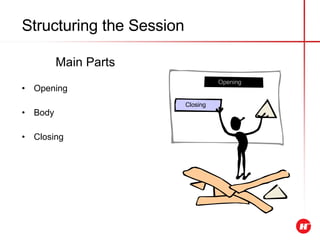
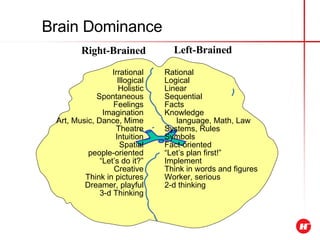
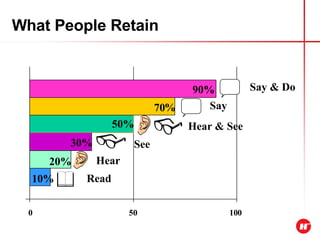
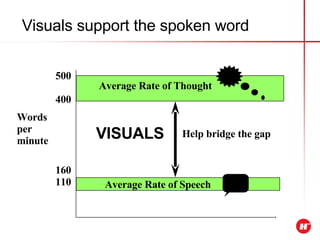
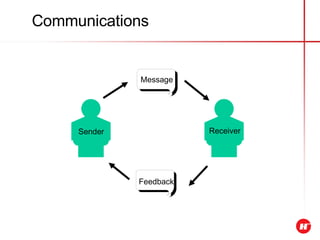
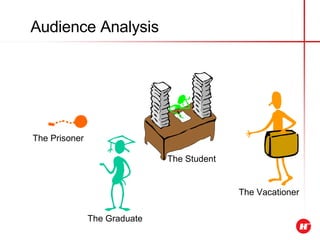
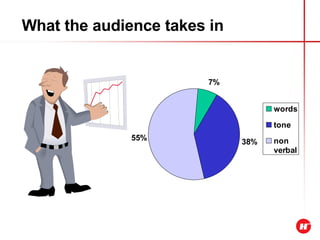
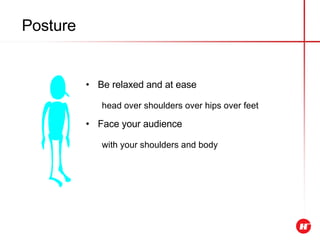
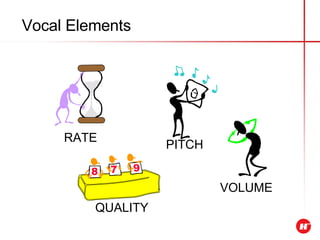
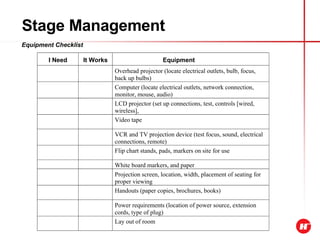
The document outlines the objectives and content of a presentation skills course. The key objectives are to structure presentations effectively, deliver presentations confidently using visual aids, and understand audience analysis. The document also covers various topics that will be taught such as opening and closing presentations effectively, analyzing learning styles, and overcoming nerves.