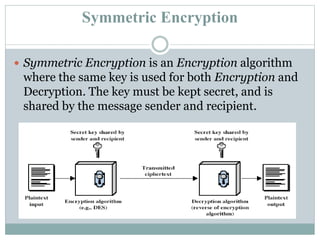
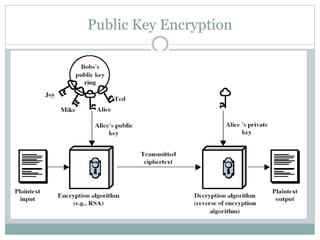
This document provides an overview of cyber security fundamentals including definitions of key concepts like cryptography, symmetric and public key encryption, firewalls, virtualization, and radio-frequency identification (RFID). It defines cyber security as protecting computers and networks from unauthorized access through technologies and processes. Some key advantages are defending against attacks while allowing secure browsing and data protection. Cyber crimes include illegal access, data interference, and fraud. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encryption and decryption while public key encryption uses separate public and private keys.