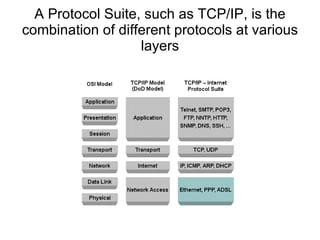
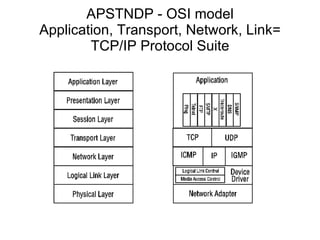
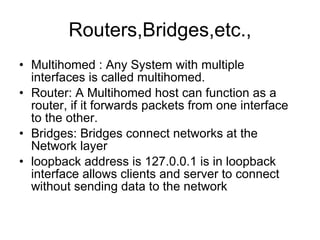
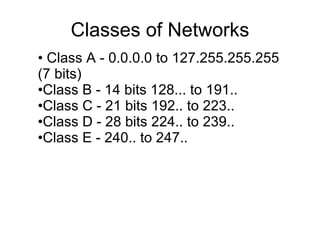
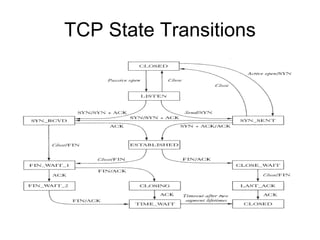
The document discusses the TCP/IP protocol suite and its layers - application, transport, internet and link layer. It describes the functionality of each layer and the data encapsulation between layers. It also discusses protocols like TCP, UDP, IP, ICMP and their usage. Network concepts like routers, bridges, classes of networks and sockets are explained along with examples.



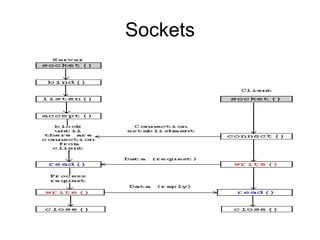





![Server import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class Server { public static void main(String[] ar) { int port = 6666; try { ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(port); Socket socket = ss.accept(); InputStream sin = socket.getInputStream(); OutputStream sout = socket.getOutputStream(); DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(sin); DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(sout); String line = null; while(true) { line = in.readUTF(); System.out.println(line); out.writeUTF(line); out.flush(); } } catch(Exception x) { x.printStackTrace(); } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vasutcpip-1208208619141817-9/85/TCP-IP-17-320.jpg)
![Client import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class Client { public static void main(String[] ar) { int serverPort = 6666; String address = "127.0.0.1"; try { InetAddress ipAddress = InetAddress.getByName(address); Socket socket = new Socket(ipAddress, serverPort); InputStream sin = socket.getInputStream(); OutputStream sout = socket.getOutputStream(); DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(sin); DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(sout); String line = "something"; out.writeUTF(line); out.flush(); line = in.readUTF(); // wait for the server to send a line System.out.println(line); } catch(UnknownHostException x) { System.out.println("Got an unknown host exception"); } catch(ConnectException x) { System.out.println("Could not connect to the port"); } catch(Exception x) { } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vasutcpip-1208208619141817-9/85/TCP-IP-18-320.jpg)
![Multicast Receiver import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class MulticastReceiver { public static void main( String[] argv ) { try { // get the InetAddress of the MCAST group InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName( argv[0] ); // get the port that we will be listening on int port = Integer.parseInt( argv[1] ); // create a multicast socket on the specified local port number MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket( port ); // create an empty datagram packet DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(new byte[128], 128); //Join a multicast group and wait for some action ms.joinGroup(ia); System.out.println( "waiting for a packet from "+ia+"..."); ms.receive(dp); // print out what we received and quit System.out.println( new String(dp.getData() )); ms.leaveGroup(ia); ms.close(); } catch (IOException e) {} } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vasutcpip-1208208619141817-9/85/TCP-IP-19-320.jpg)
![Multicast Sender import java.net.*; import java.io.*; public class MulticastSender { public static void main( String[] argv ) { try { // get the InetAddress of the MCAST group InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName( argv[0] ); // get the port that the MCAST group members will be listening on int recvPort = Integer.parseInt( argv[1] ); // create a datagram with a suitable message String str = "Hello from: "+InetAddress.getLocalHost(); byte[] data = str.getBytes(); DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length, ia, recvPort); // create a multicast socket bound to any local port MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket(); //Join the multicast group ms.joinGroup(ia); // send the message with a Time-To-Live (TTL)=1 ms.send(dp, (byte)1); // tidy up - leave the group and close the socket ms.leaveGroup(ia); ms.close(); } catch (IOException e) {} } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vasutcpip-1208208619141817-9/85/TCP-IP-20-320.jpg)