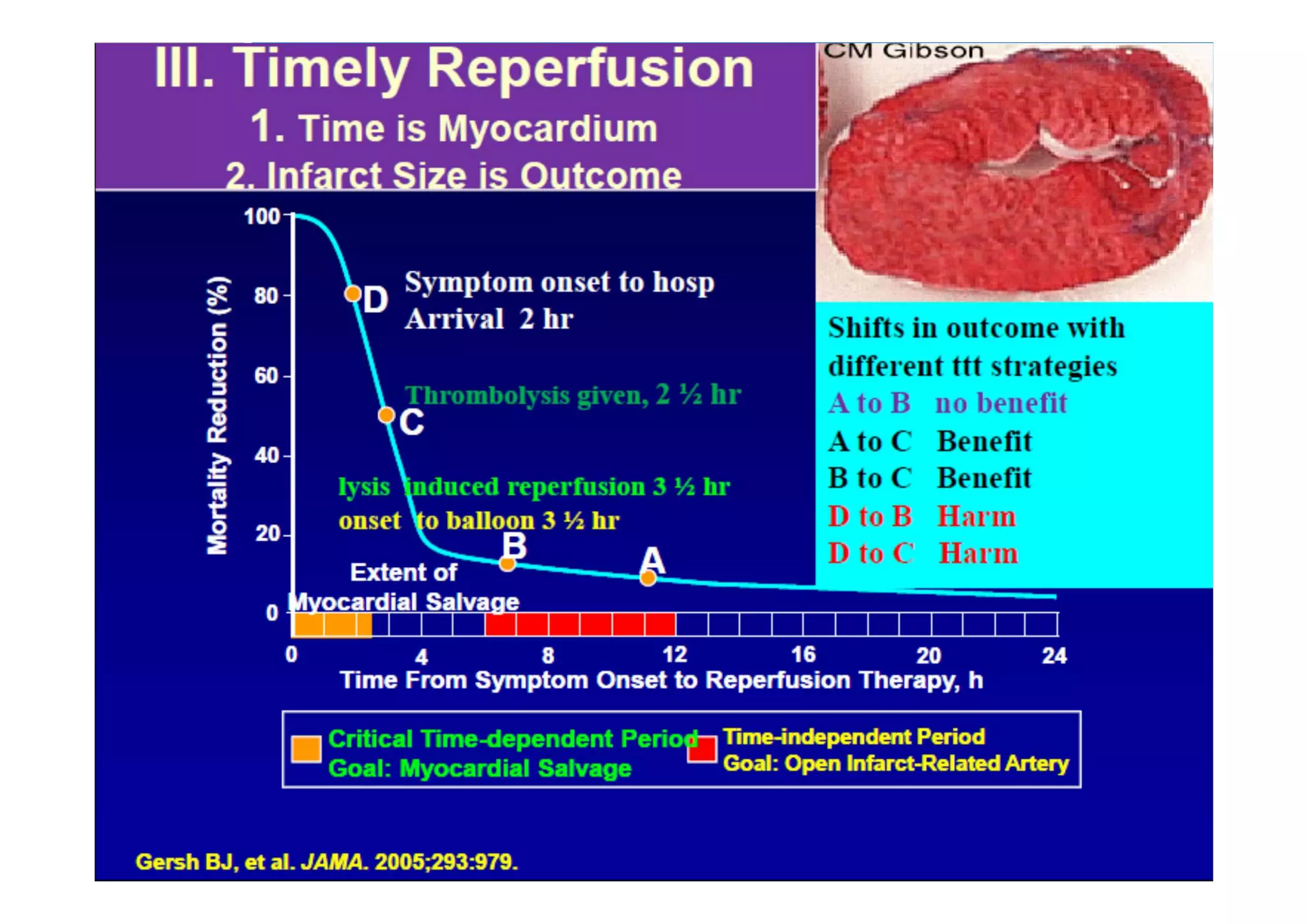
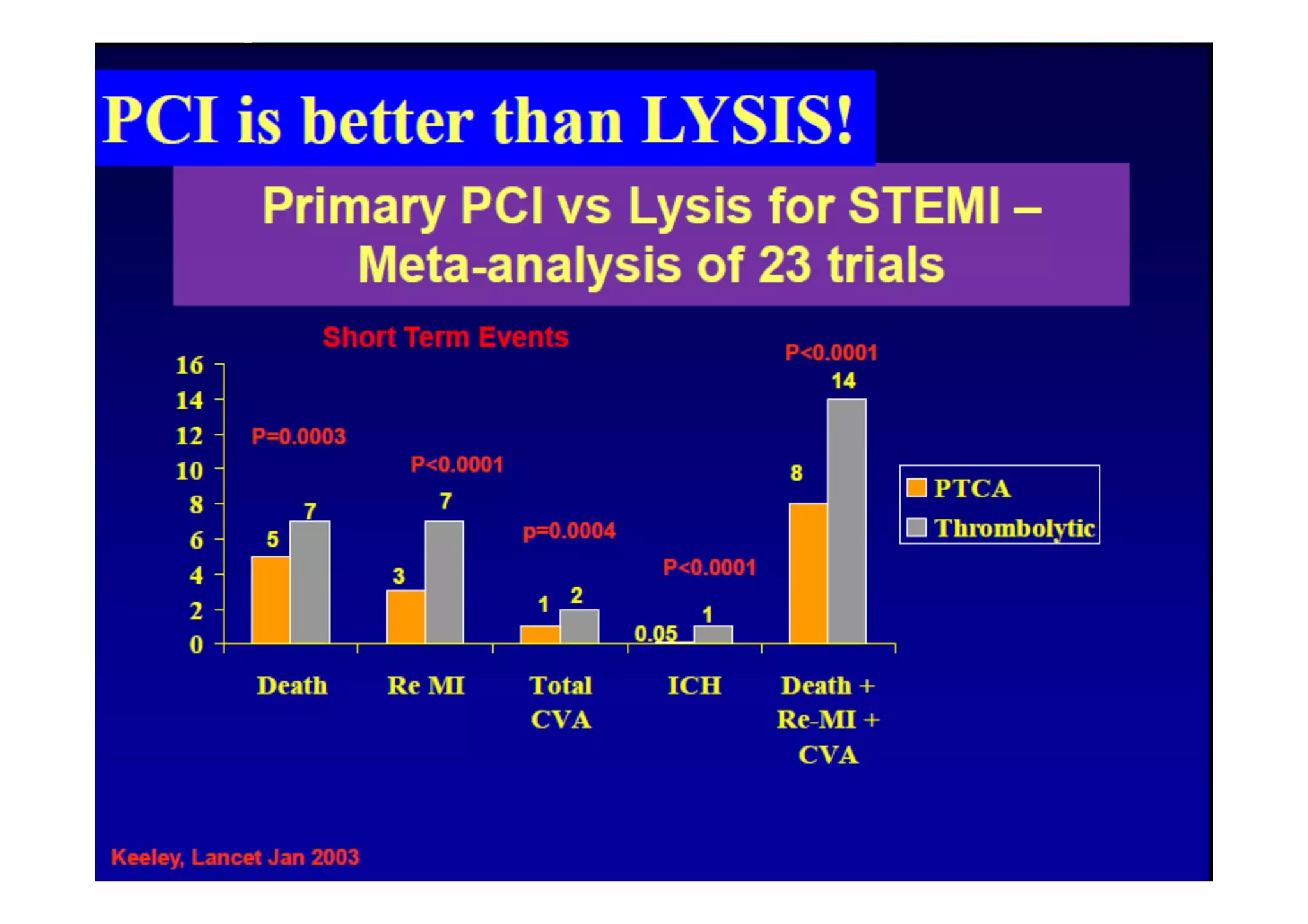
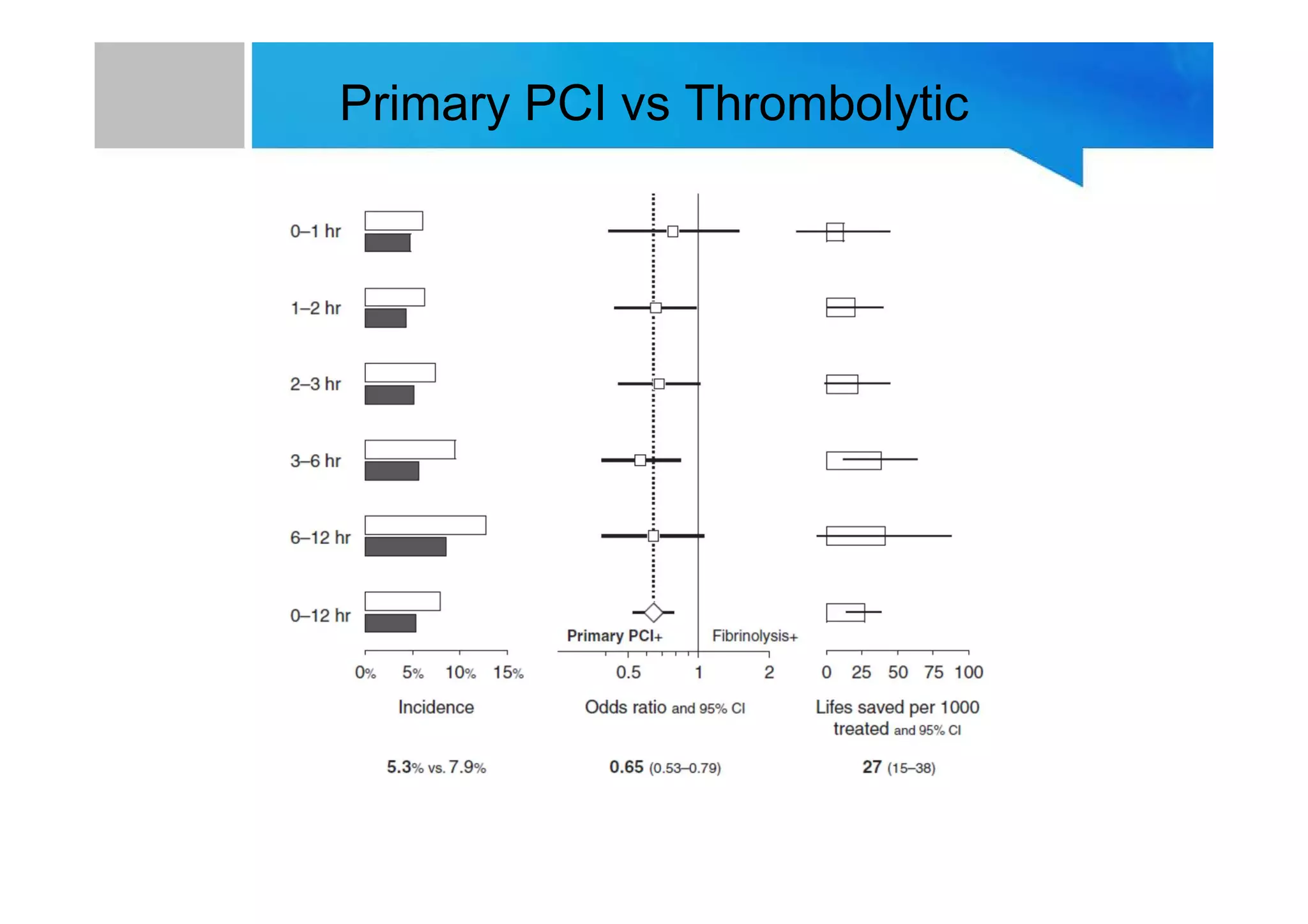
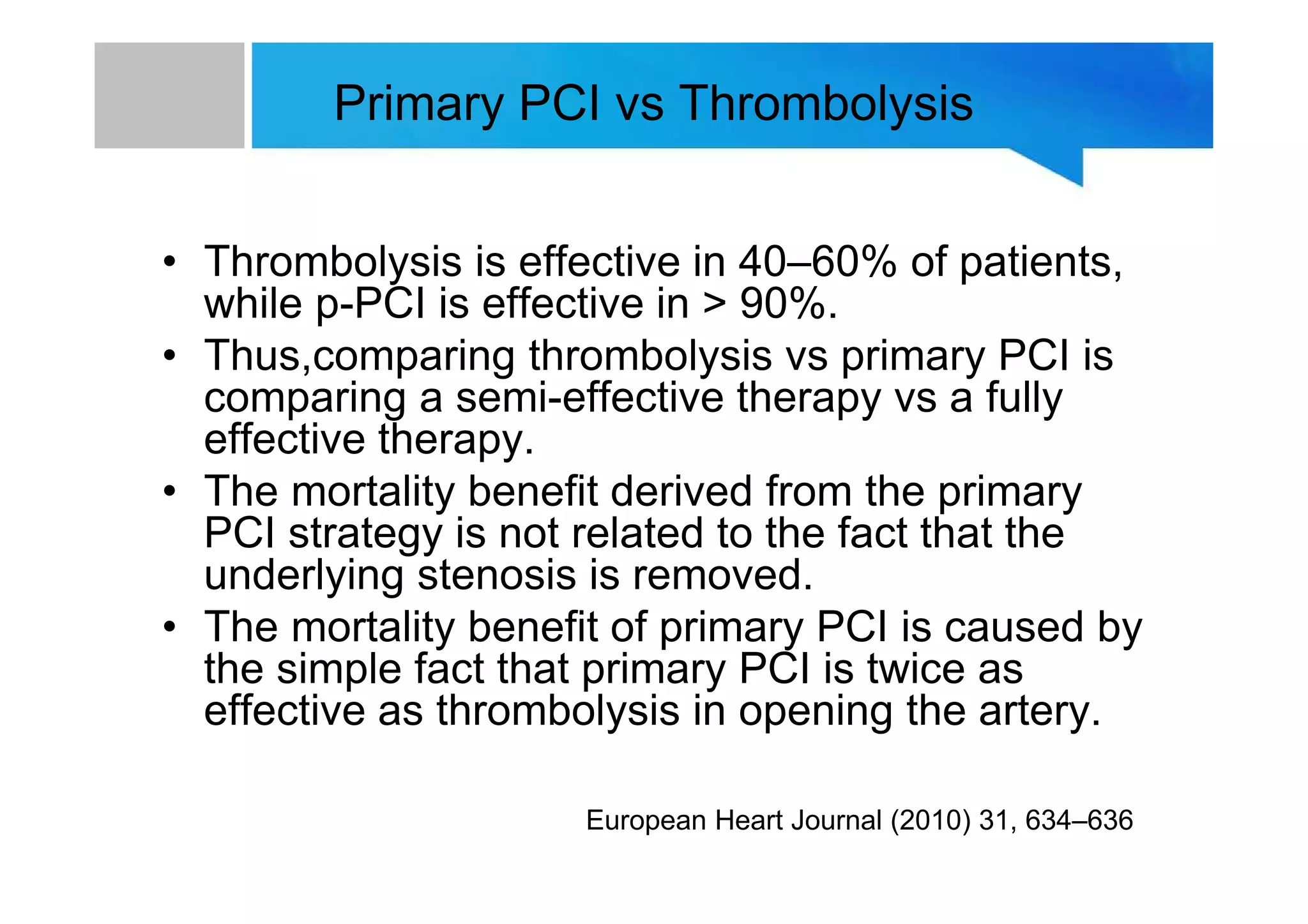
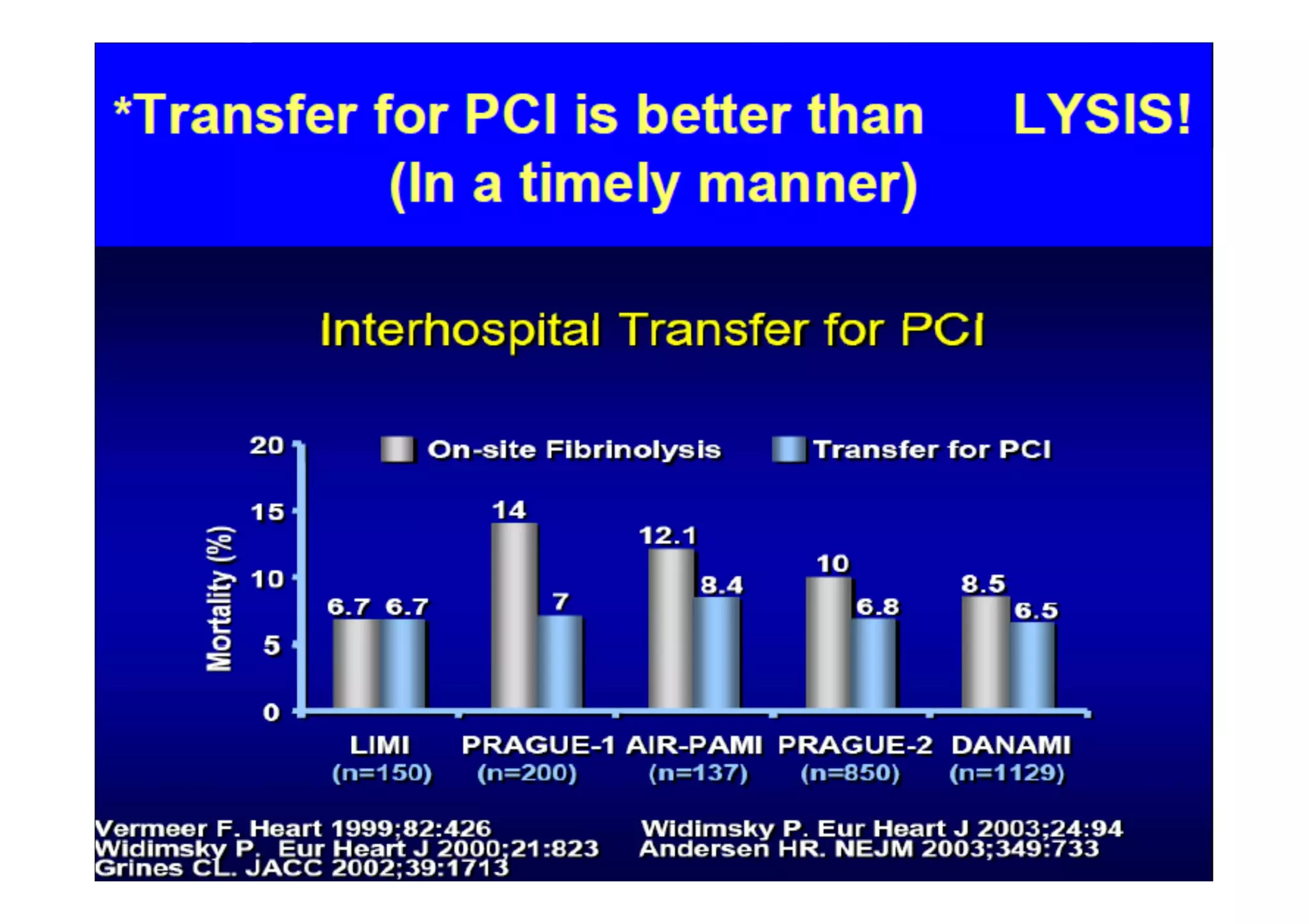
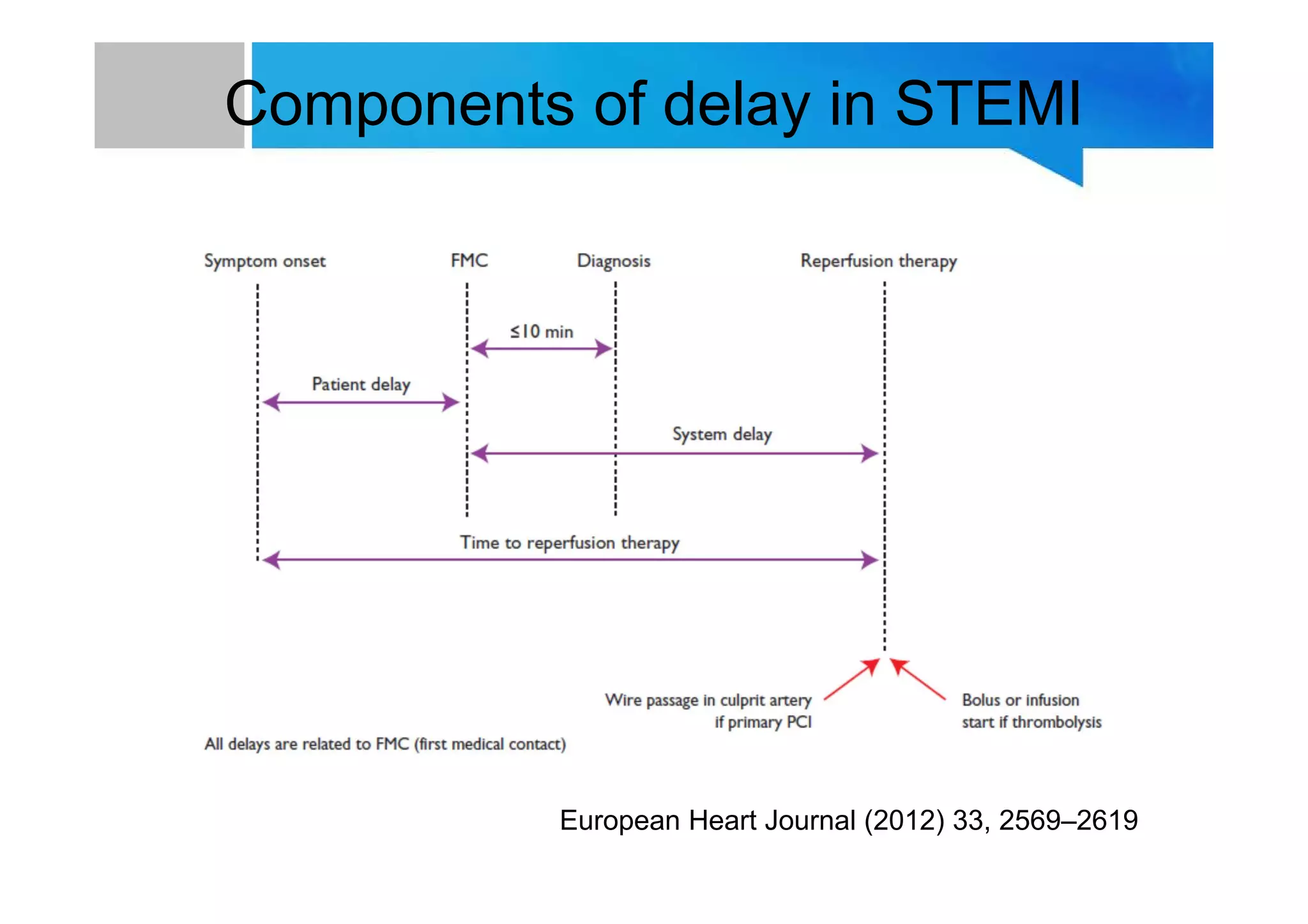
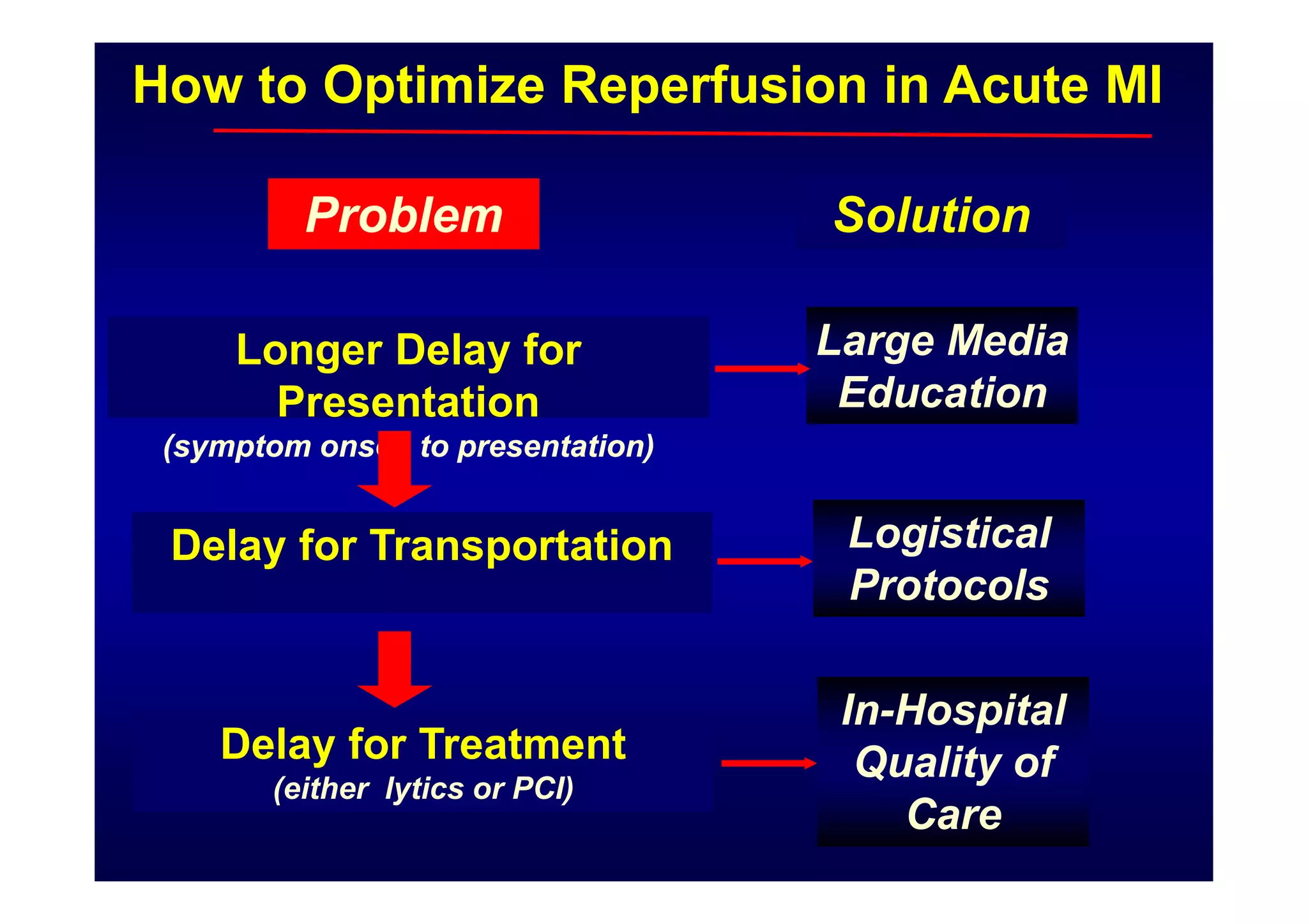
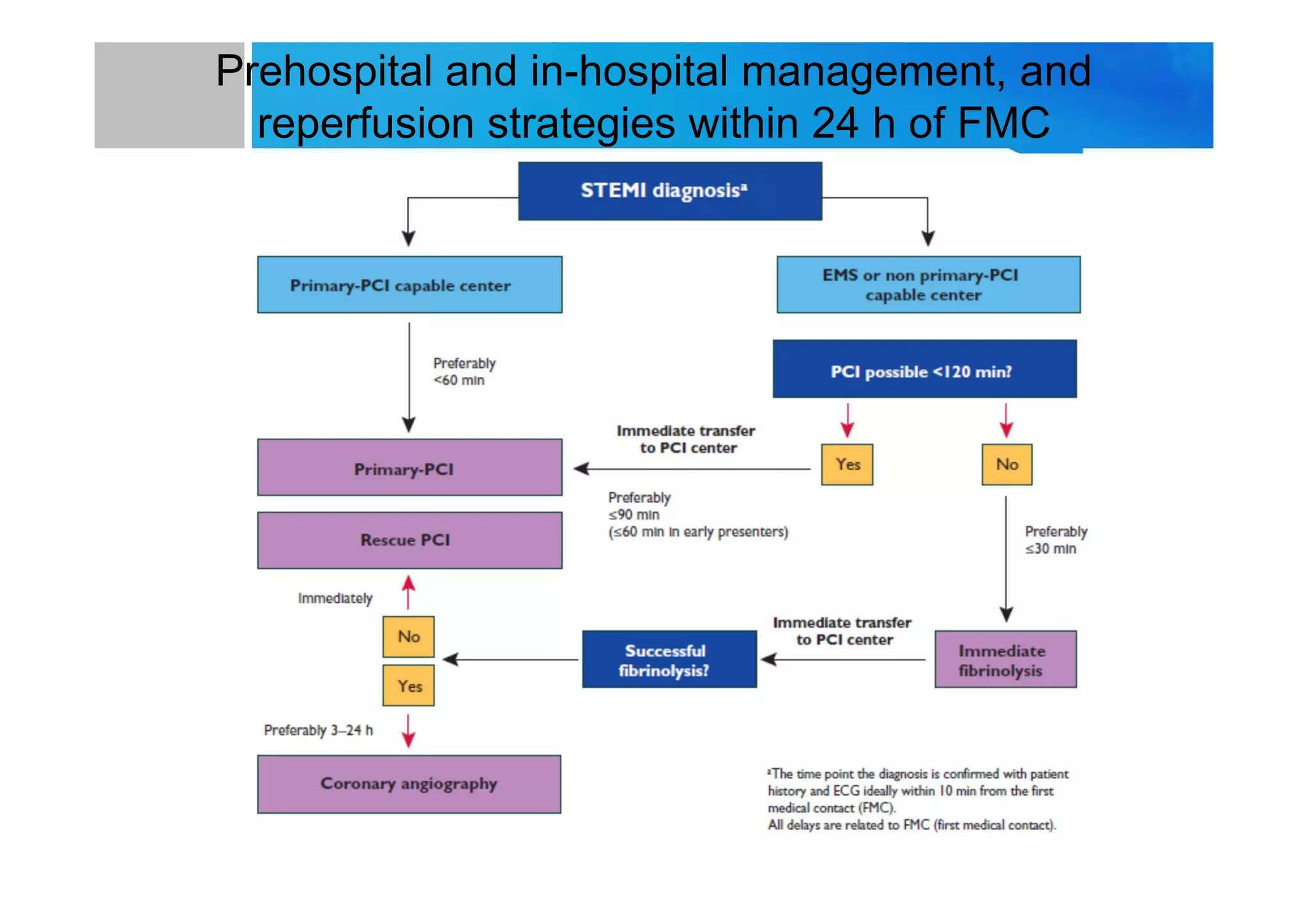
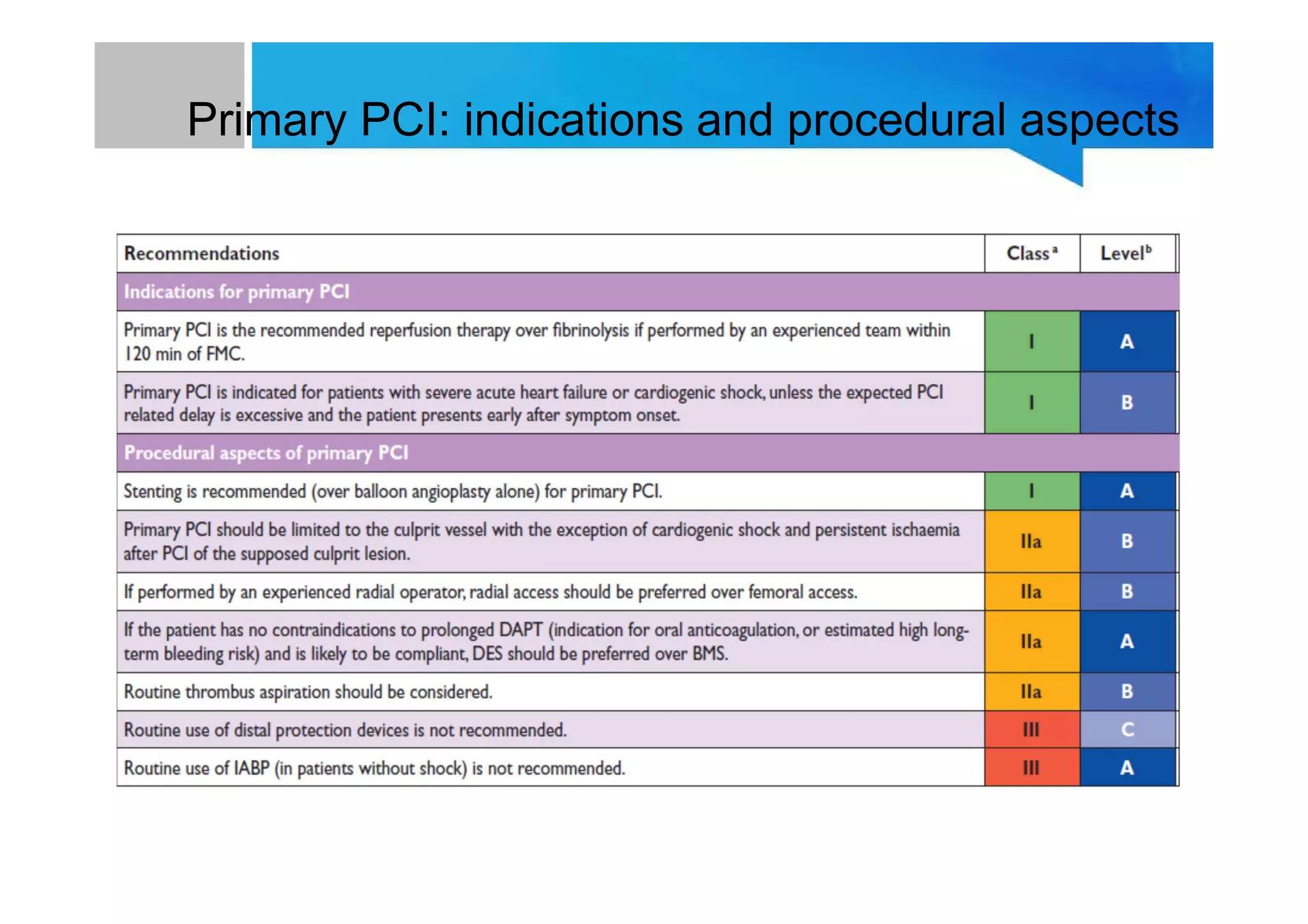
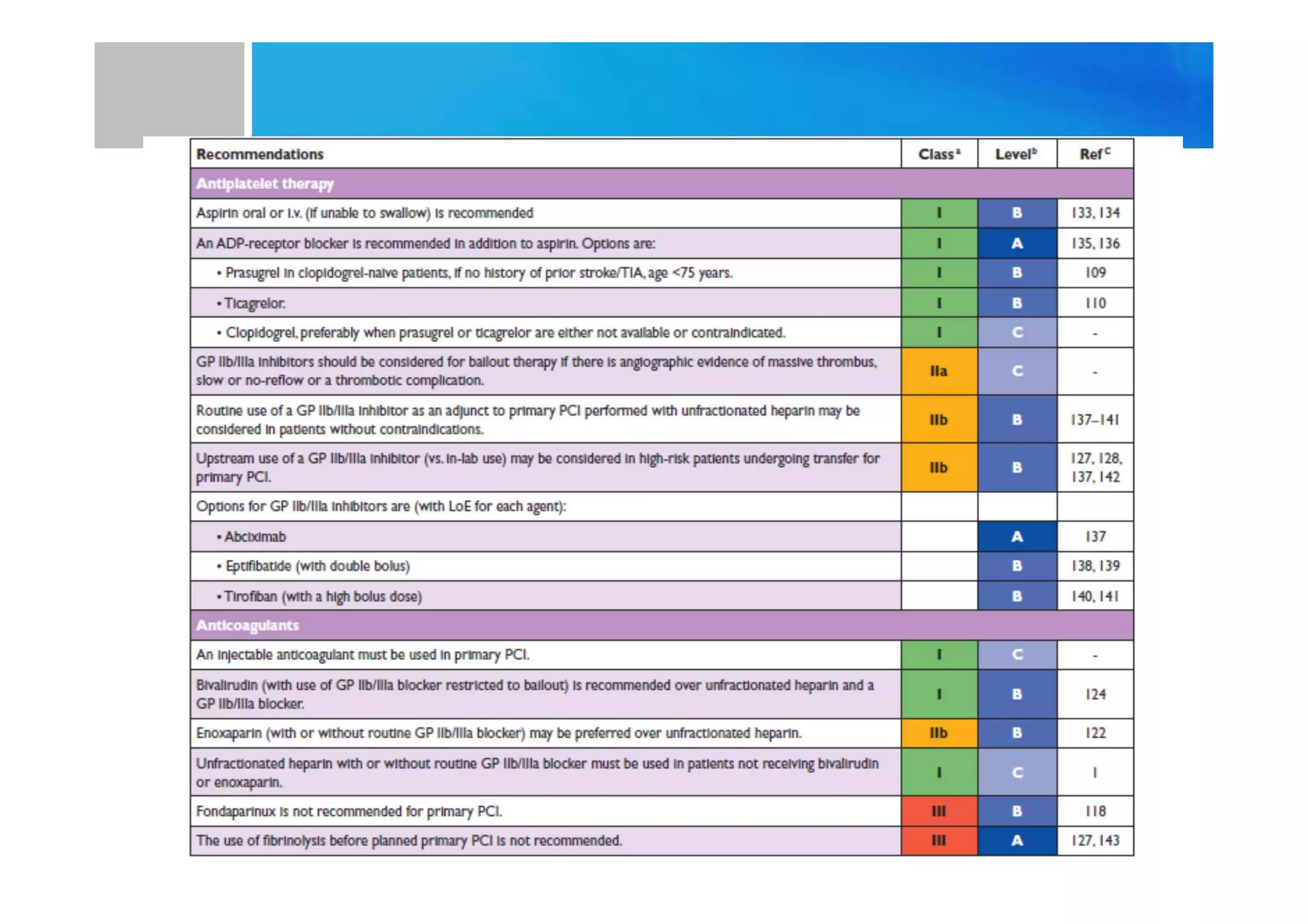
Primary PCI is the preferred emergency treatment for ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), outperforming thrombolysis with over 90% effectiveness compared to 40-60%. The mortality benefits from primary PCI are primarily due to its superior ability to open blocked arteries rather than the removal of underlying stenosis. Key considerations for successful primary PCI include optimizing prehospital and in-hospital management, adopting a radial access approach, and using drug-eluting stents.