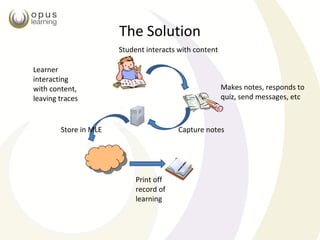
The document describes a digital workbook (DWB) created by Opus Learning to track student interactions and reflections during online learning. The DWB records student notes, quiz responses, and messages as they interact with content. This data provides insights into learning behaviors and needs for intervention. It also forms an audit trail for authentication and a longitudinal record of learning for assessment. Benefits of the DWB include improved content through learner feedback, rich data for analysis, and a holistic assessment strategy across courses. The DWB aims to enhance the social learning experience by facilitating personal, peer, and instructor interactions.