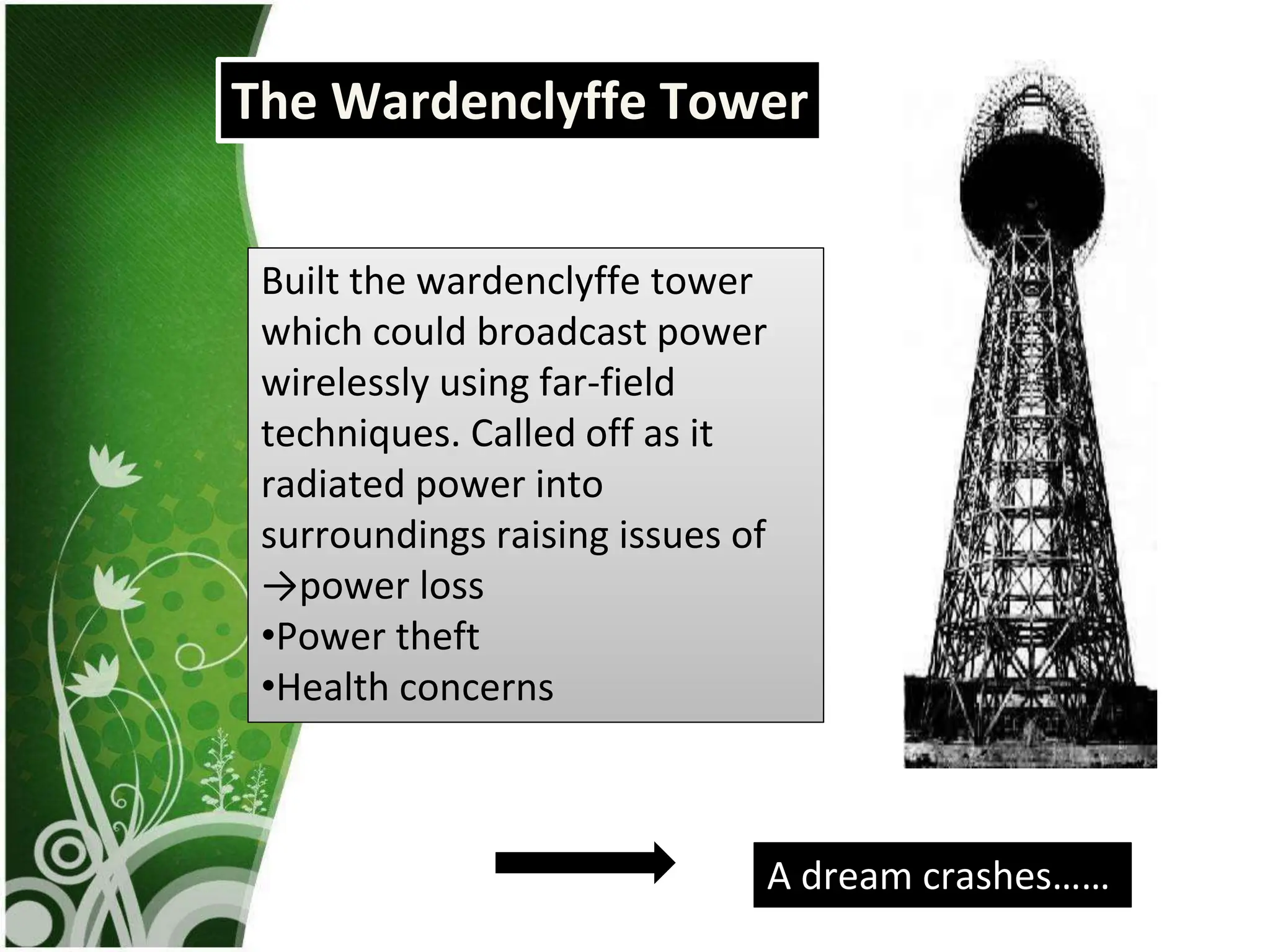
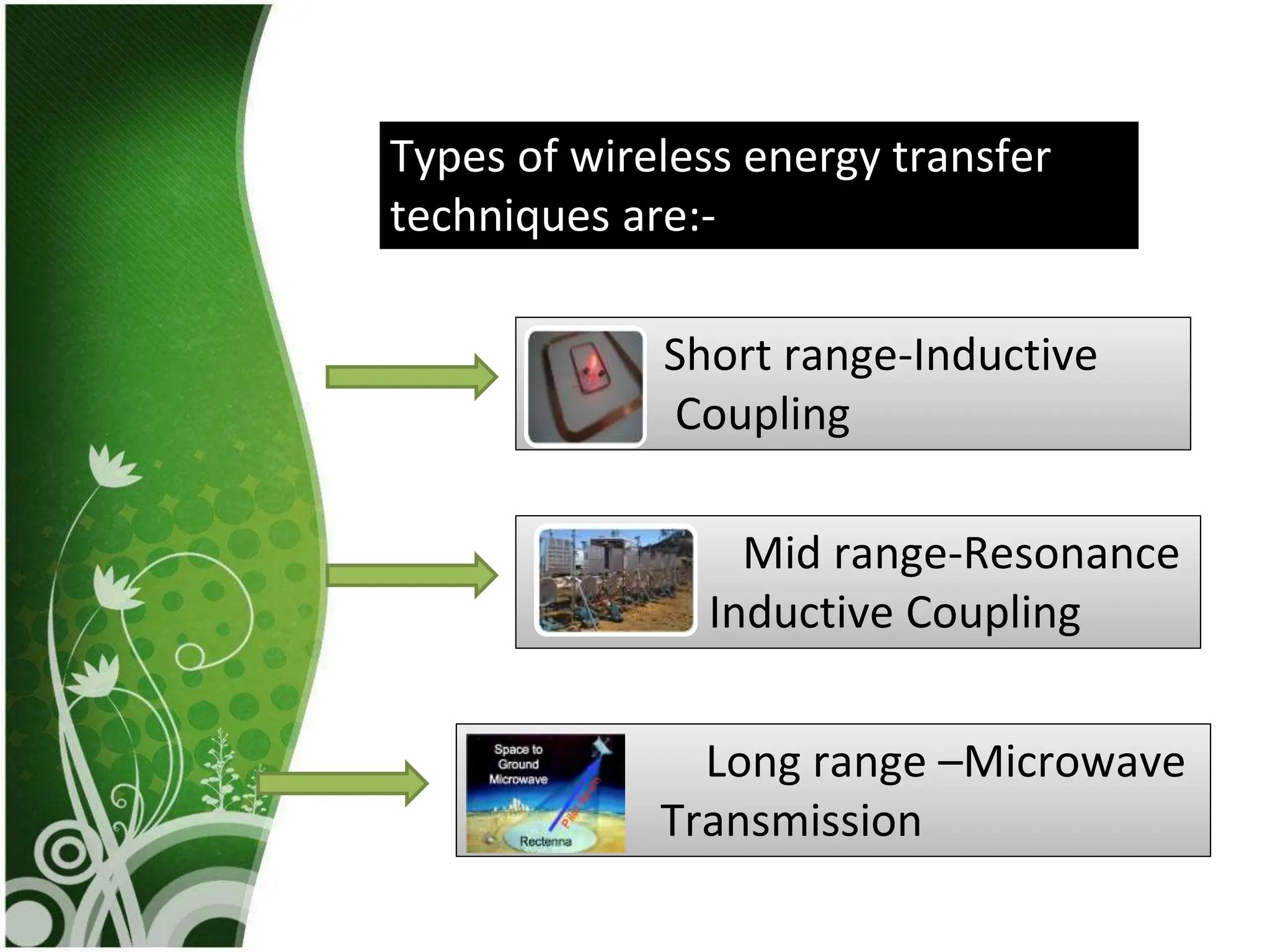
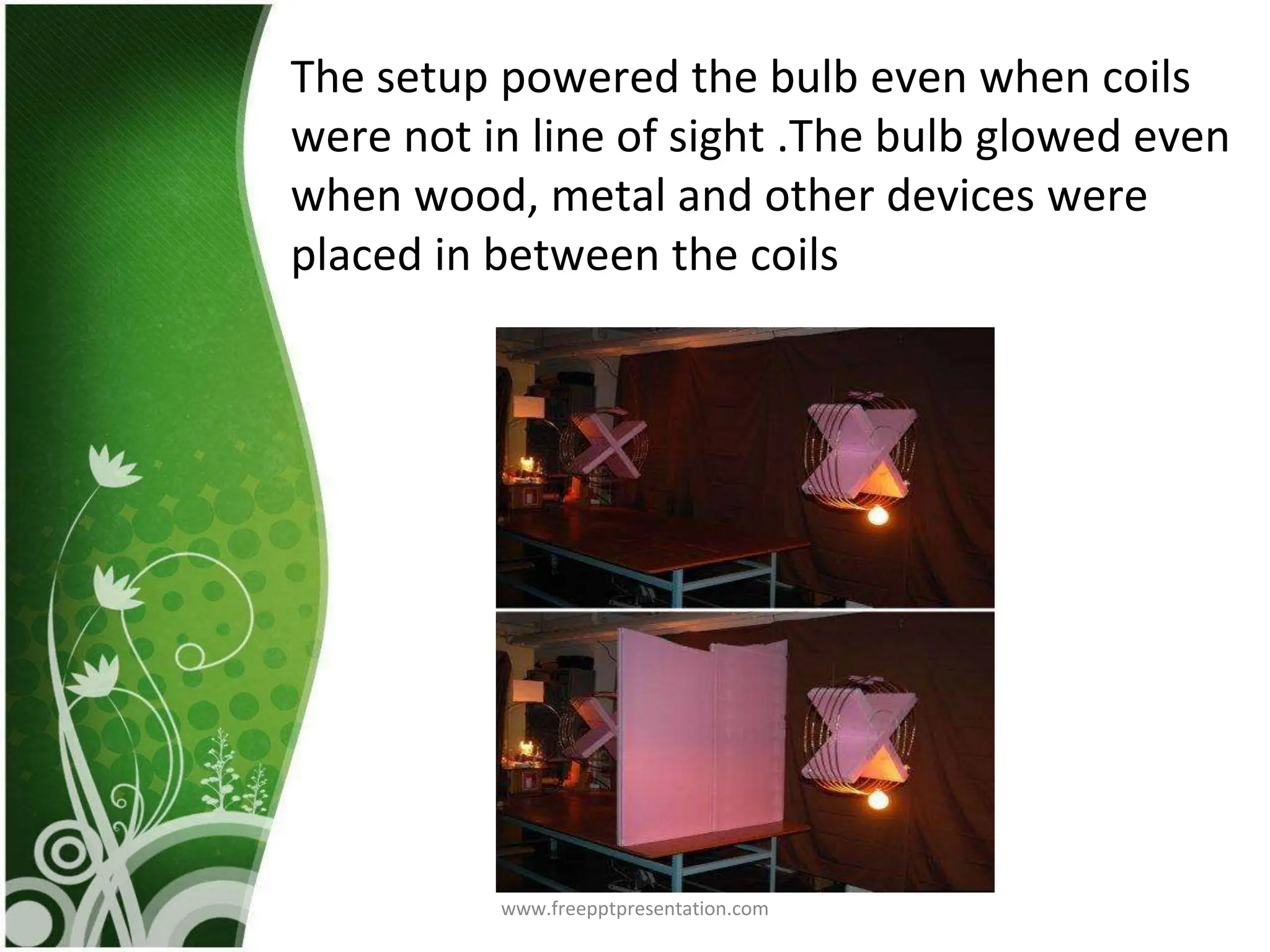
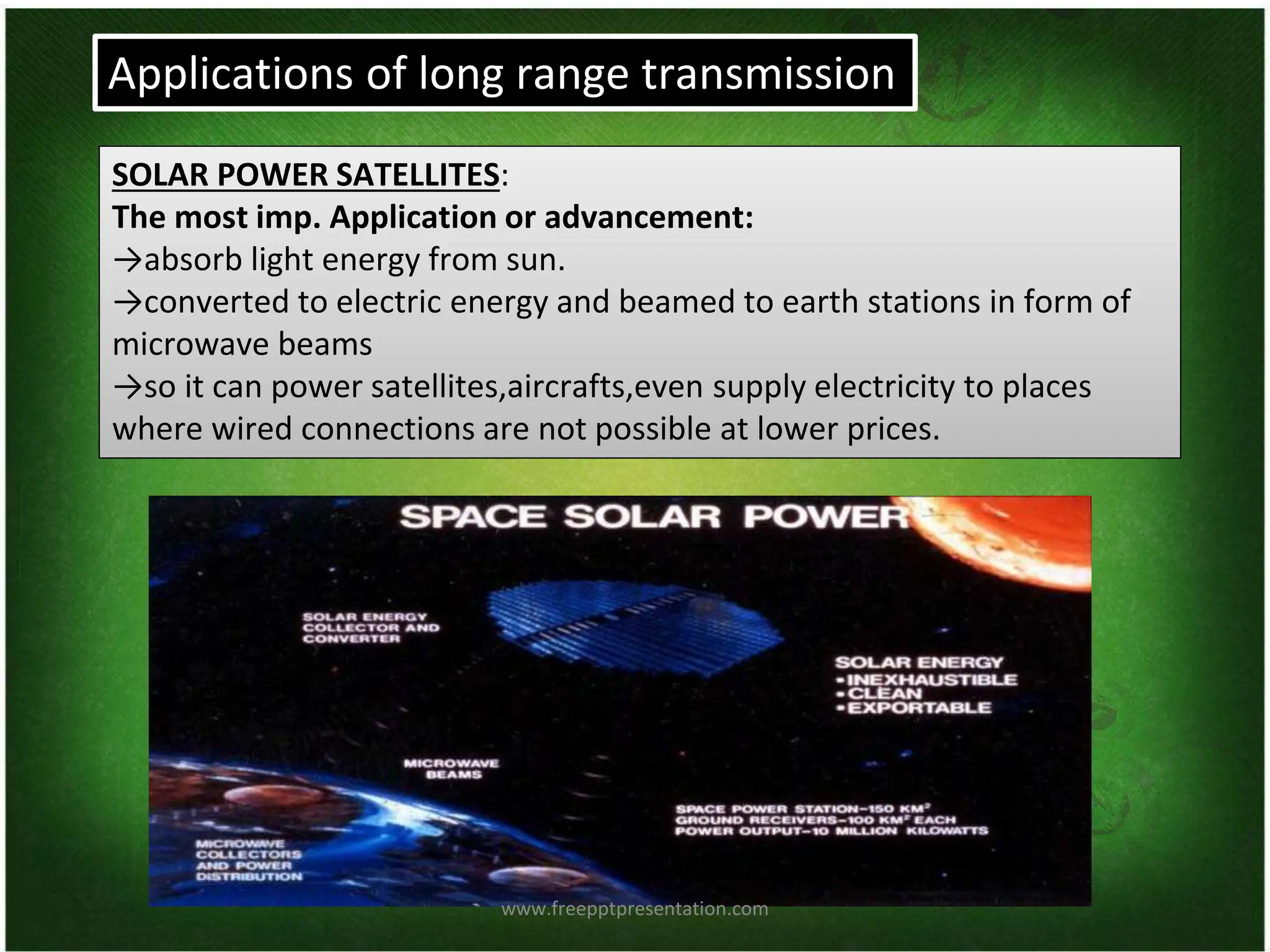
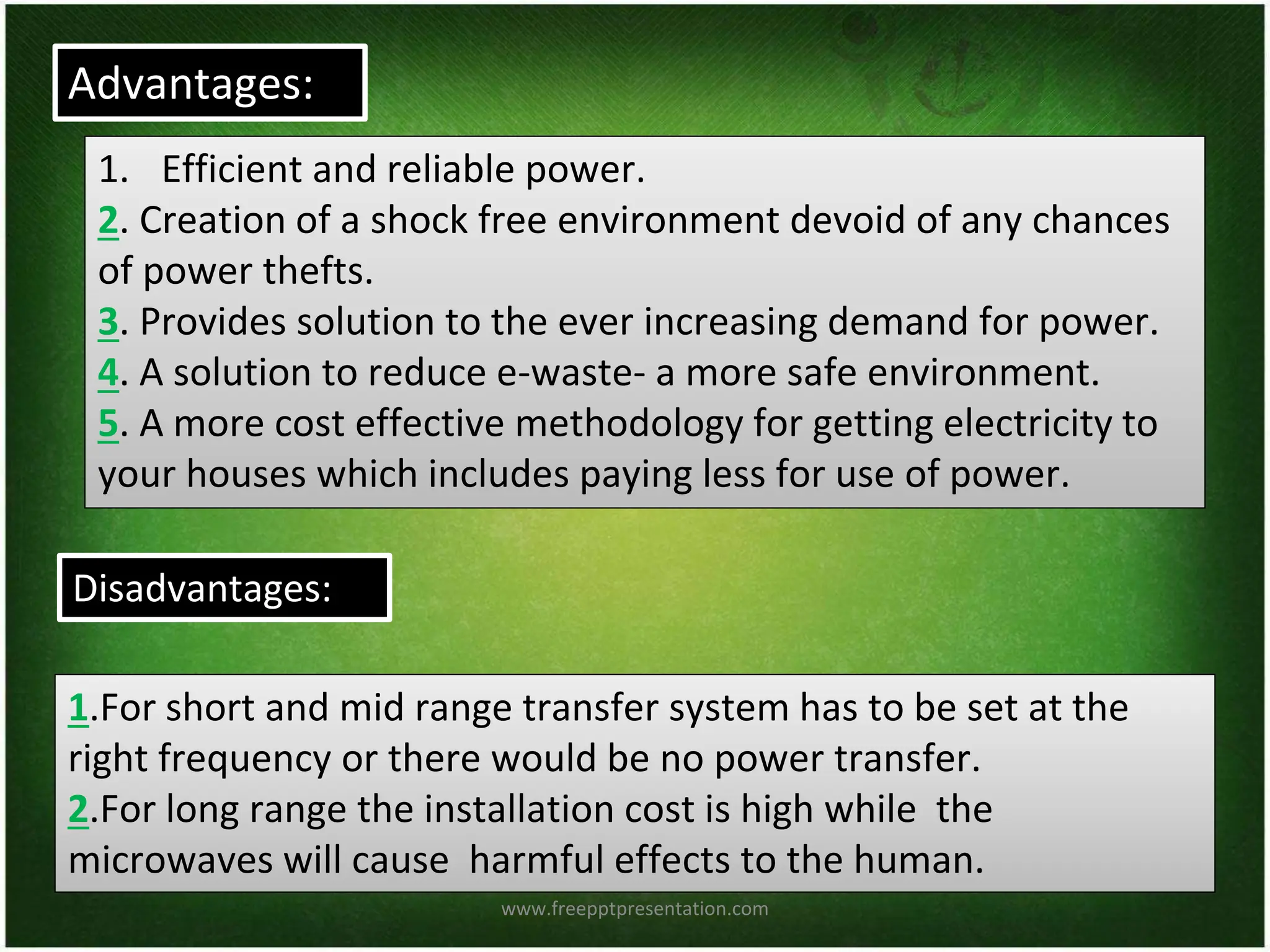
This document discusses wireless electricity (witricity), including its definition, need, history, techniques, applications, pros and cons, and future. Witricity involves transmitting energy through the air without wires using techniques like inductive coupling for short ranges and resonant inductive or microwave transmission for longer ranges. Nikola Tesla first proposed wireless power in 1891 but it was not practical until recent developments. Witricity has applications like charging electric vehicles and devices and could help meet increasing power demands in an eco-friendly way without wires, but health and safety concerns remain for long-range techniques. The future aims to make the world fully wireless for power transmission.