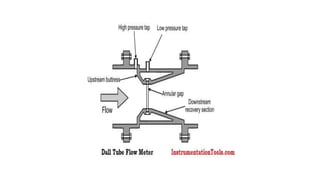
The document discusses the Dall tube, which is a type of flow meter that combines aspects of a Venturi tube and an orifice plate. It features a tapering intake like a Venturi tube but has a shoulder like an orifice plate to create a sharp pressure drop. It is commonly used for large flow applications where it has lower pressure drops than an orifice plate. The Dall tube works by measuring the differential pressure created by the restriction between the converging and diverging cones within the tube to determine flow rate. It has advantages over Venturi tubes like higher pressure developed for lower pressure lost and is more compact, making it suitable for large flows.