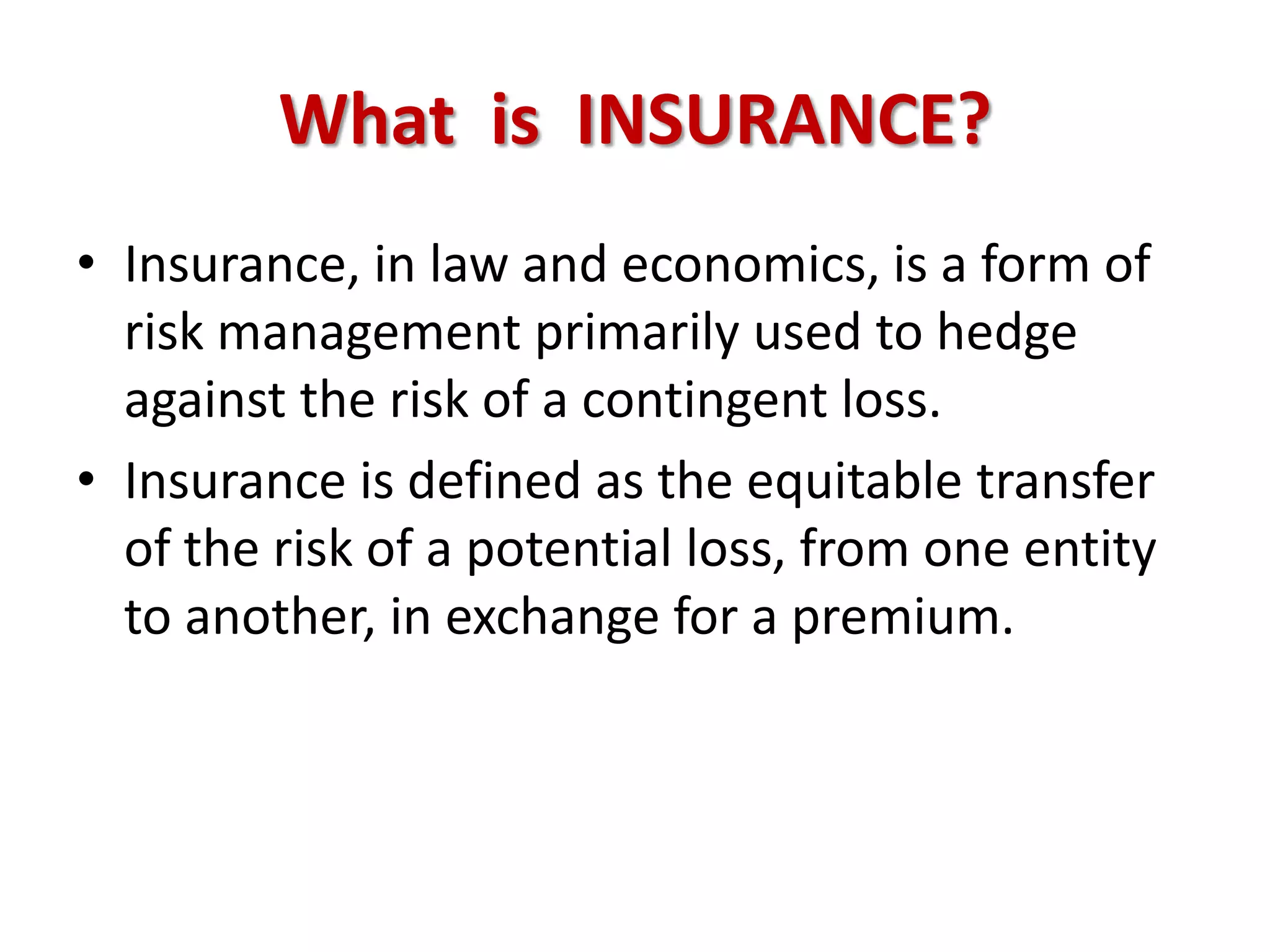
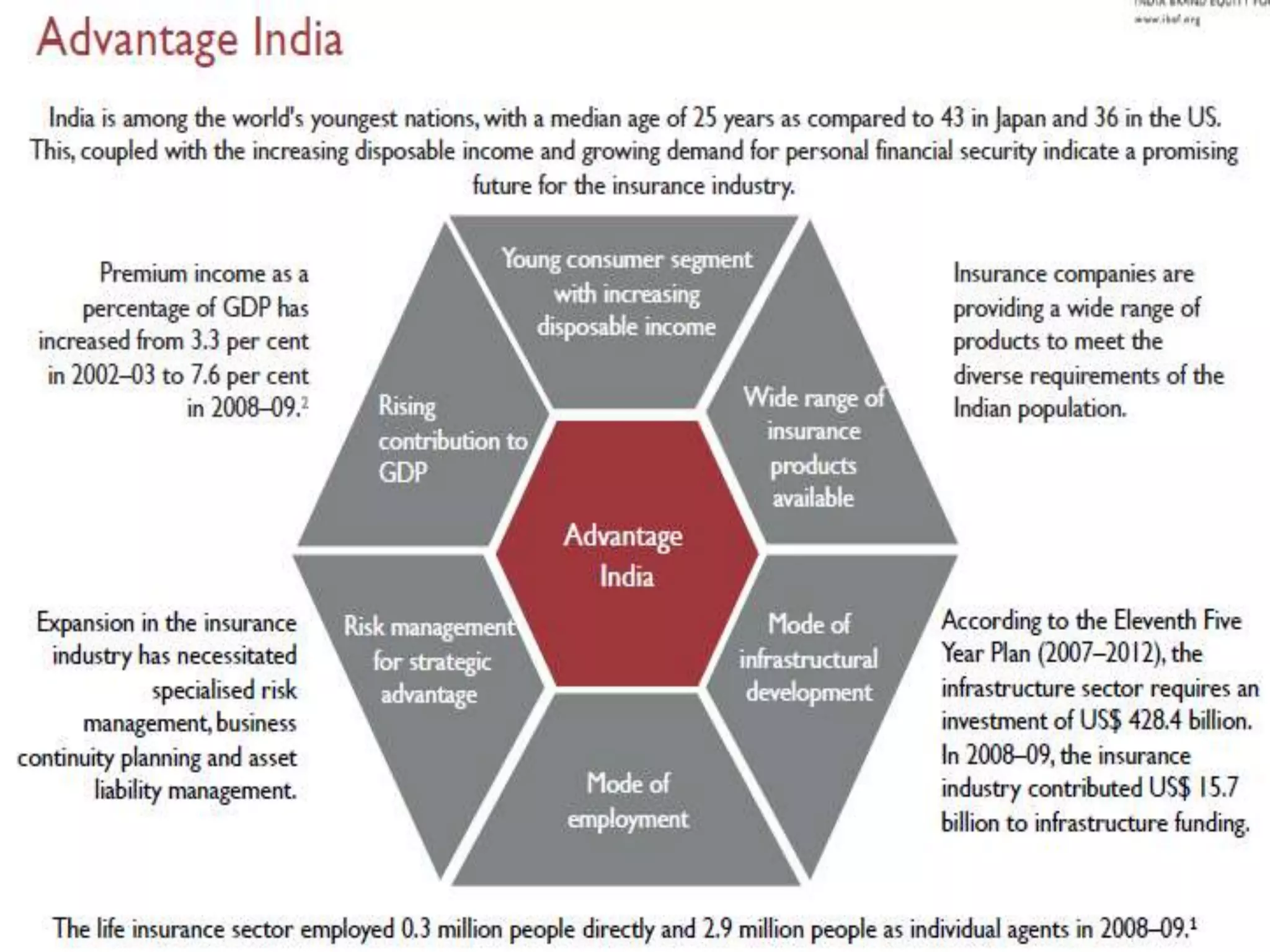
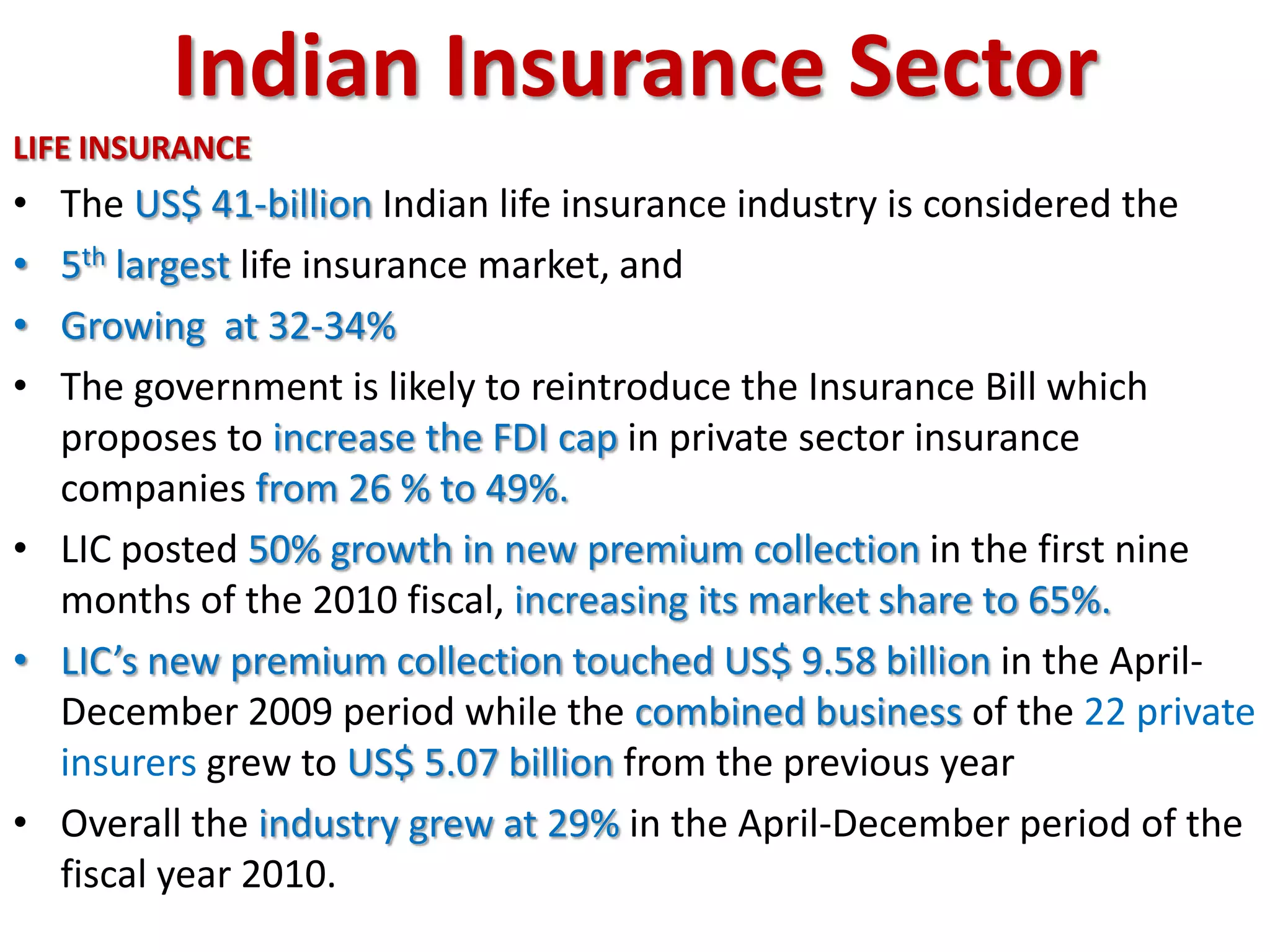
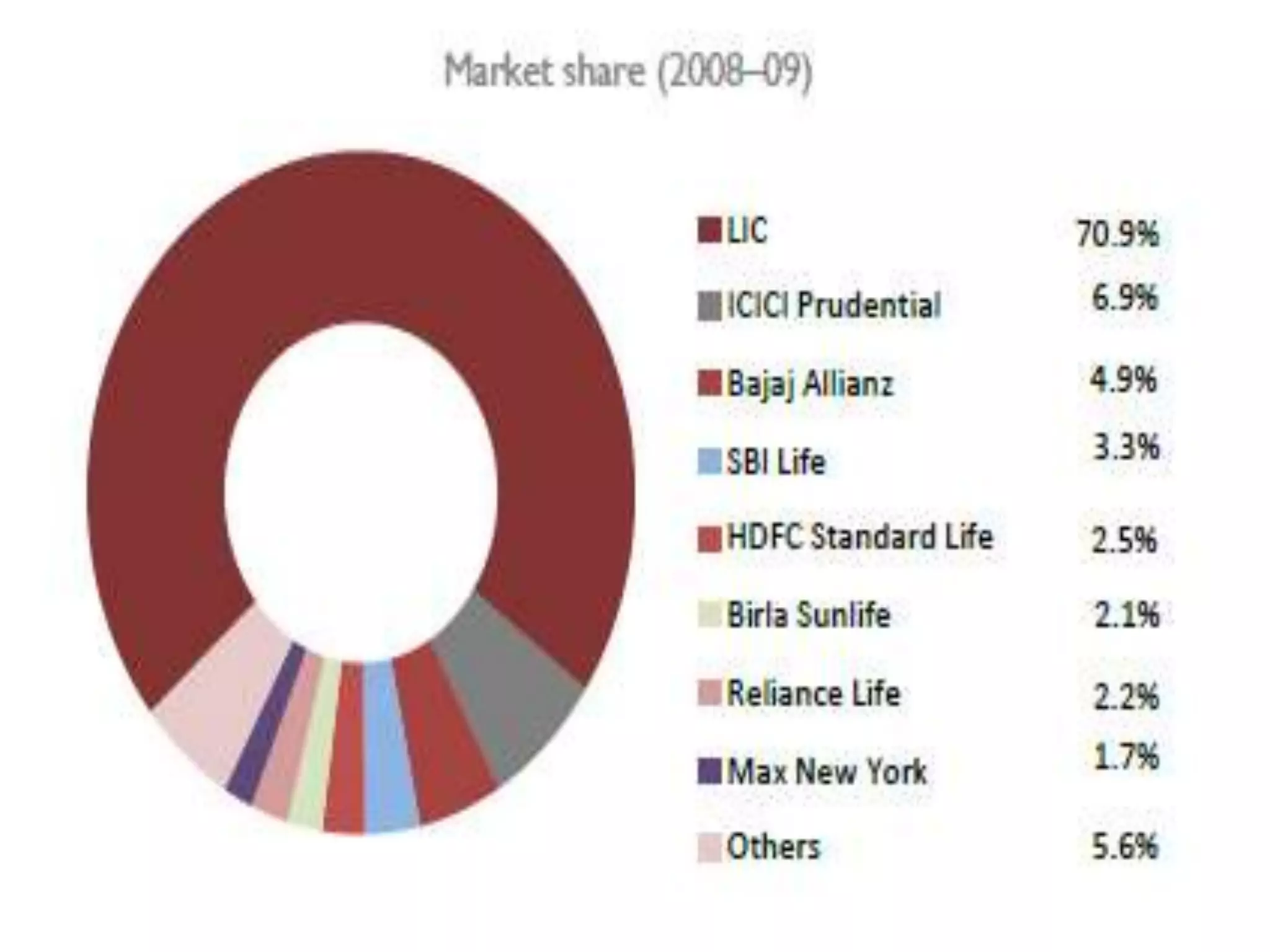
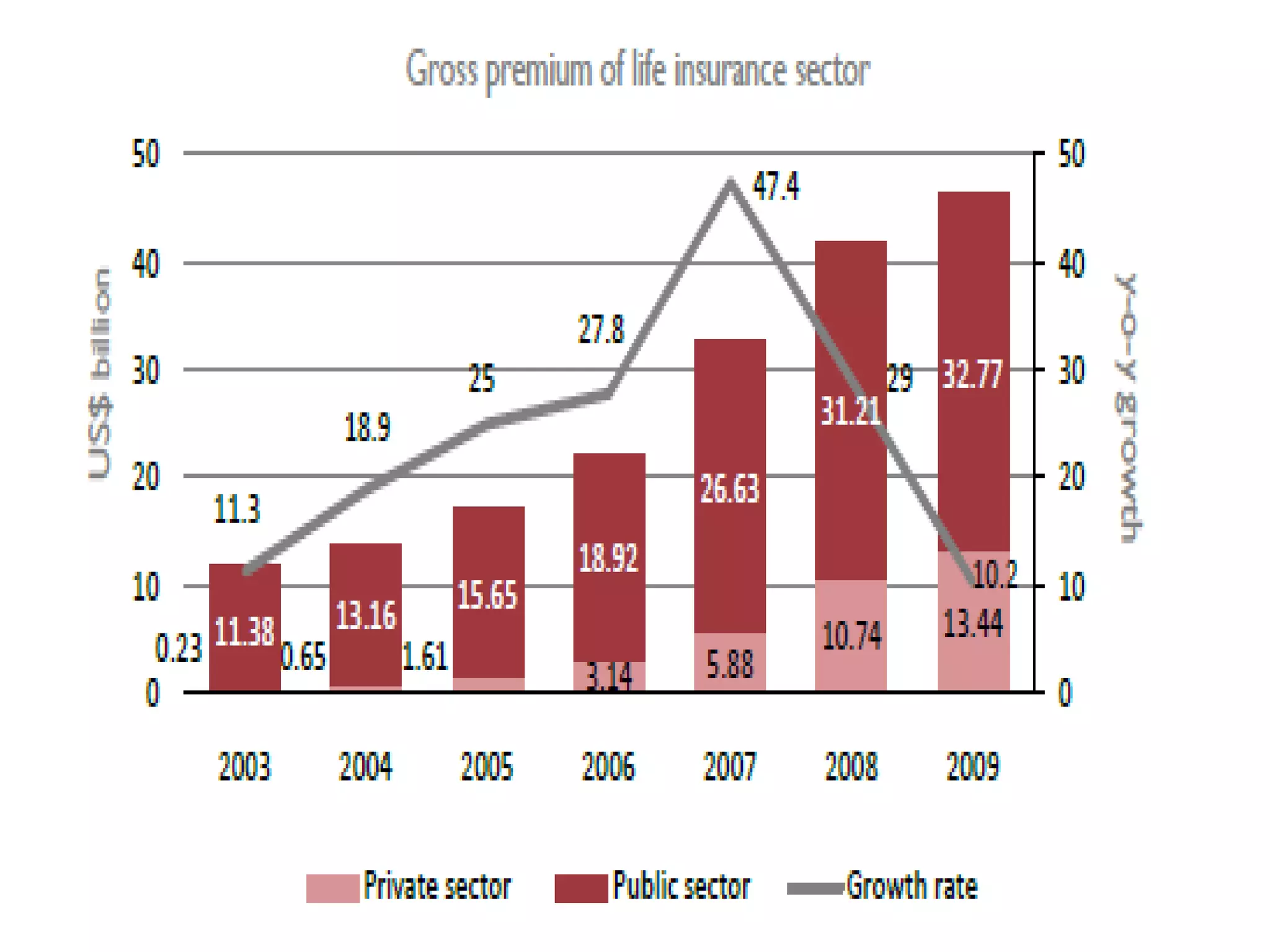
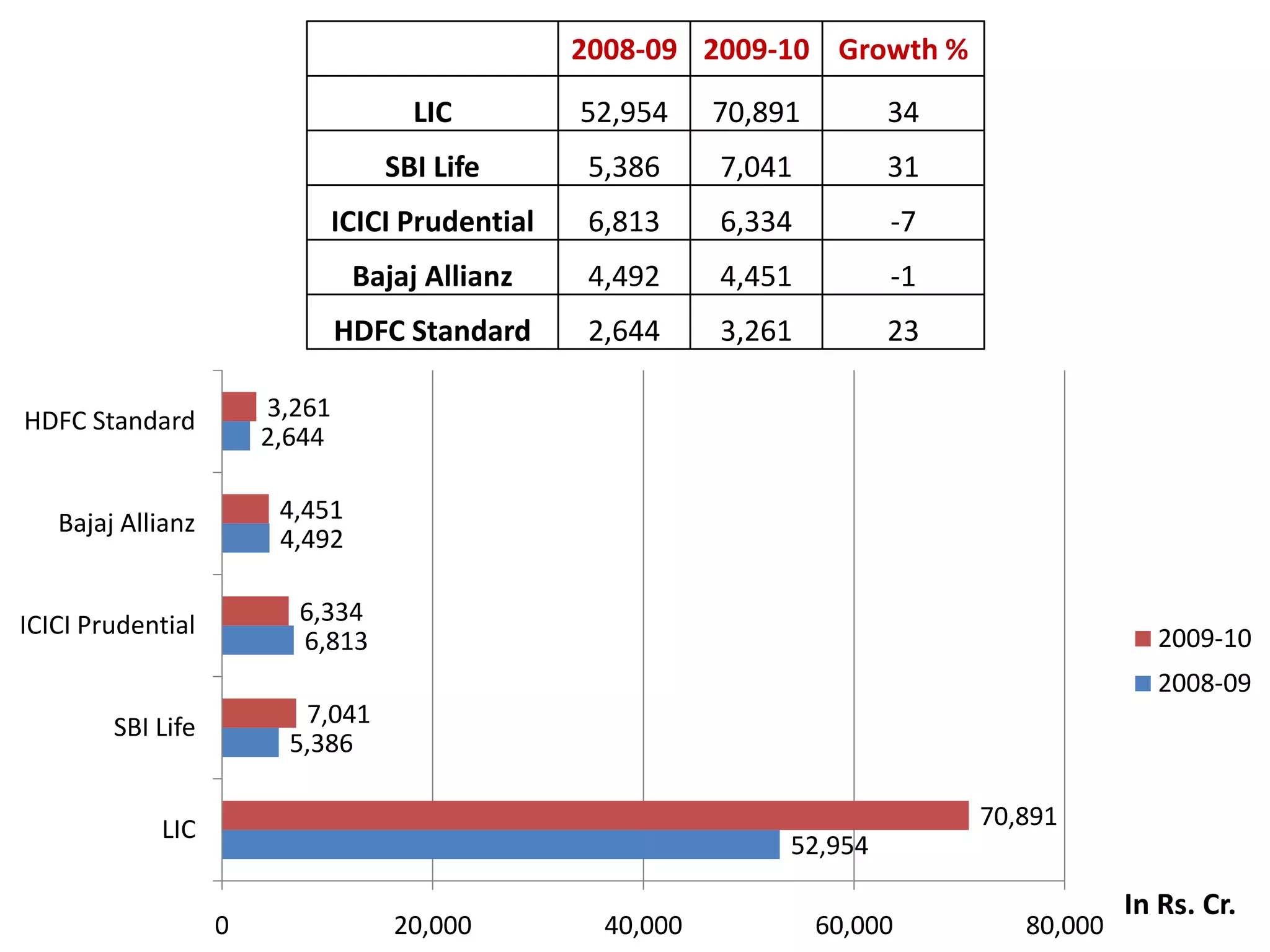
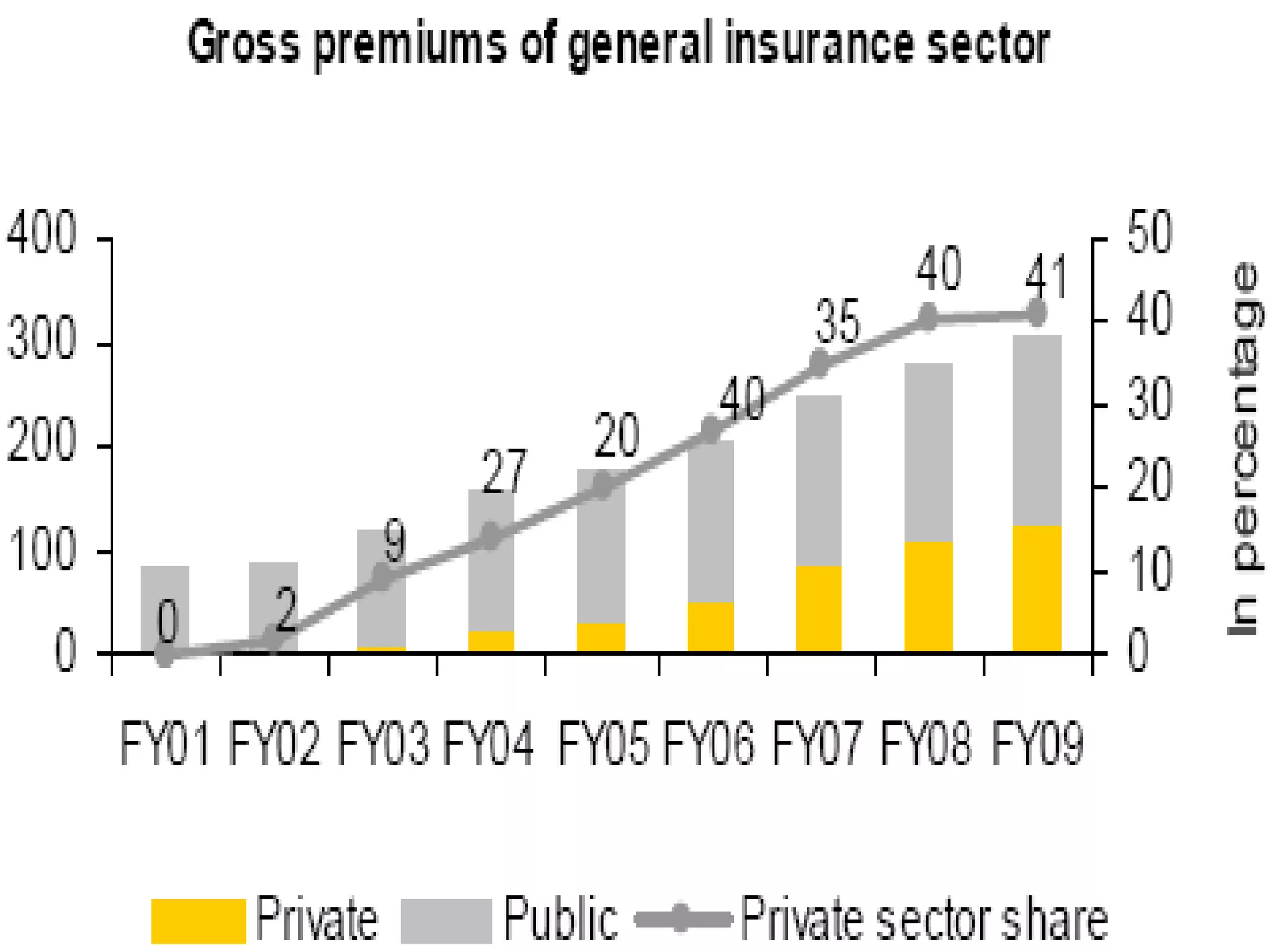
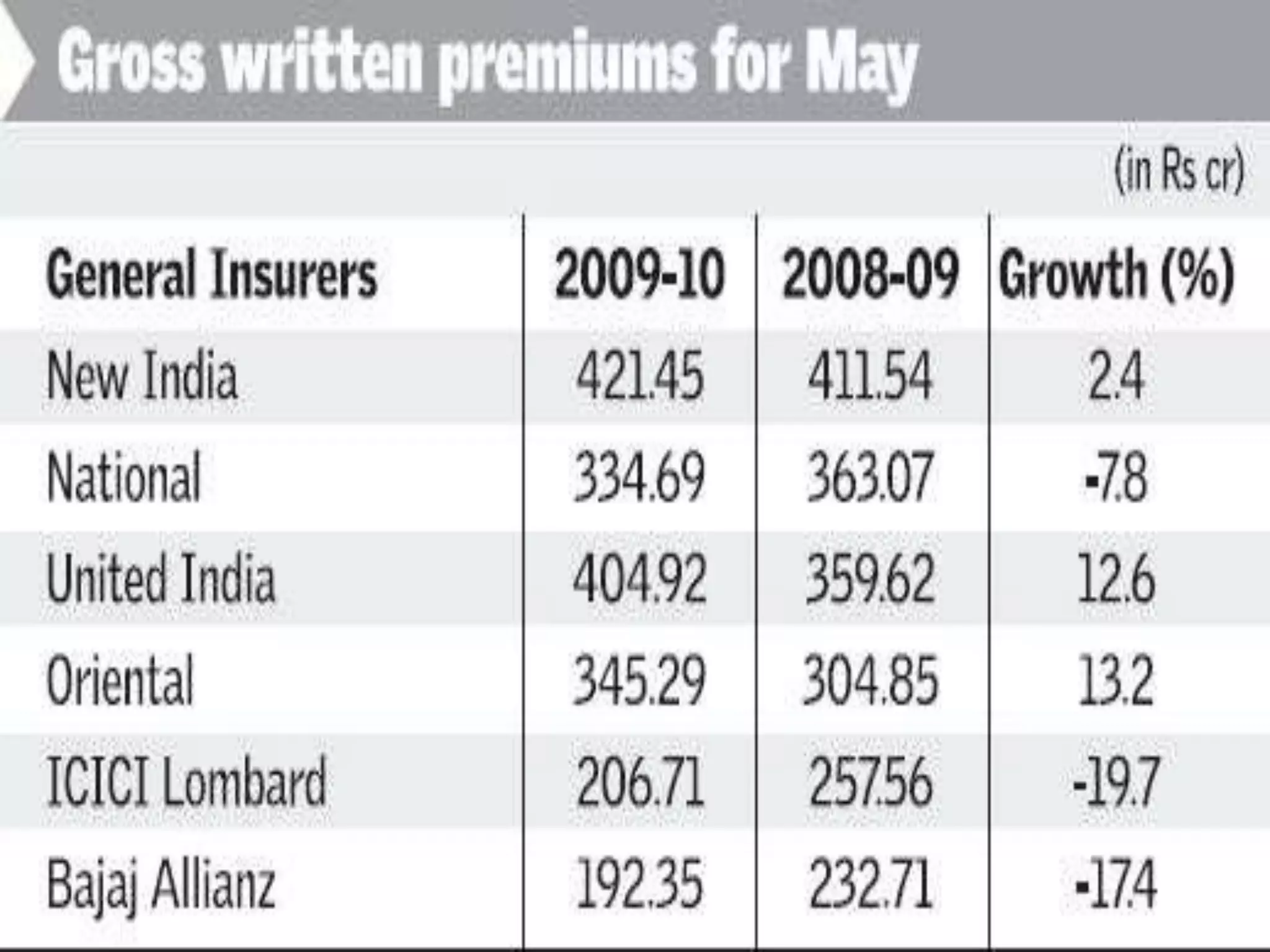
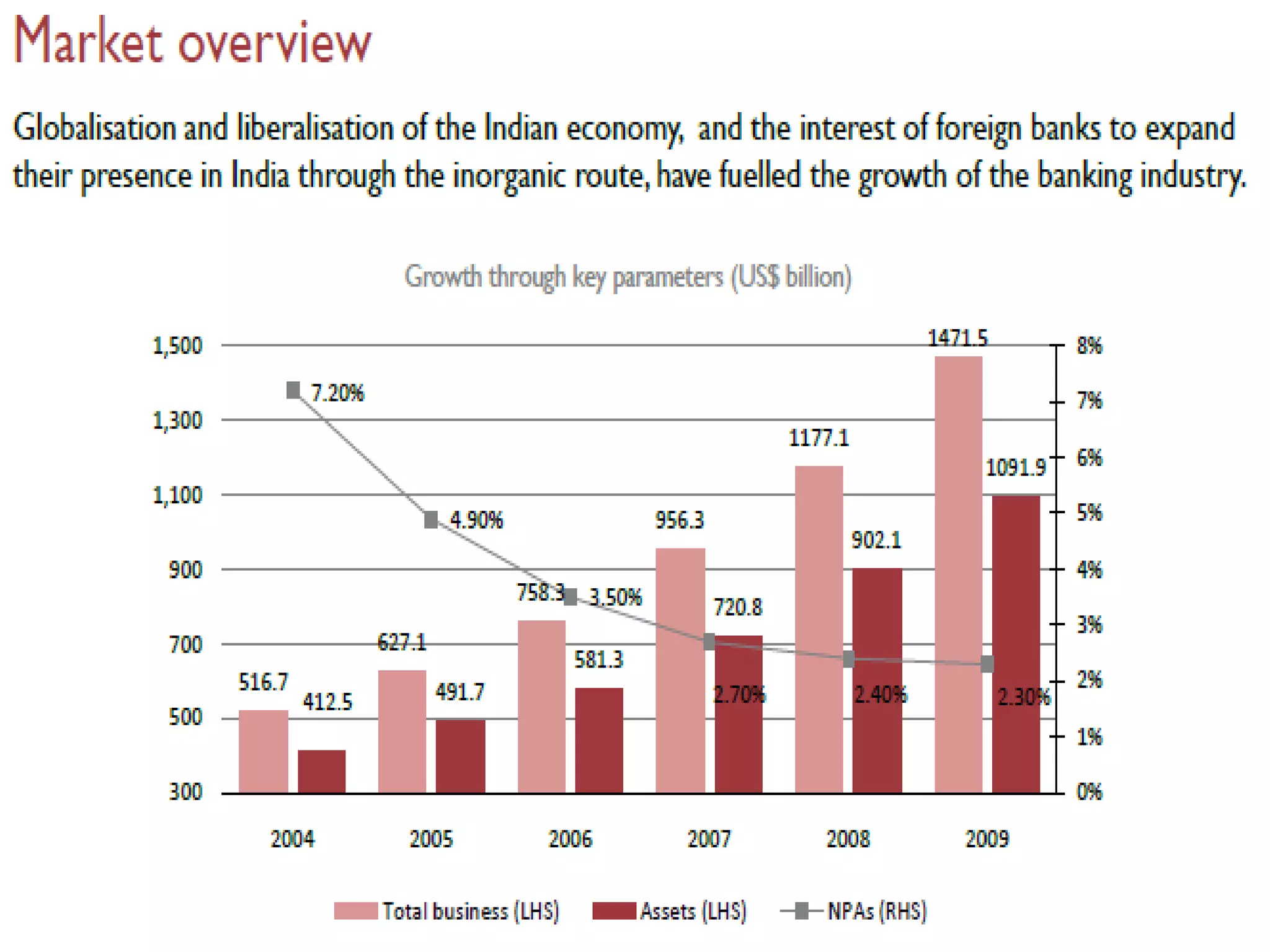
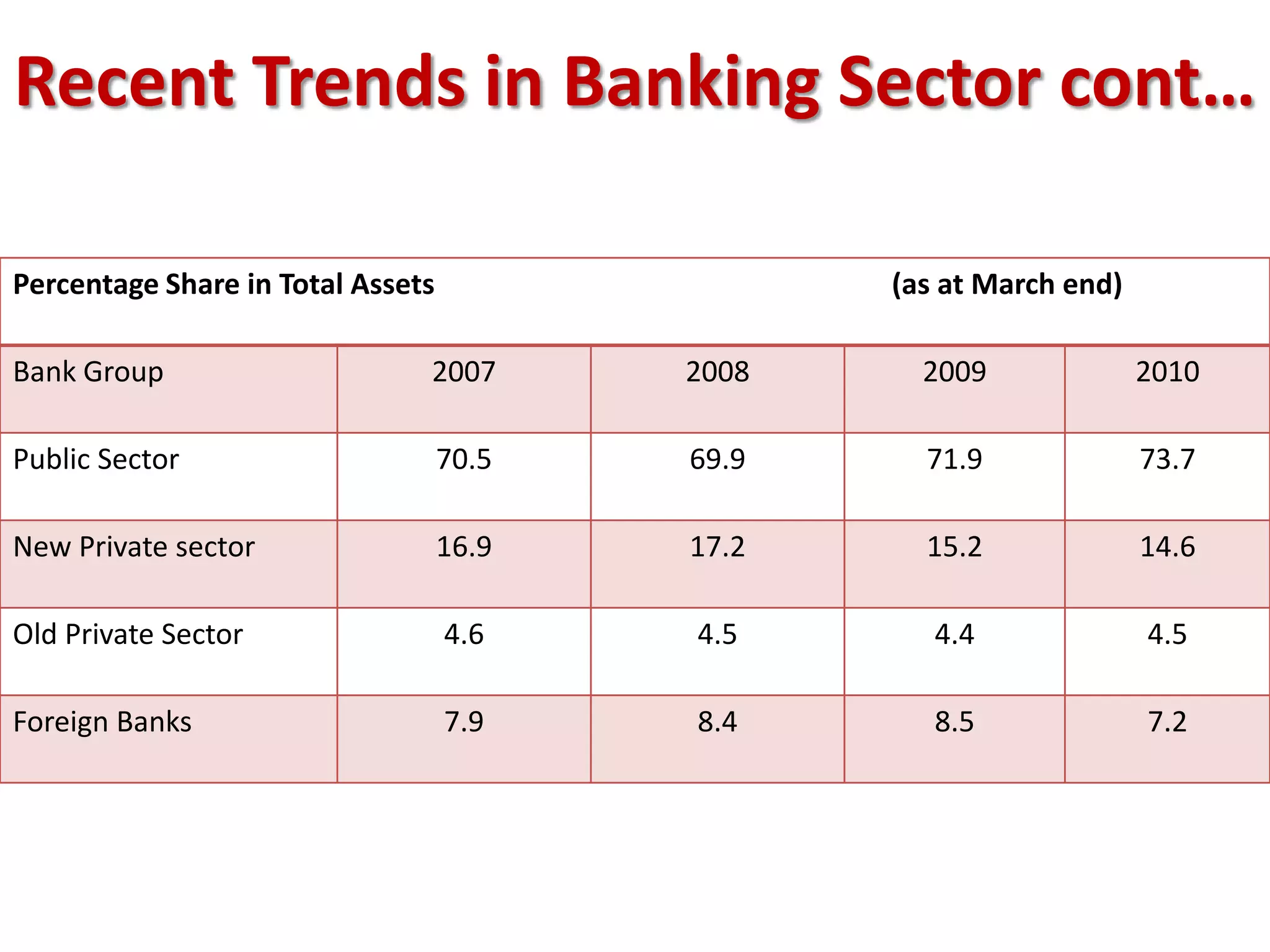
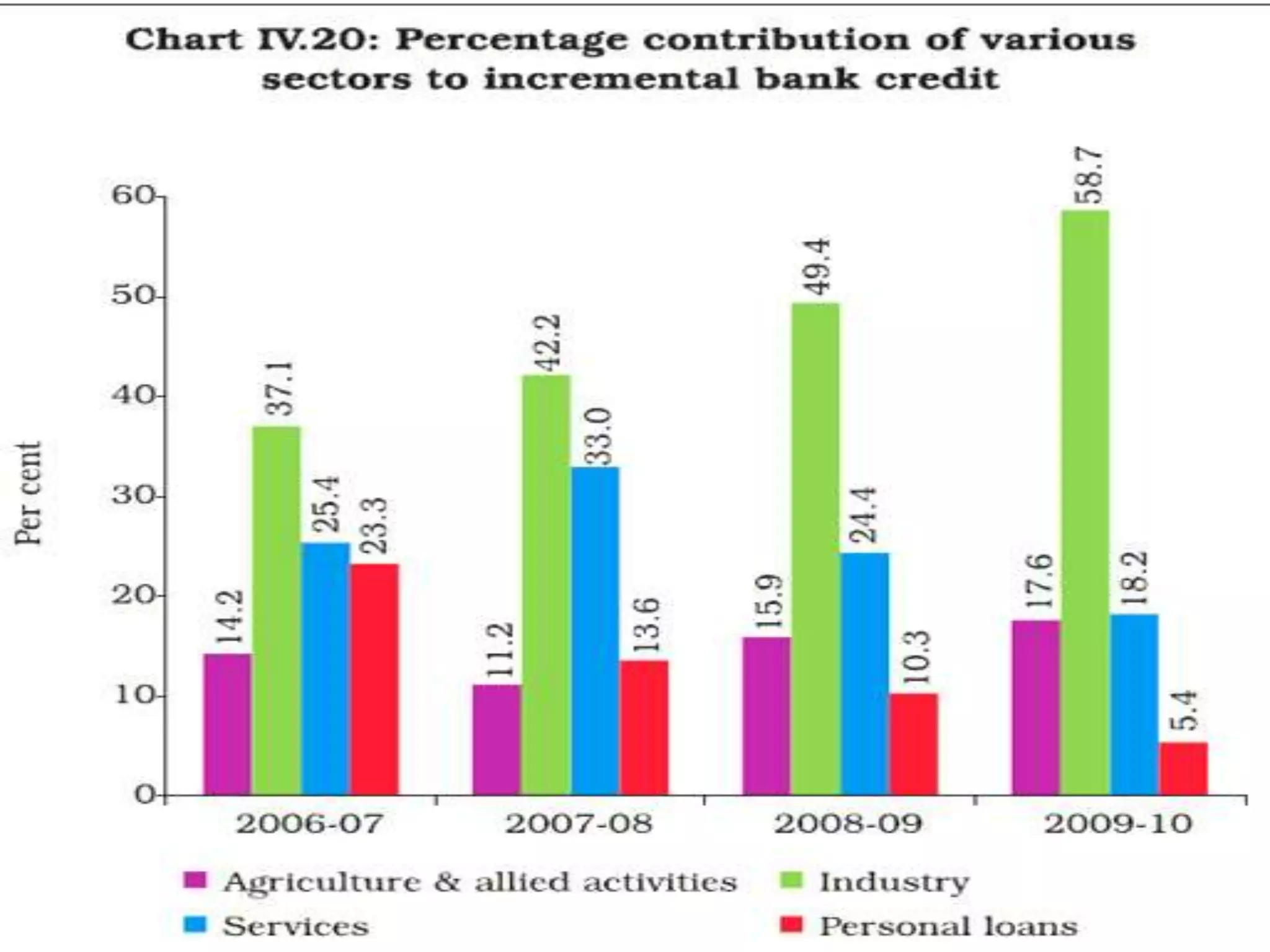
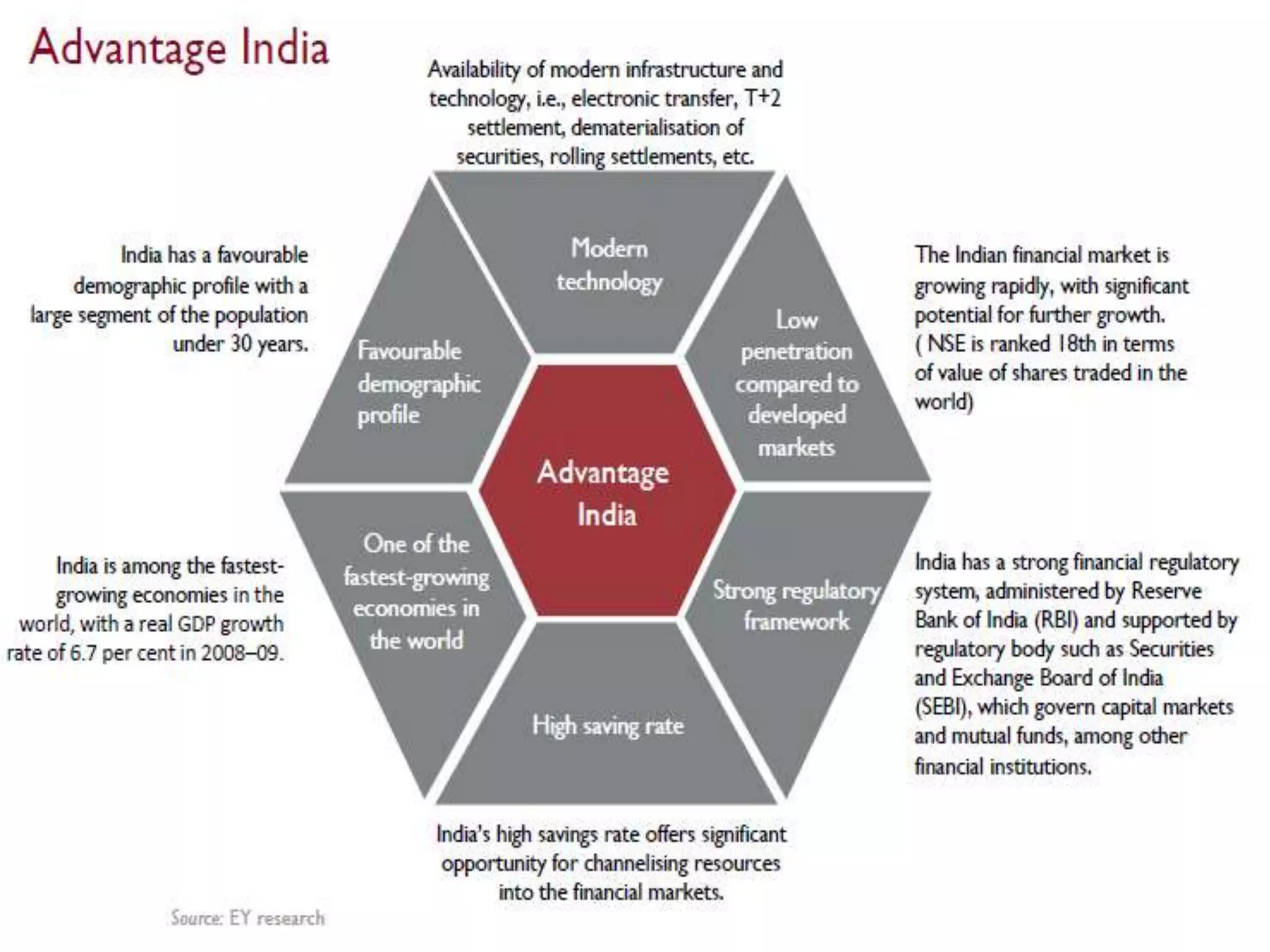
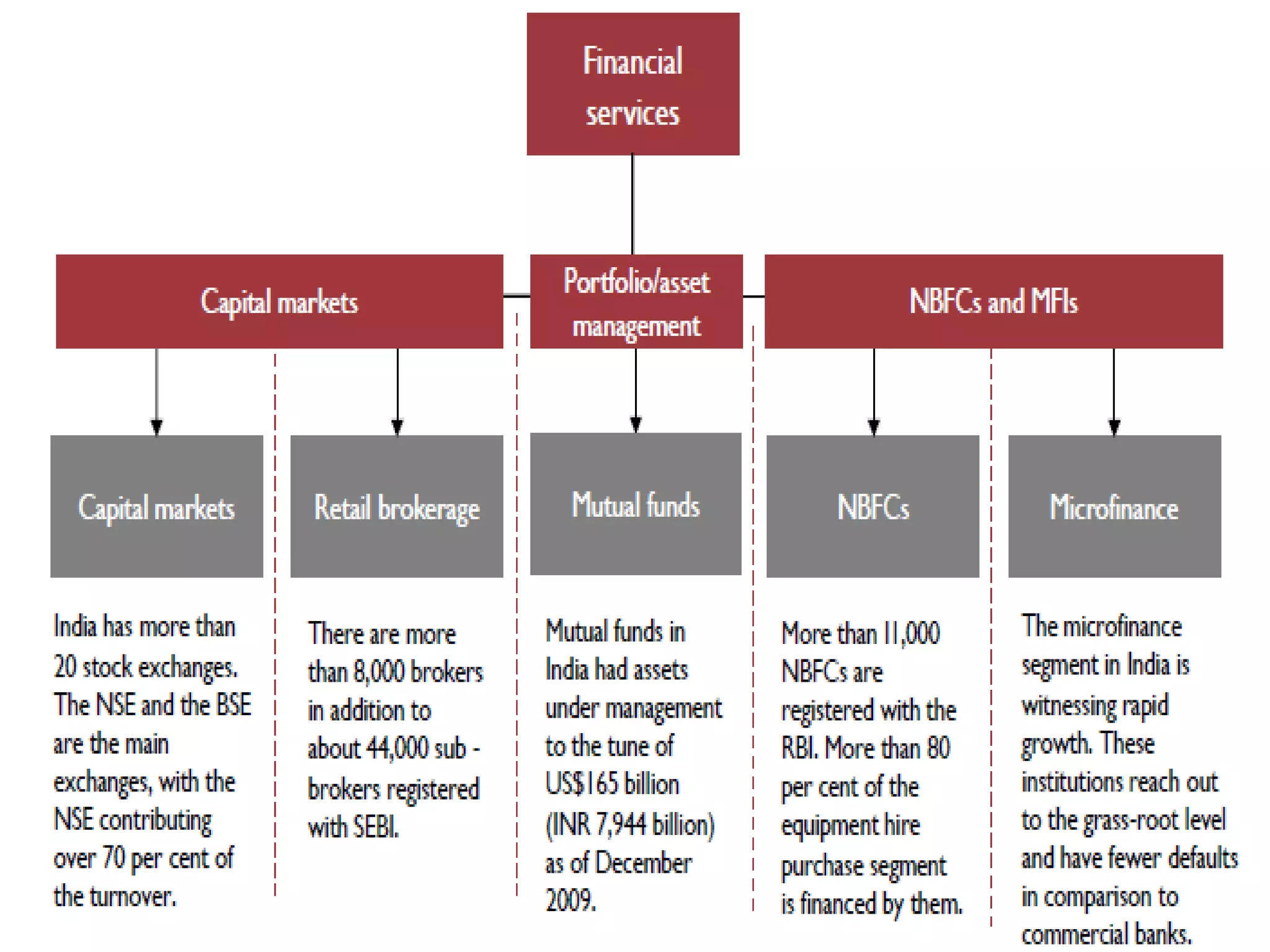
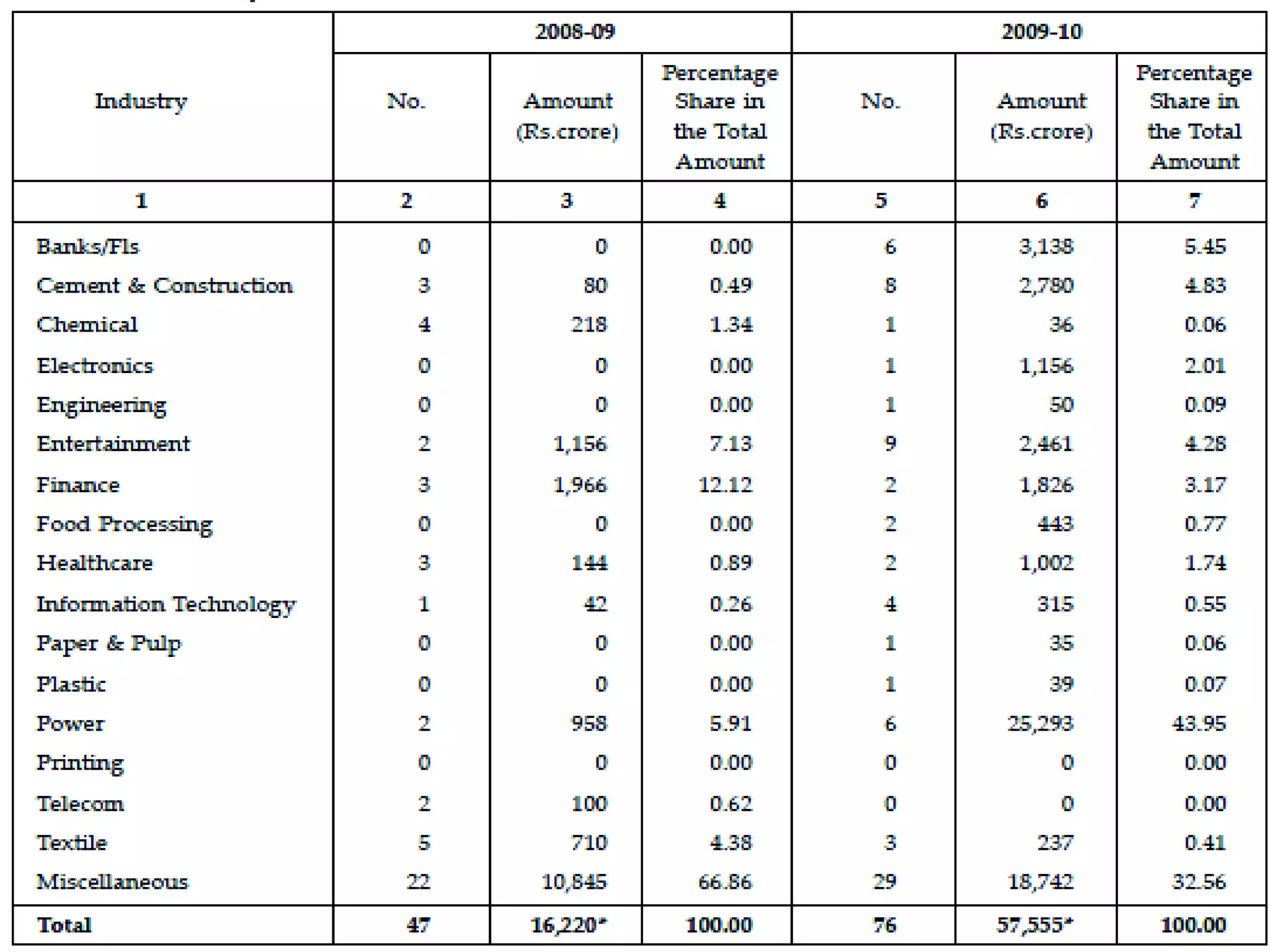
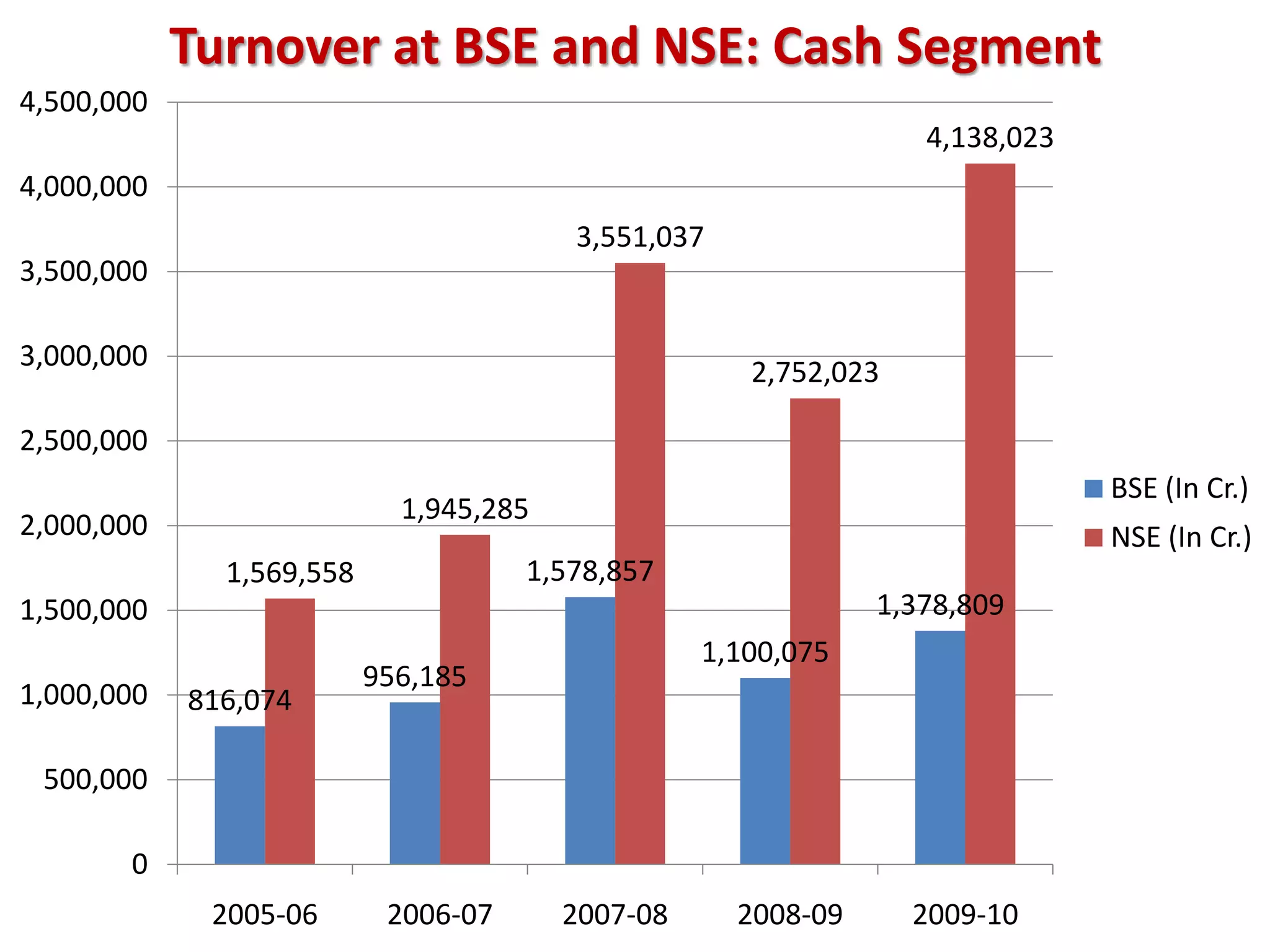
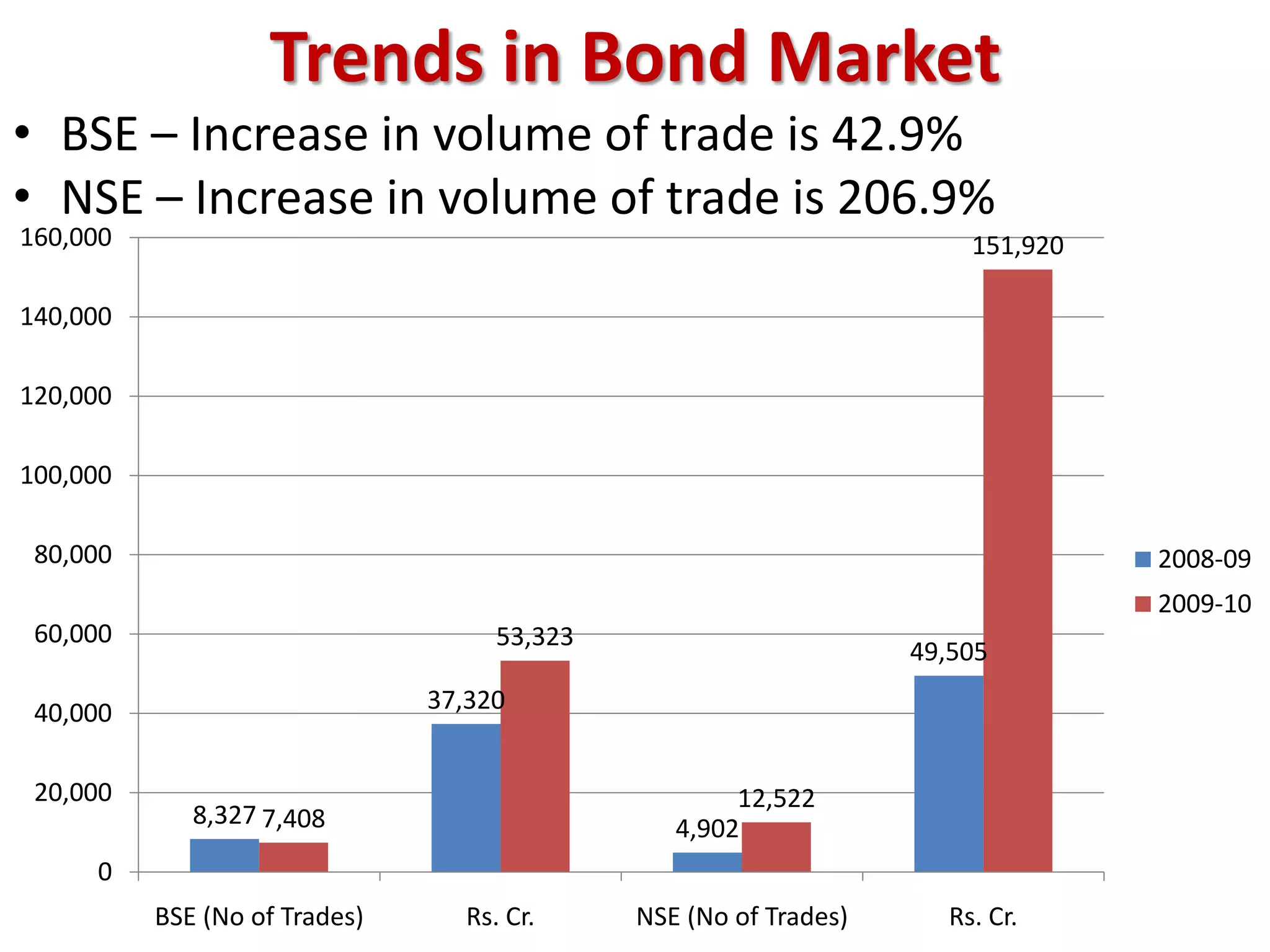
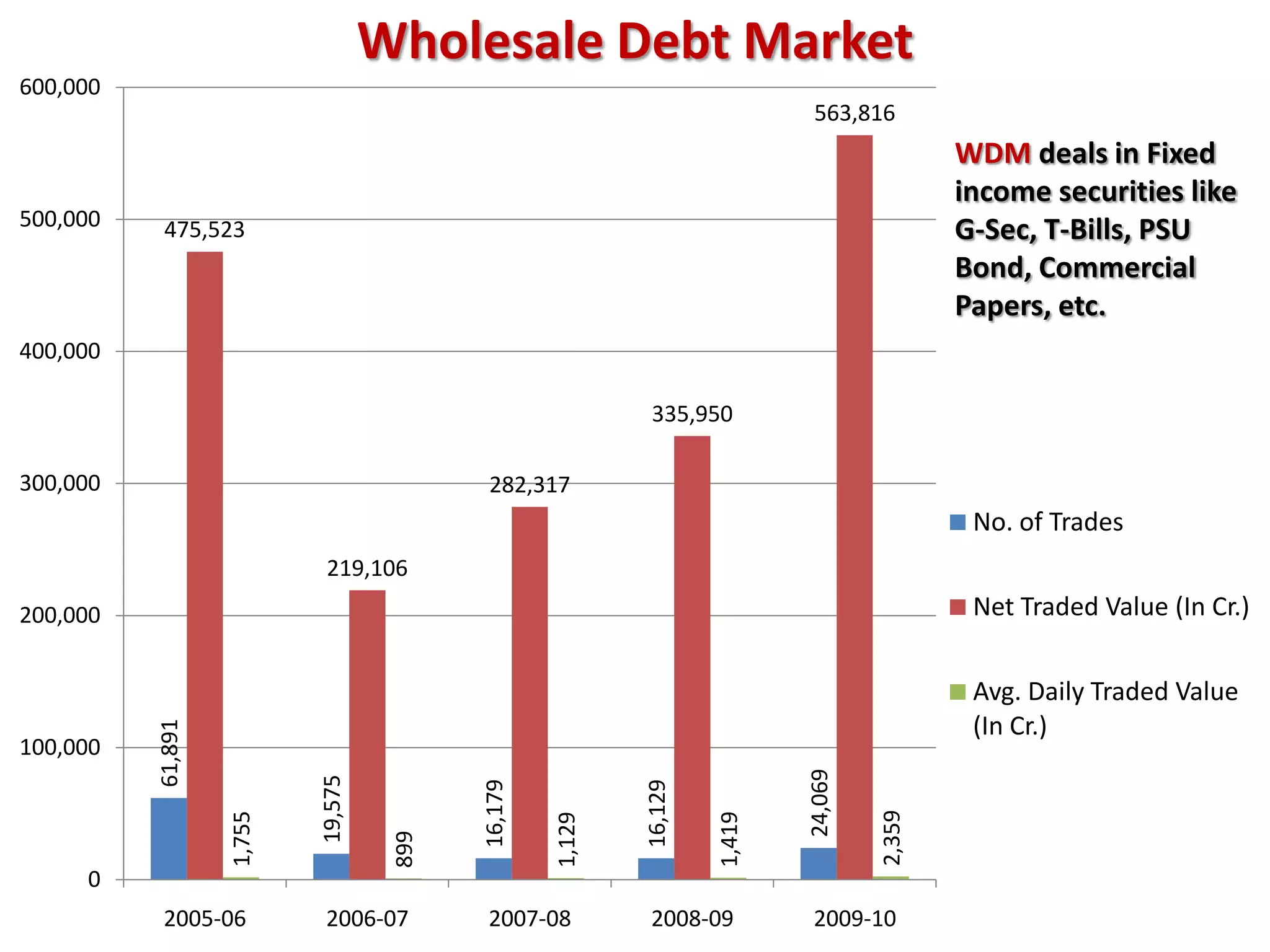
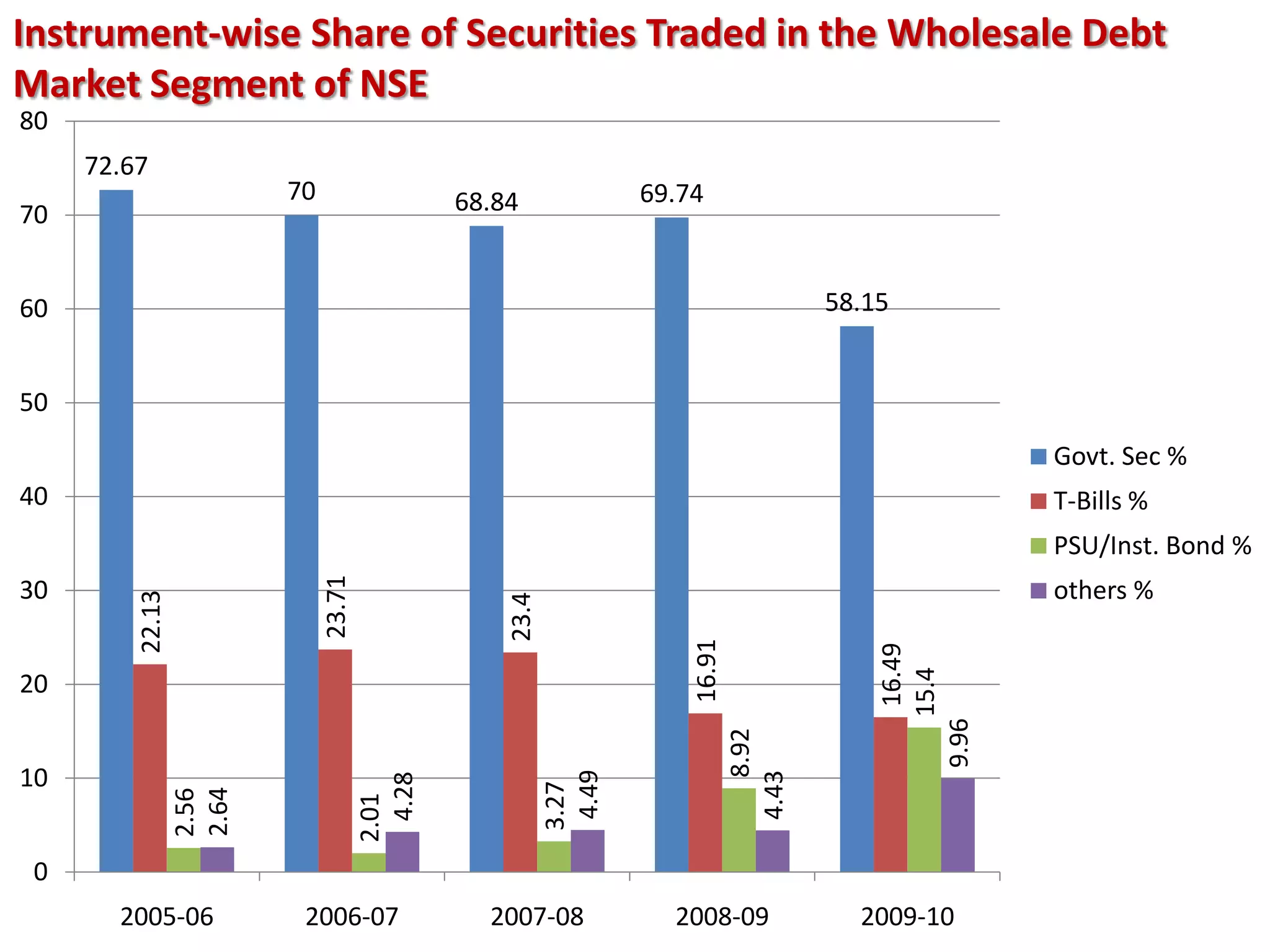
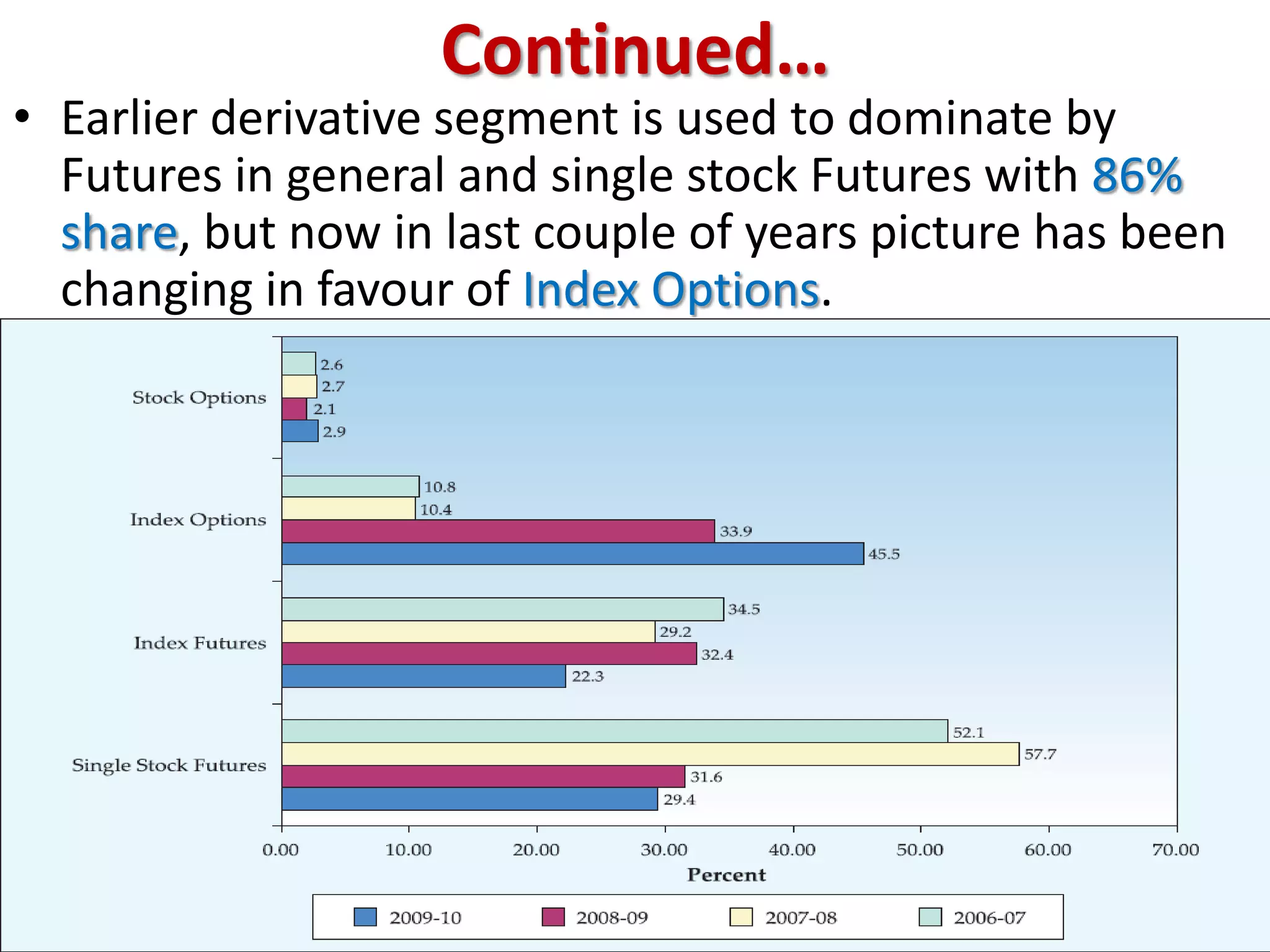
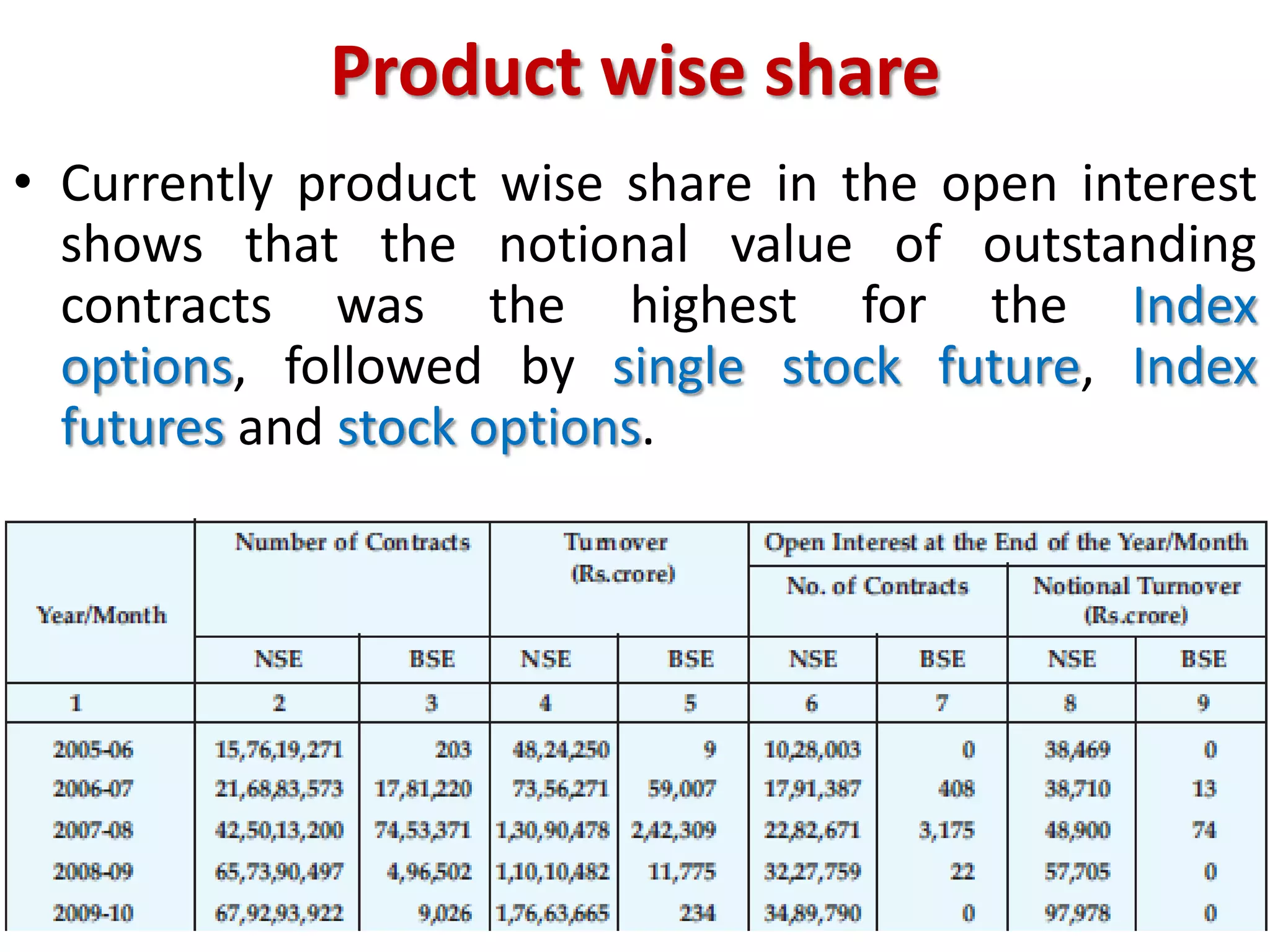
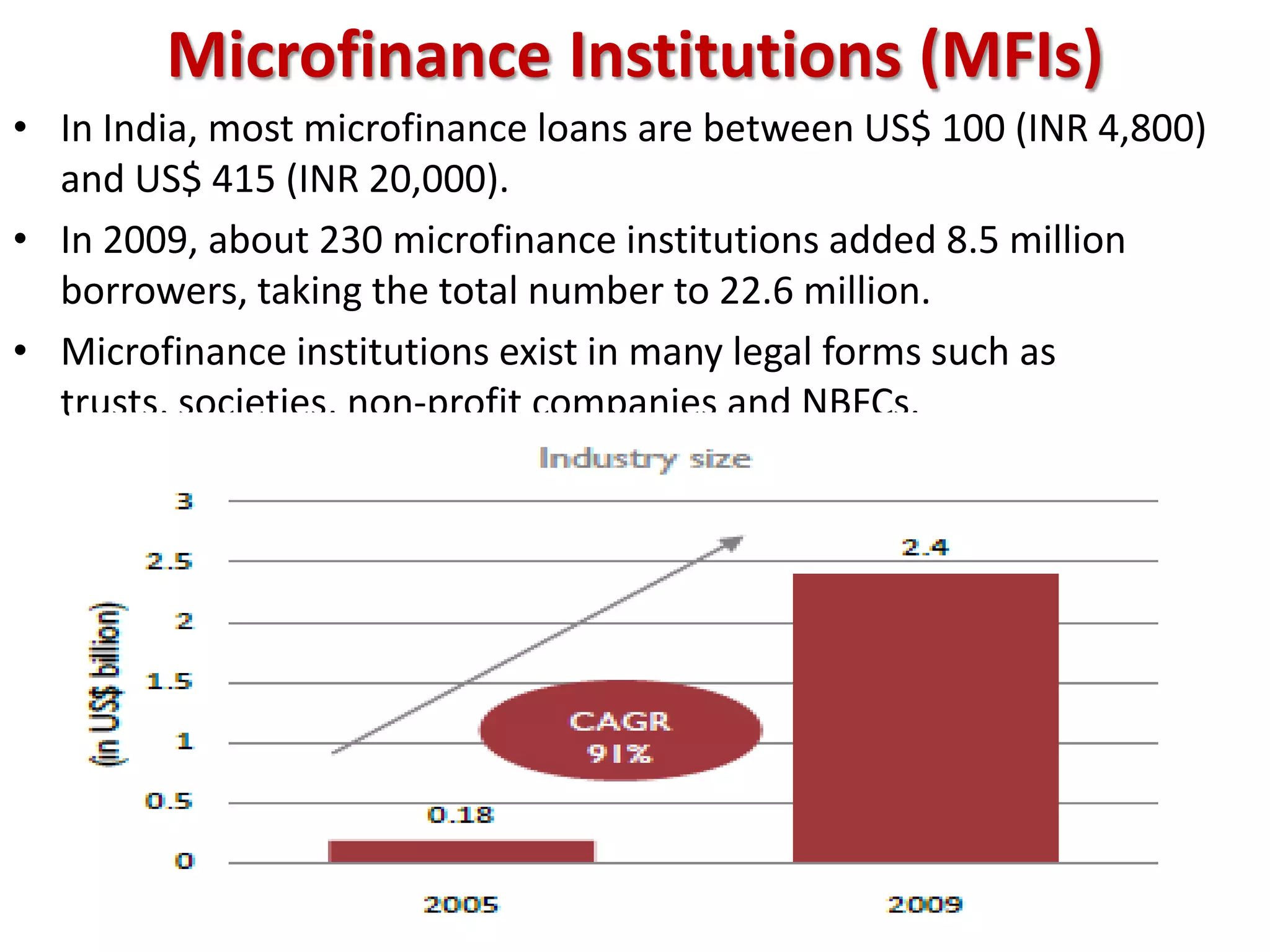
The financial sector in India has grown significantly in recent years and includes banking, insurance, capital markets and other non-banking financial institutions. Banking has expanded with new branches and ATMs, while the insurance sector is growing rapidly led by life insurance. The capital markets have also increased in size and importance with the primary market helping companies raise funds and the secondary market seeing increased trading volumes. Overall the financialization of the Indian economy has accelerated and further reforms are expected to make the sector more effective in allocating resources and supporting economic growth.