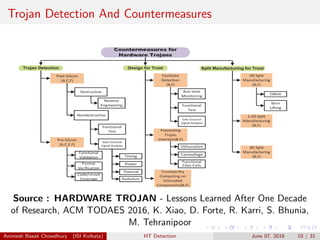
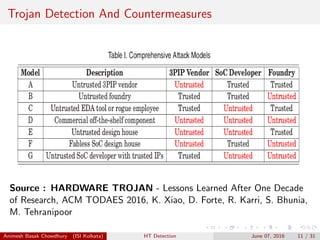
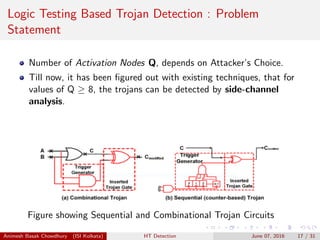
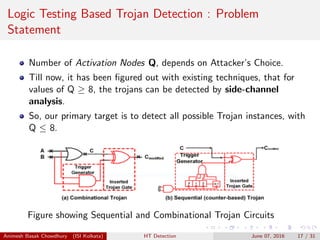
This document describes hardware trojans and techniques for detecting them. It discusses how modern design practices have increased security risks by outsourcing fabrication and using third-party IP. Hardware trojans maliciously tamper with designs by adding a small number of gates. Detection methods discussed include logic testing, side-channel analysis, and design-for-trust techniques. A statistical approach called MERO generates test patterns to activate rare events in the design in order to detect trojans added by combining rare trigger conditions. The focus is on detecting trojans with eight or fewer activation nodes.










![Introduction : Hardware Trojan (HT)
Why HARDWARE TROJAN are inserted in the Design :
Modify functionality.
Gain unauthorized access to the system.
Leak out sensitive information.
Launch denial-of-service attack.
Vunerable phases of IC development Cycle [Wolff10]
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 8 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-13-320.jpg)

![Trojan Detection : Pre-Silicon Stage
Pre-Silicon Verification and Validation
Use functional and formal Verification Techniques.
Assertion Based Verification flow have proven to be ineffective,
especially when the trojan triggering acts as time-bomb.[Beamont11]
Most of the ASICs, are relatively very large and complex. Formal
Tools suffer from scalability issues, inability to produce a
counter-example upto a certain level doesn’t guarantee the
design to be Trojan Free. [Beamont11]
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 12 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-17-320.jpg)
![Trojan Detection : Post-Silicon Stage
Side Channel Analysis
Use Current [Dak07], Path Delay [Jin08], Power Signatures [Rad10]
for comparision.
Requirement of Trusted IC for reference.
Unable to detect trojans, if additional 10-12 gates are introduced to
insert trojan.
False positive result on comparision of Golden IC with IC Under Test,
when smaller trojans are inserted.
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 13 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-18-320.jpg)
![Trojan Detection : Post-Silicon Stage
Design-for-TRUST and Logic Testing Based Techniques
Lesser explored area.
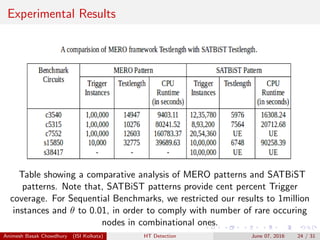
MERO Test Patterns : Significant contribution in reporting trojans of
smaller sizes using Statistical Approach. [RSubhra09]
DFTT : Design for Trojan Test , a framework defined to make
insertion of Trojan extremely difficult at design level and
Manufacturing level. [Jin10]
ODETTE: A non-scan design-for-test methodology for Trojan
detection in ICs. Effective for uncovering Trojans in Sequential
Circuits. [Banga11]
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 14 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-19-320.jpg)








![MERO Test Pattern : A statistical approach For HT
Detection
Chakraborty, R.S. proposed a testing framework MERO, which is an
ATPG designed for detecting Trojan in a given netlist, minimizing the
number of test patterns.[RSubhra09]
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 18 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-34-320.jpg)
![MERO Test Pattern : A statistical approach For HT
Detection
Chakraborty, R.S. proposed a testing framework MERO, which is an
ATPG designed for detecting Trojan in a given netlist, minimizing the
number of test patterns.[RSubhra09]
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 18 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-35-320.jpg)
![MERO Test Pattern : A statistical approach For HT
Detection
Chakraborty, R.S. proposed a testing framework MERO, which is an
ATPG designed for detecting Trojan in a given netlist, minimizing the
number of test patterns.[RSubhra09]
MERO utilizes the concept of N-detect ATPG scheme. The
framework generates test patterns which can activate the Activation
Node to its RARE valued logic at least N times.
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 18 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-36-320.jpg)
![MERO Test Pattern : A statistical approach For HT
Detection
Chakraborty, R.S. proposed a testing framework MERO, which is an
ATPG designed for detecting Trojan in a given netlist, minimizing the
number of test patterns.[RSubhra09]
MERO utilizes the concept of N-detect ATPG scheme. The
framework generates test patterns which can activate the Activation
Node to its RARE valued logic at least N times.
The underlying assumption is, increasing the value of N, would also
increase the testset length, which increases the possibility of
simultaneous occurrence of rare logic at the Trigger instances, thereby
triggering the trojan.
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 18 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-37-320.jpg)
![MERO Test Pattern : A statistical approach For HT
Detection
Chakraborty, R.S. proposed a testing framework MERO, which is an
ATPG designed for detecting Trojan in a given netlist, minimizing the
number of test patterns.[RSubhra09]
MERO utilizes the concept of N-detect ATPG scheme. The
framework generates test patterns which can activate the Activation
Node to its RARE valued logic at least N times.
The underlying assumption is, increasing the value of N, would also
increase the testset length, which increases the possibility of
simultaneous occurrence of rare logic at the Trigger instances, thereby
triggering the trojan.
Though the framework is a huge achievement over ATPG patterns
and Random test patterns in Trojan Detection, still the technique
suffers from scalability bottleneck and larger testset compared to
sample size.
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 18 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-38-320.jpg)



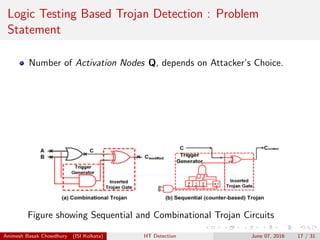
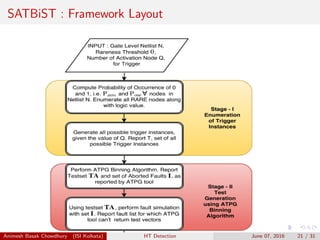
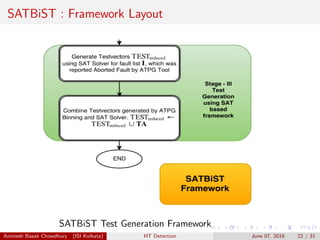
![SATBiST : Scalable ATPG Binning and SAT Based
Approach For HT Detection
Points Considered while designing the Framework
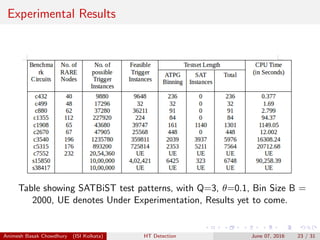
We have taken value of Rareness threshold θ, to be 0.1.
The trigger instances consist of 3 Activation Nodes, i.e. Q=3.
The trigger instances directly corrupt a primary output(PO) or a
set of POs.
We use the tools like ATALANTA ATPG tool [ATALANTA], HOPE
fault Simulator [HOPE], Transition Probability Calculator(TPC)
[Salmani12] from trust-hub.org and zchaff SAT Solver [zChaff].
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 20 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-42-320.jpg)


![References
Chakraborty, Rajat Subhra, et al. [RSubhra09]
”MERO: A statistical approach for hardware Trojan detection.” Cryptographic
Hardware and Embedded Systems-CHES 2009. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2009.
396-410.
Salmani, Hassan, Mohammad Tehranipoor, and Jim Plusquellic [Salmani12]
”A novel technique for improving hardware trojan detection and reducing trojan
activation time.” Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, IEEE Transactions
on 20.1 (2012): 112-125.
Wolff, Francis, Chris Papachristou, Swarup Bhunia, and Rajat S. Chakraborty.
[Wolff08]
”Towards Trojan-free trusted ICs: Problem analysis and detection scheme.”
Proceedings of the conference on Design, automation and test in Europe. ACM,
2008.
Tehranipoor, Mohammad, and Farinaz Koushanfar [Teh101]
”A survey of hardware Trojan taxonomy and detection.” (2010).
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 27 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-49-320.jpg)
![References
Tehranipoor, Mohammad, et al. [Teh102]
”Trustworthy hardware: Trojan detection and design-for-trust challenges.”
Computer 7 (2010): 66-74.
Jin, Y. , Makris, Y. [Jin08]
”Hardware Trojan detection using path delay fingerprint.” Hardware-Oriented
Security and Trust, 2008. HOST 2008. IEEE International Workshop on. IEEE,
2008.
Agrawal, Dakshi, et al. [Dak07]
”Trojan detection using IC fingerprinting.” Security and Privacy, 2007. SP’07. IEEE
Symposium on. IEEE, 2007
Rad, Reza, Jim Plusquellic, and Mohammad Tehranipoor [Rad10]
A sensitivity analysis of power signal methods for detecting hardware Trojans under
real process and environmental conditions.” Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
Systems, IEEE Transactions on 18.12 (2010): 1735-1744.
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 28 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-50-320.jpg)
![References
Jin, Yier, Nathan Kupp, and Yiorgos Makris [Jin10]
”DFTT: Design for Trojan test.” Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS), 2010
17th IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2010.
Banga, Mainak, and Michael S. Hsiao [Banga11]
”ODETTE: A non-scan design-for-test methodology for trojan detection in ics.”
Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), 2011 IEEE International
Symposium on. IEEE, 2011.
Lee, Hyung Ki, and Dong Sam Ha [HOPE]
”HOPE: An efficient parallel fault simulator for synchronous sequential circuits.”
Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, IEEE Transactions on
15.9 (1996): 1048-1058.
Ha, D. S. [ATALANTA]
ATALANTA: An ATPG Tool.” Bradley Department of Electrical Engineering,
Virginia Polytechnic and State University, Blacksburg, VA (1994).
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 29 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-51-320.jpg)
![References
Eggersgl, Stephan, and Rolf Drechsler [Rolf]
High Quality Test Pattern Generation and Boolean Satisfiability. Springer Science
Business Media, 2012.
Moskewicz, M. W., Madigan, C. F., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Malik, S. [zChaff]
”CHAFF: Engineering an efficient SAT solver.” Proceedings of the 38th annual
Design Automation Conference. ACM, 2001.
Beamont, Mark et al. [Beamont11]
”Hardware Trojan : Threat, Prevention and Countermeasures, A Literature survey.”
Unclassified Report, Australian Government, Department of Defence. 2011
Animesh Basak Chowdhury (ISI Kolkata) HT Detection June 07, 2016 30 / 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b4e68c53-f2e9-4def-bf20-8b18e4984191-160613165009/85/presentation_DRDO-52-320.jpg)
