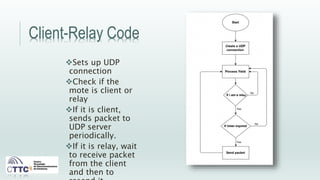
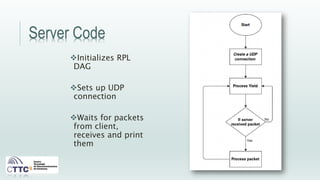
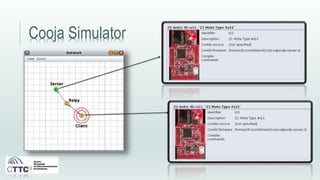
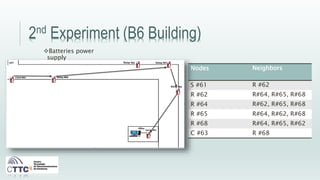
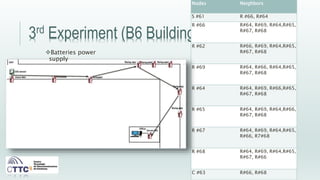
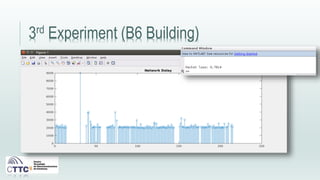
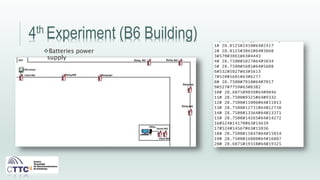
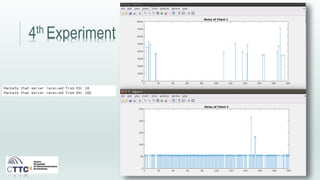
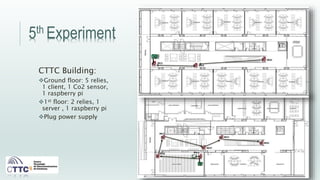
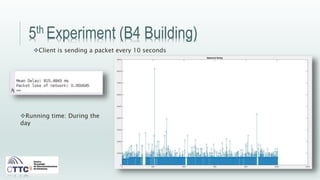
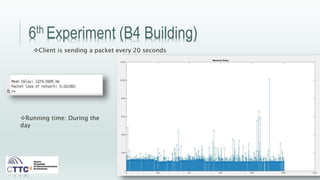
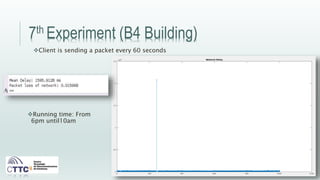
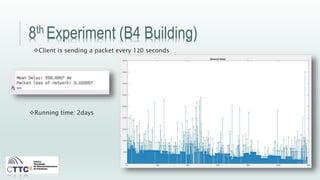
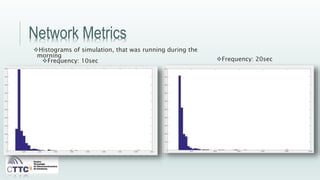
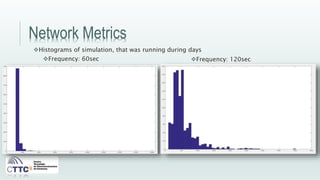
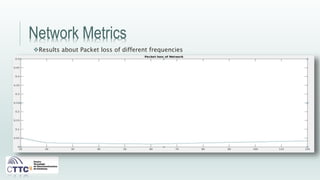
This document discusses experiments conducted using the Contiki operating system and RPL routing protocol in wireless sensor networks. It describes setting up networks with different numbers of relay and client nodes. Experiments were run with sensor nodes sending data at various frequencies to measure network performance over time periods ranging from a day to multiple days. Results on packet loss are presented. Further work is proposed to conduct more extensive RPL testing under additional configurations and add sensor nodes to track object movement.