This document provides an overview of oligopoly market structure. Key points include:
- Oligopoly is characterized by a small number of large, dominant sellers that are interdependent in their decision making.
- Firms monitor each other's actions closely and reactions can trigger countermoves, like aggressive advertising campaigns.
- Entry into the market is difficult due to barriers like economies of scale, control of inputs, and high capital requirements.
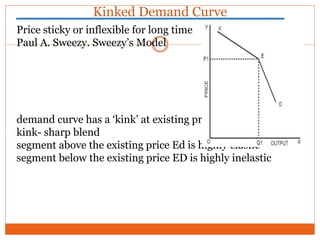
- There is no single pattern of pricing behavior - firms may cooperate tacitly or engage in price wars, leading to price rigidity.
- The demand curve is indeterminate due to uncertainty around competitors' reactions to price changes.