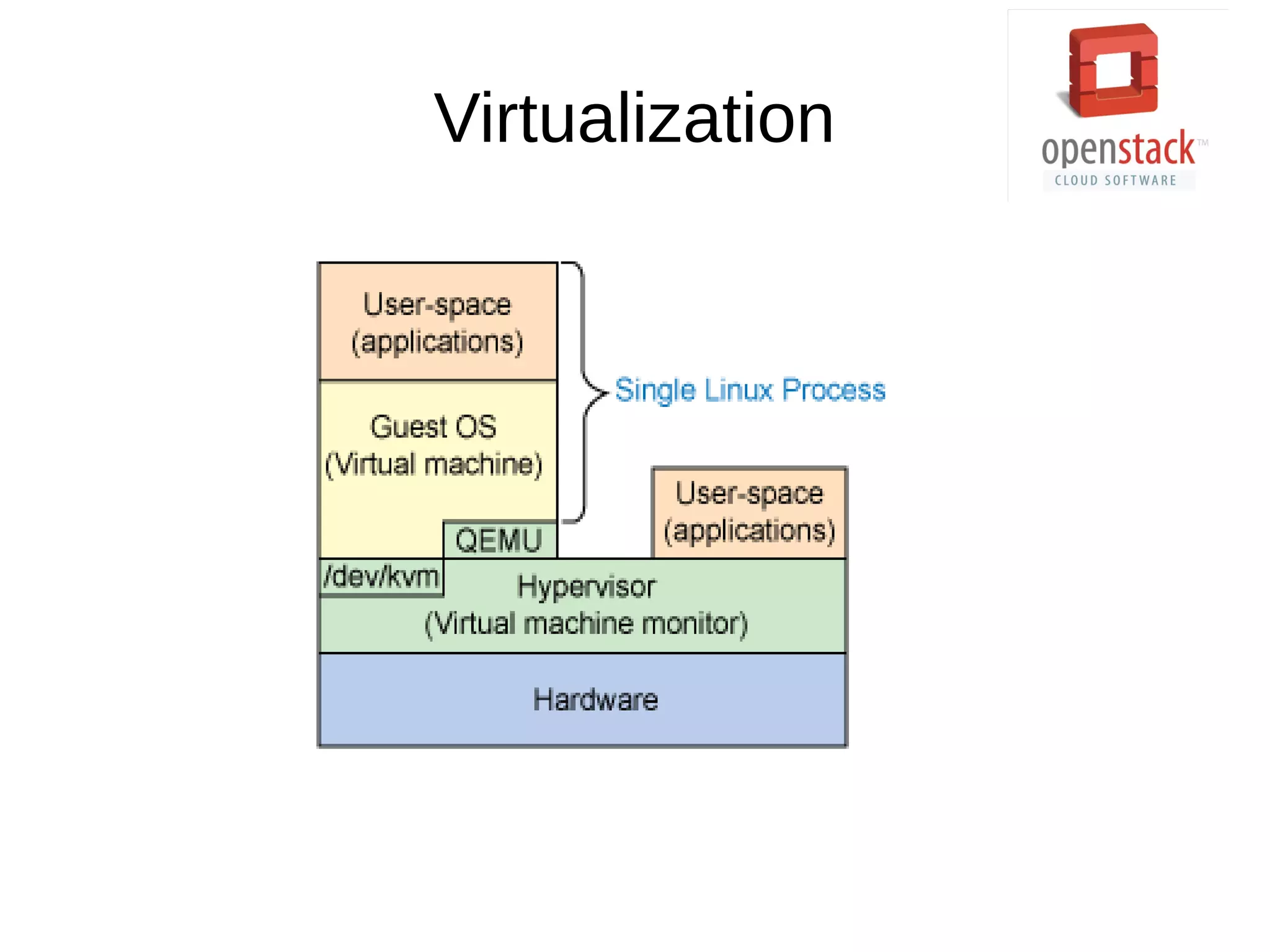
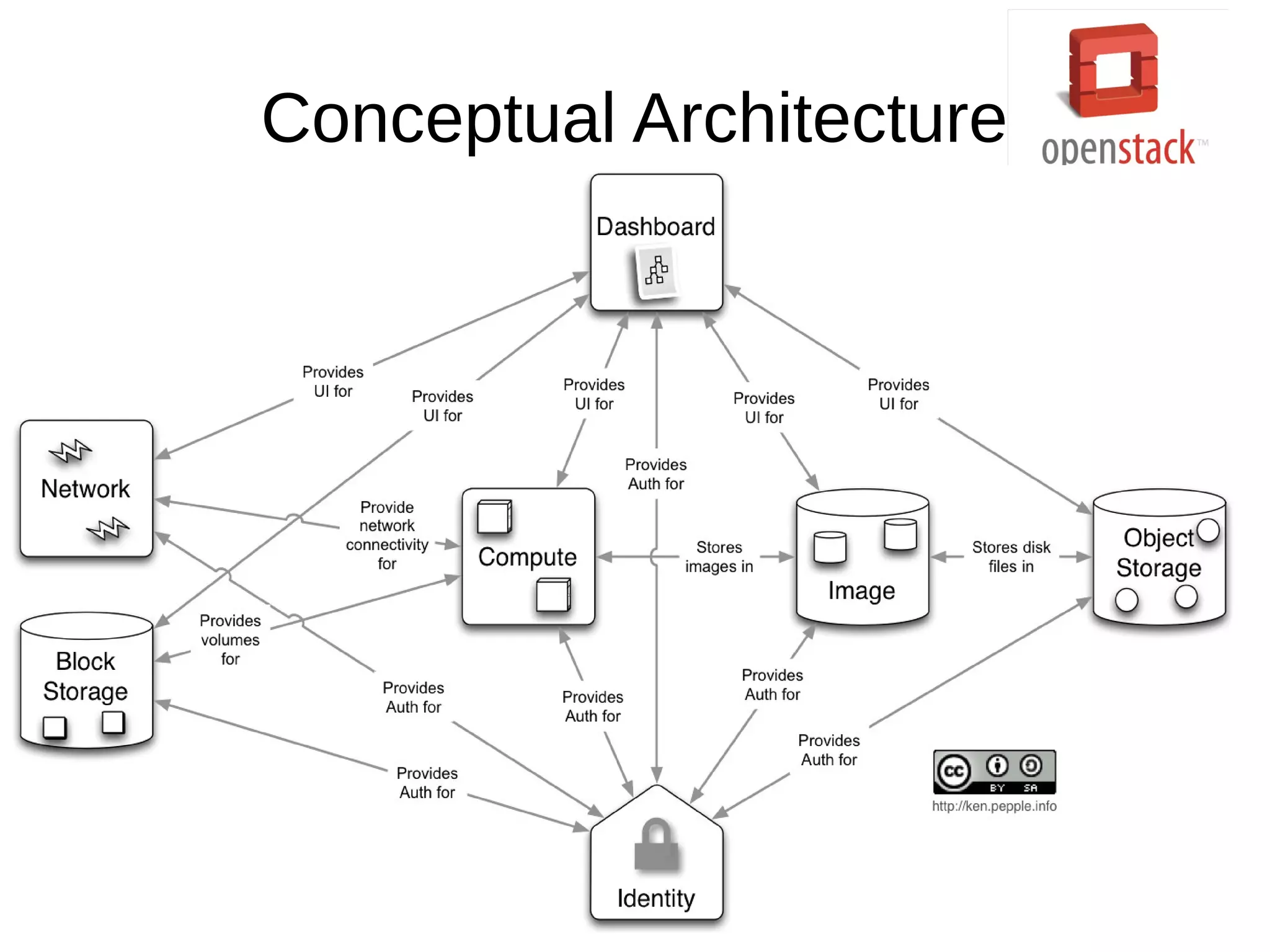
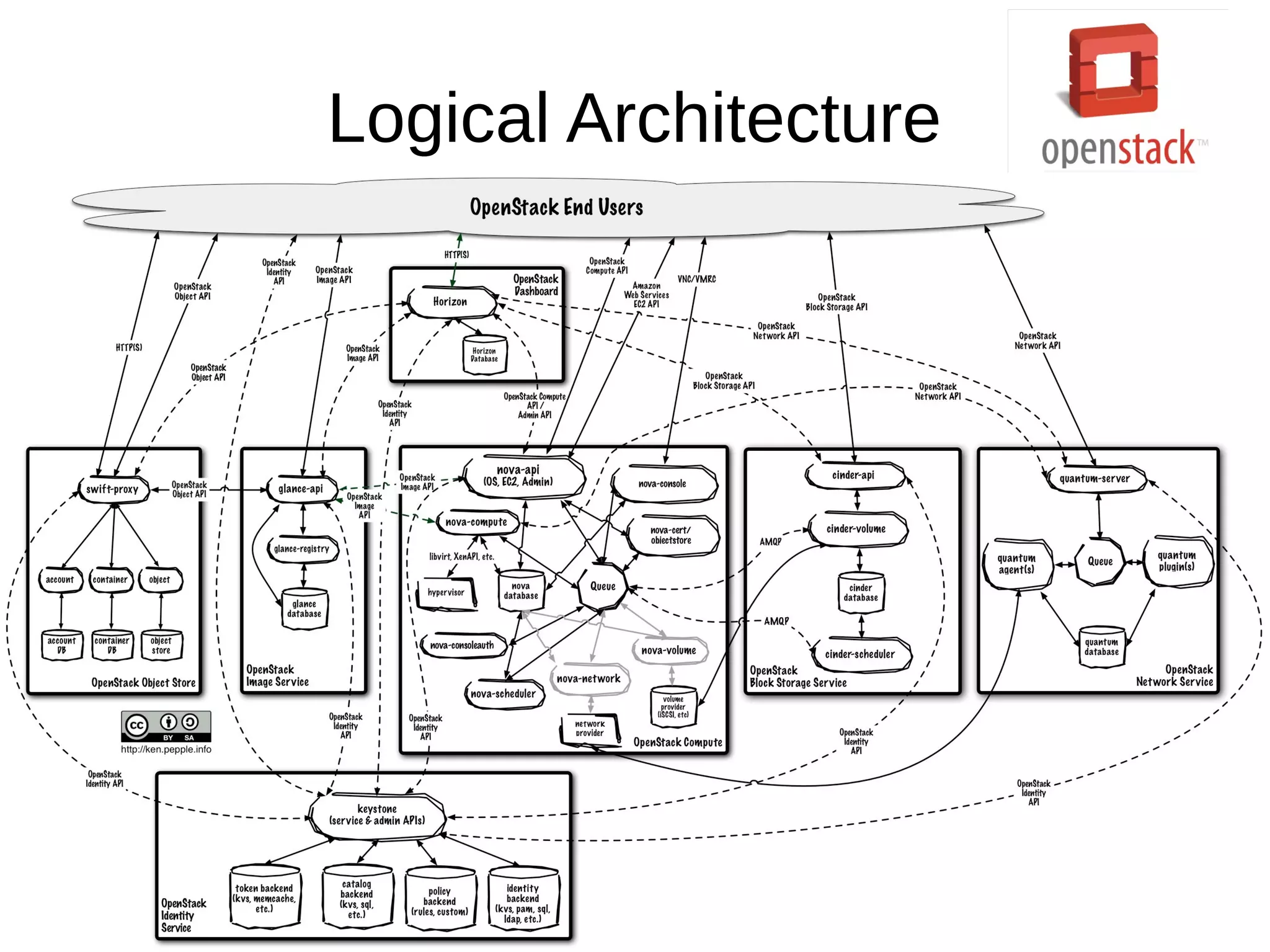
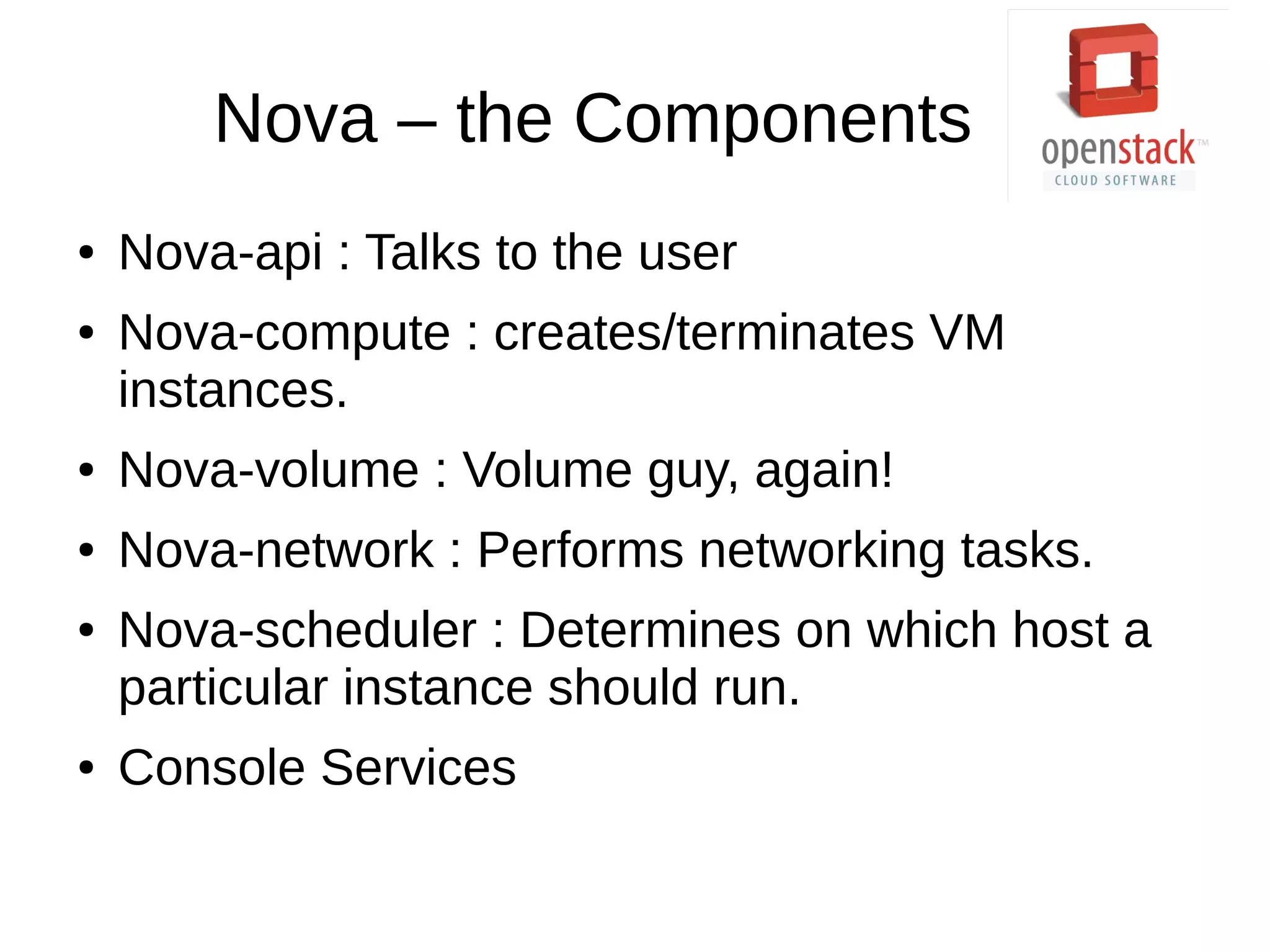
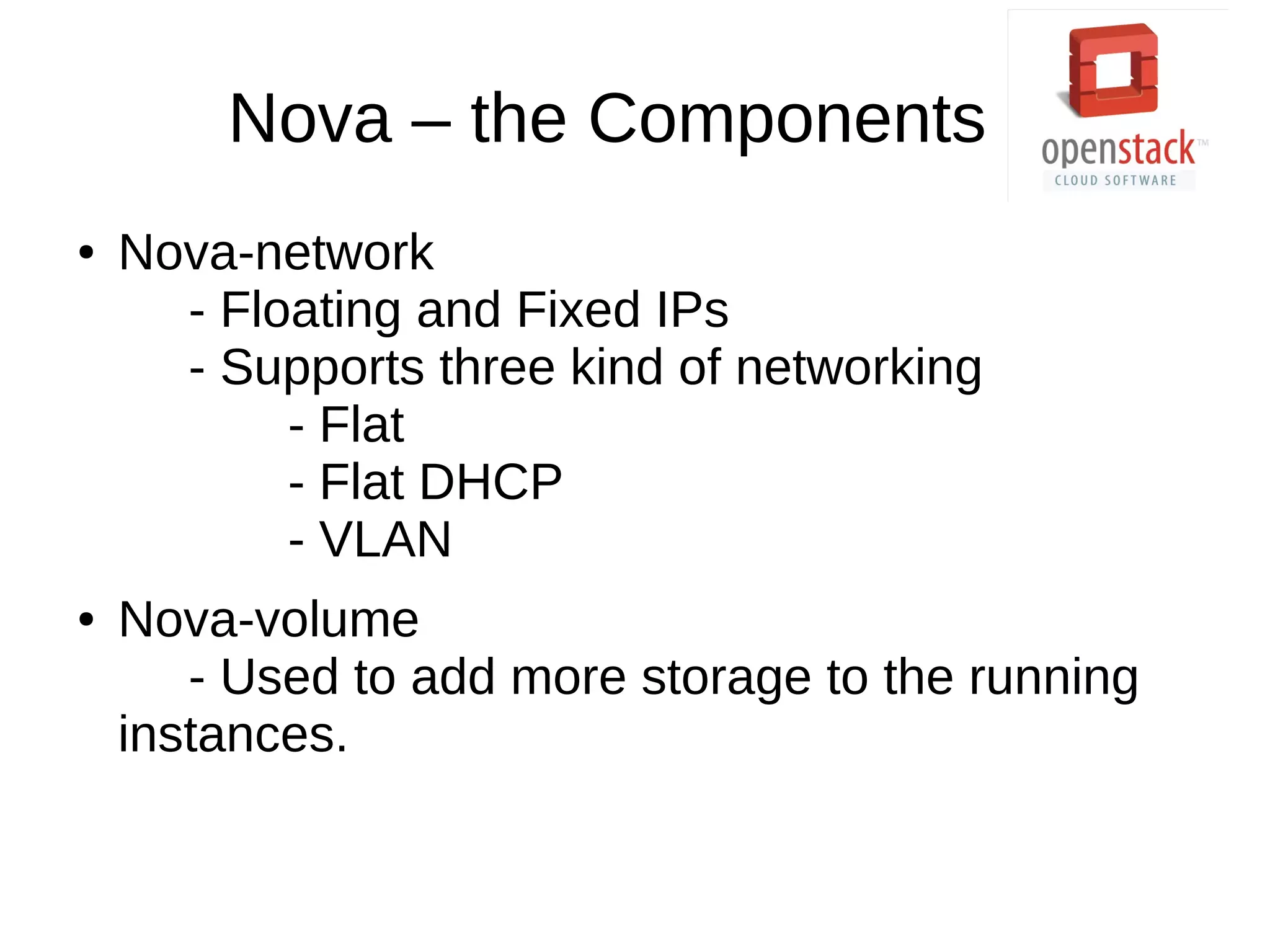
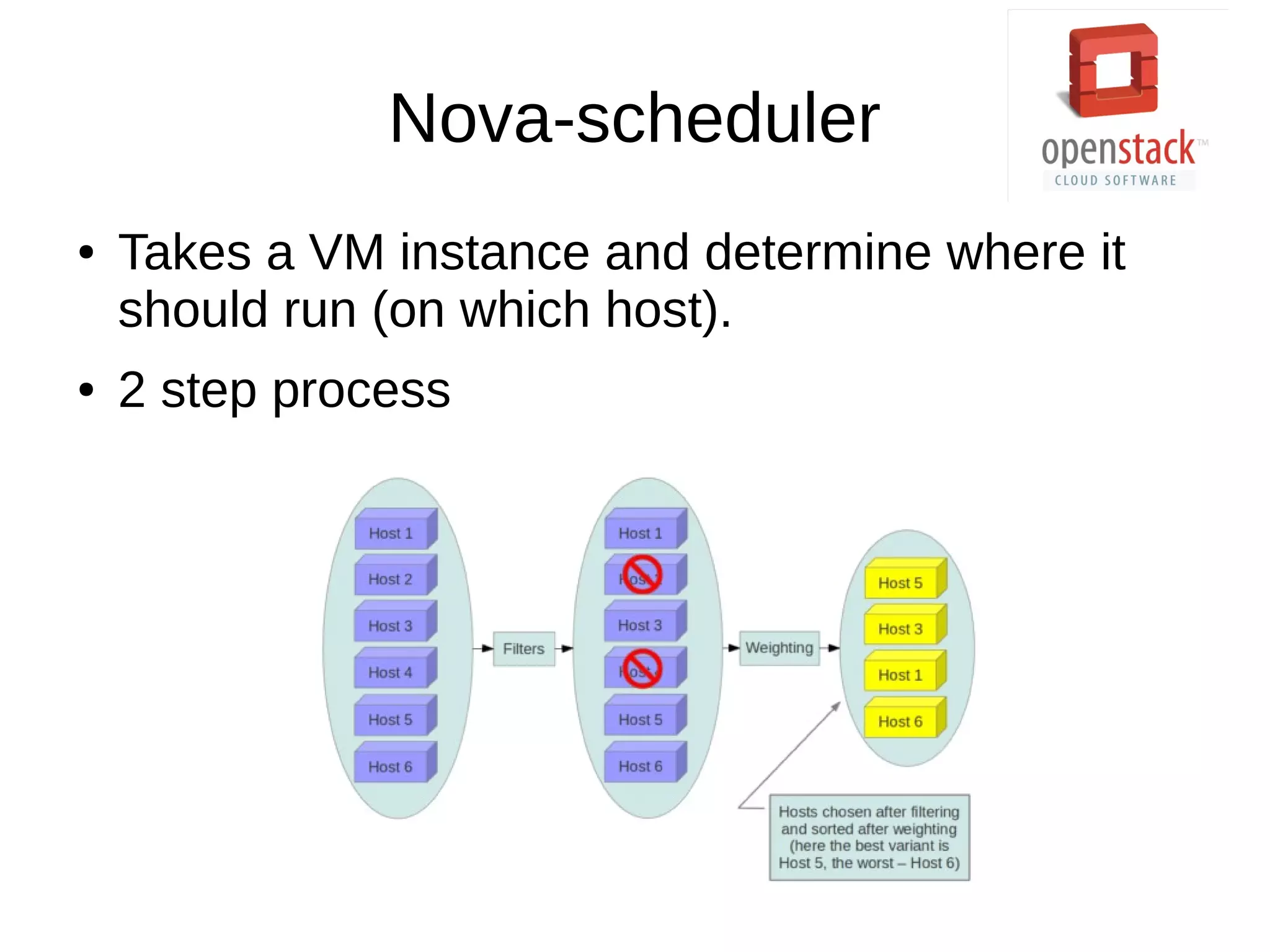
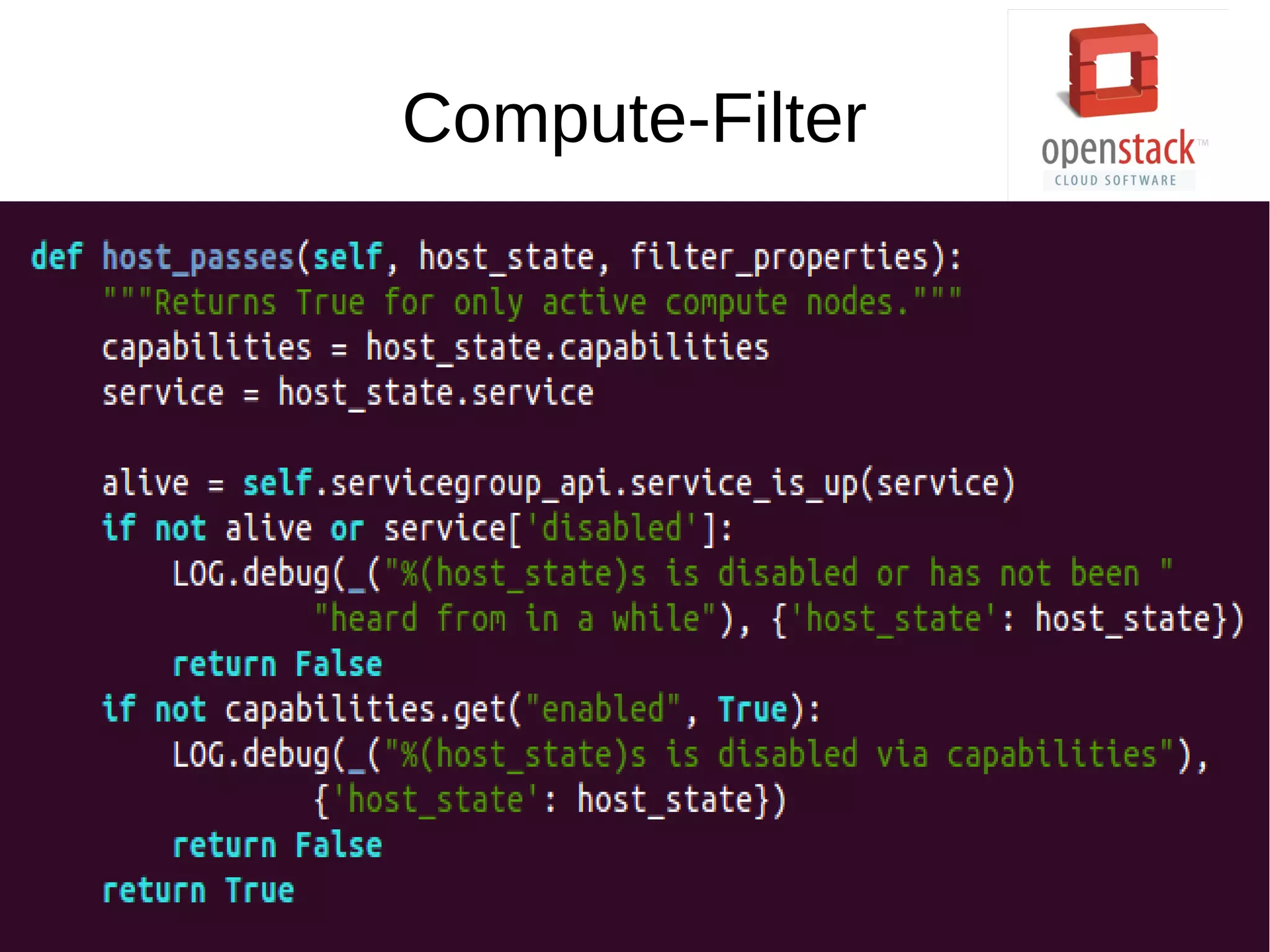
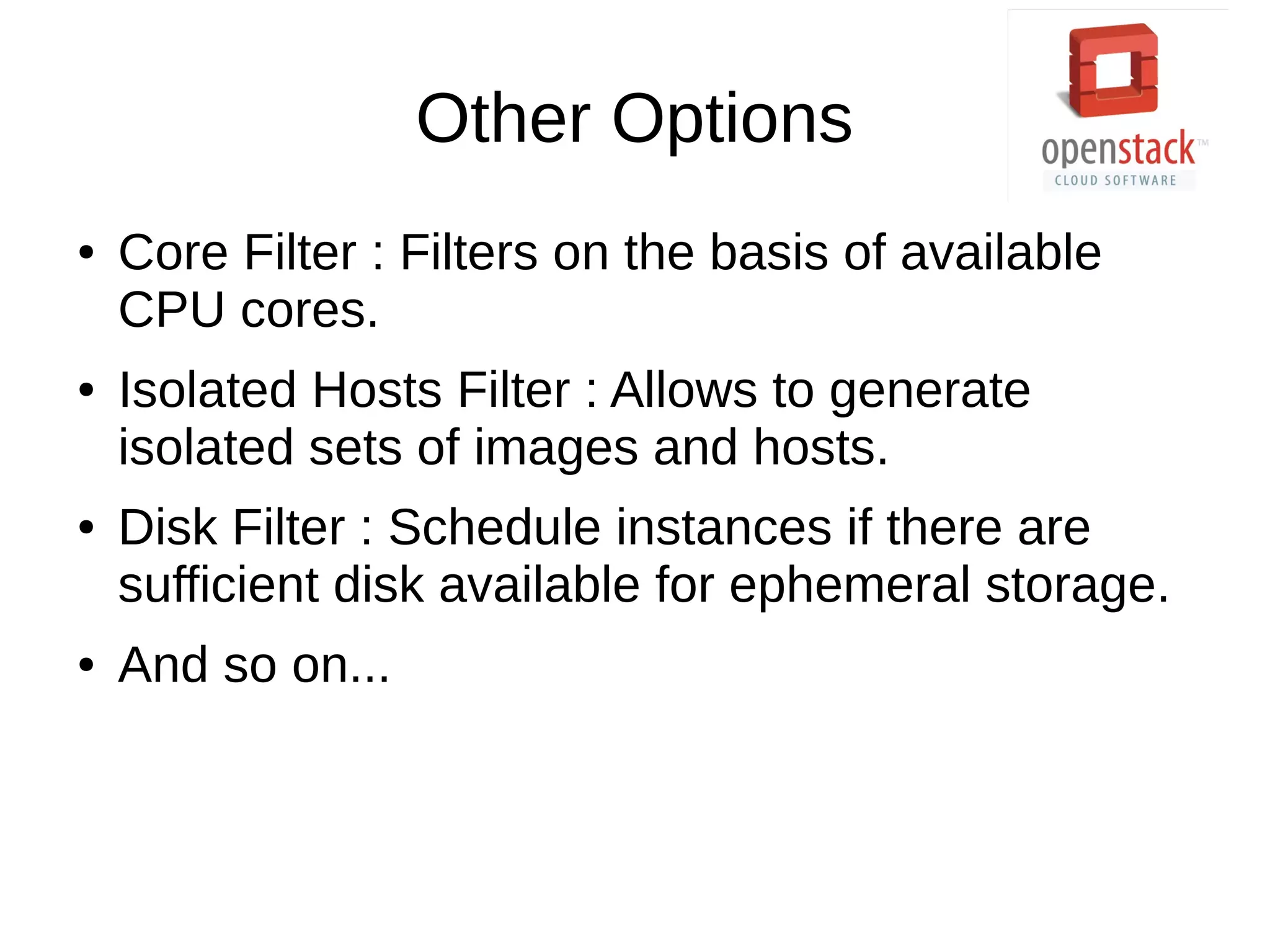
OpenStack is an open source cloud operating system that provides on-demand provisioning of compute, storage, and networking resources. It consists of several interconnected components that are managed through a dashboard interface. The key components include Horizon (dashboard), Keystone (authentication), Swift (object storage), Glance (image repository), Nova (compute), Quantum (networking), and Cinder (block storage). Nova is responsible for running virtual machine instances by retrieving images from Glance and scheduling instances on compute hosts using the Nova scheduler. The Nova scheduler uses filters and weights to determine the most suitable host for an instance based on availability, capabilities, and load.