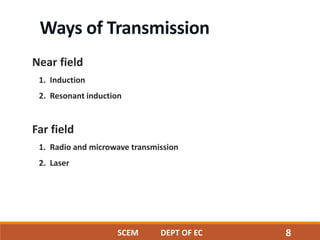
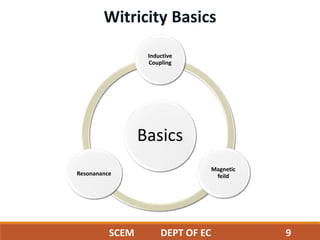
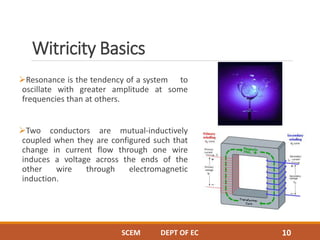
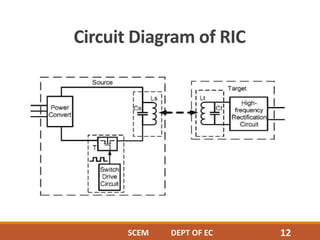
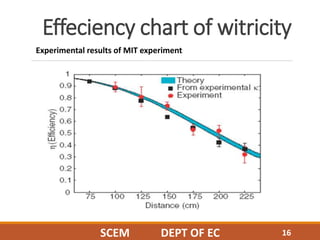
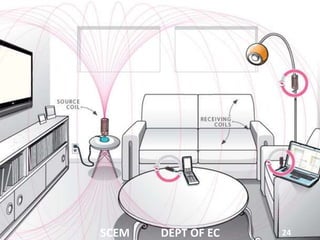
This document discusses wireless power transmission through resonant inductive coupling, also known as Witricity. It begins with a brief history of wireless power, including Nikola Tesla's early proposals and recent work by MIT engineers to use resonant induction. The document then covers the basics of Witricity, including near and far field transmission methods, inductive coupling, and creating resonant induction circuits. It discusses efficiency and applications like charging electric cars wirelessly. Finally, it addresses the future potential of creating wireless power hotspots everywhere to eliminate the need for charging batteries with wires.