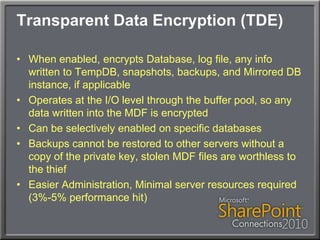
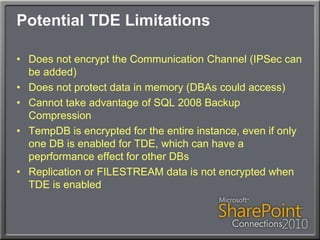
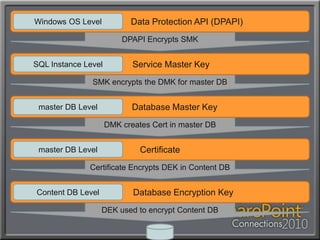
This document discusses using Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) in SQL Server 2008 to encrypt SharePoint content databases. TDE encrypts data at the page level and is transparent to applications like SharePoint. The document outlines the key management process for TDE including creating a database master key, certificate, database encryption key, and enabling encryption on a database. It also addresses restoring an encrypted database to another server and monitoring the encryption process.