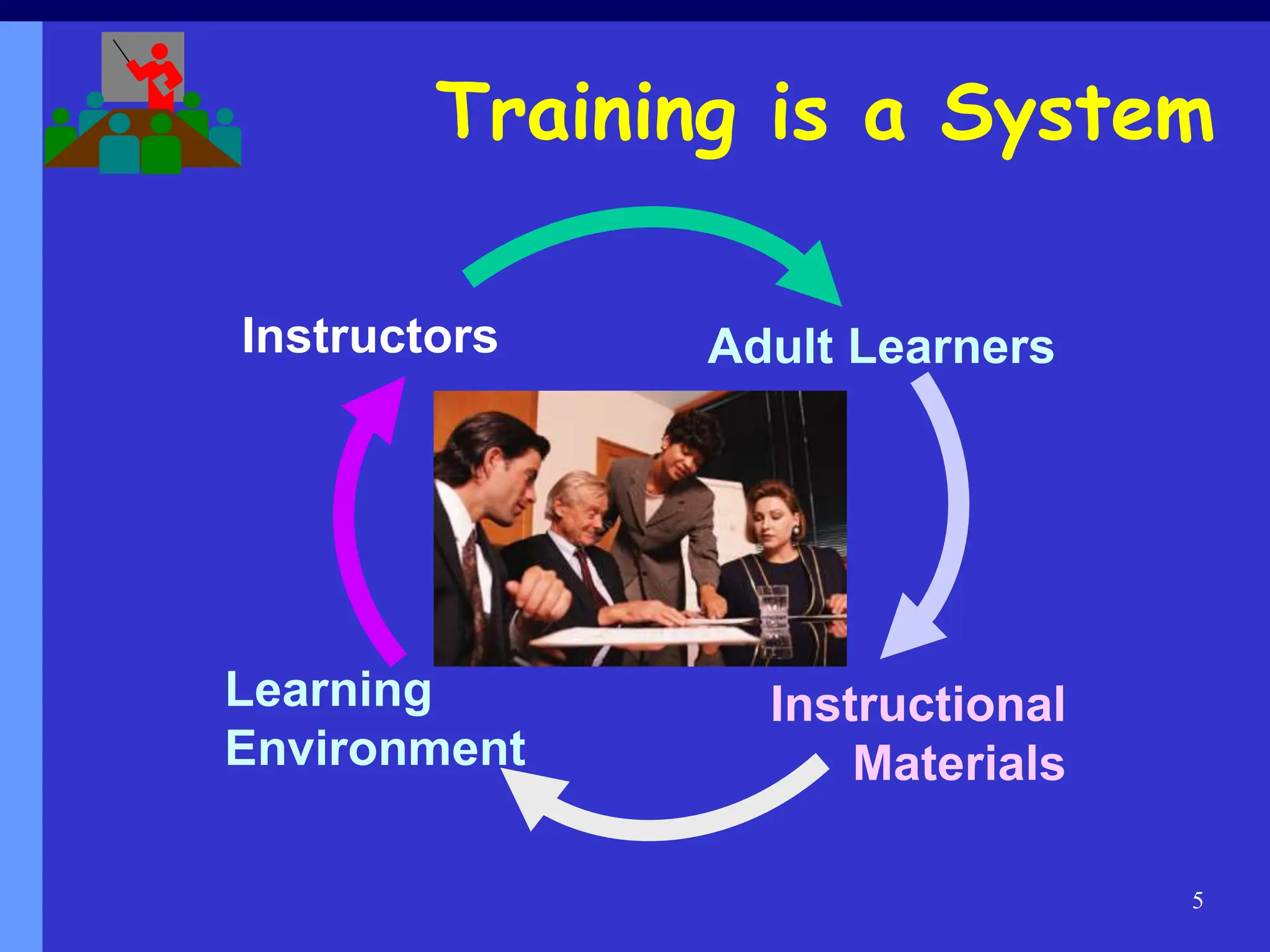
The document discusses effective training techniques specifically designed for adult learners, emphasizing the importance of understanding the characteristics and needs of adult students. It outlines a systematic approach to training, addressing the trainer's role, instructional strategies, and the significance of creating an engaging learning environment. The text also provides practical advice on preparation, delivery skills, and common pitfalls to avoid during training sessions.