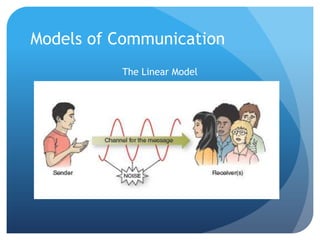
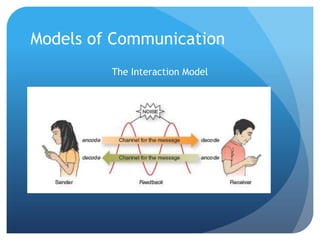
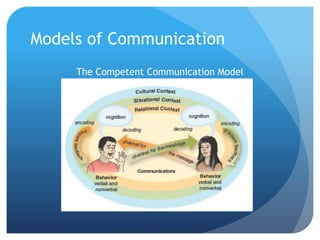
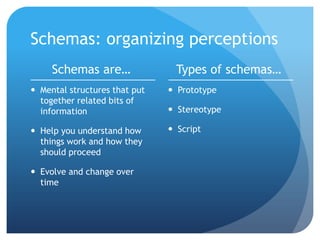
Communication is the process of exchanging information through symbols and behaviors to create shared meaning and understanding, develop relationships, and achieve goals. It is symbolic, requires a shared code, and occurs through various channels in a transactional process as depicted in models of communication. Perception involves interpreting experiences through schemas that organize information and can be influenced by factors like culture, which relates to values, beliefs, organizations, gender, and location that shape communicative behaviors. Effective intercultural communication involves listening, thinking before acting, empathy, and doing the right thing.