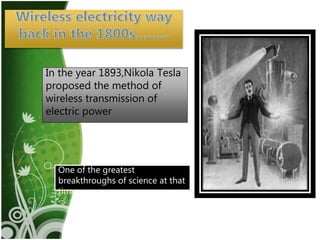
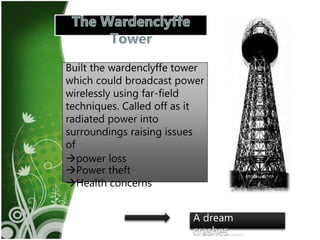
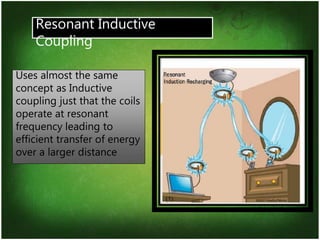
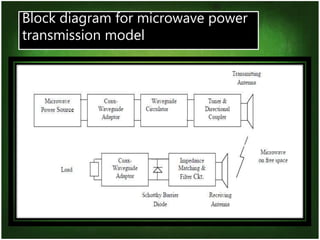
Wireless electricity has the potential to provide power anywhere without dependence on wires or batteries. Nikola Tesla first proposed wireless power transmission in 1893 with his Wardenclyffe Tower project. While promising, it was halted due to issues with power loss, theft, and health concerns. There are several techniques for wireless power transfer including inductive coupling for short ranges, resonant inductive coupling for mid-ranges, and microwave transmission for long ranges. Microwave power transmission uses a microwave generator, transmitting antenna, and rectenna to convert electrical power to microwaves and back. Potential applications include powering satellites and establishing lunar bases. However, challenges remain around installation costs, interference, and ensuring systems operate at resonant frequencies for efficient transfer.