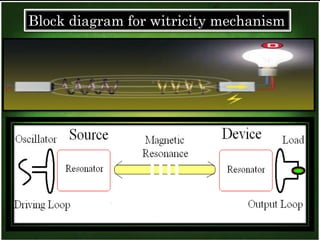
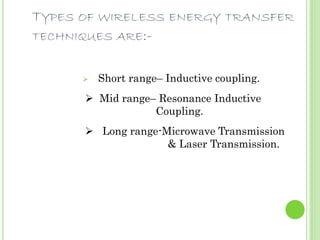
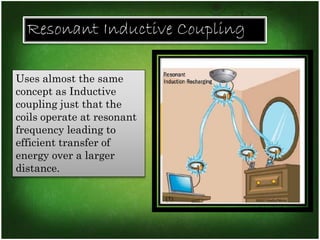
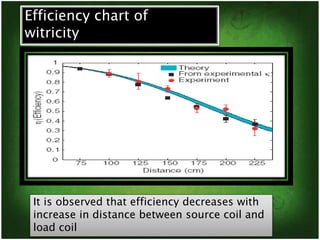
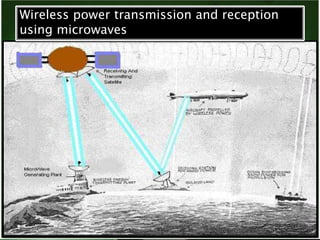
This document discusses wireless electricity or "witricity", where electrical energy is transmitted through air without wires. It begins by defining witricity and explaining that cables will be replaced. There are several reasons for needing wireless electricity, such as the demand for power everywhere and more eco-friendly options. The document then covers the different techniques for wireless energy transfer including short range inductive coupling, mid-range resonant inductive coupling, and long range microwave and laser transmission. It provides examples of applications for both short/mid range and long range wireless power including charging electric vehicles and powering satellites. In conclusion, the document states that wireless electricity is necessary to deal with energy crises, though challenges like costs and interference would need to be