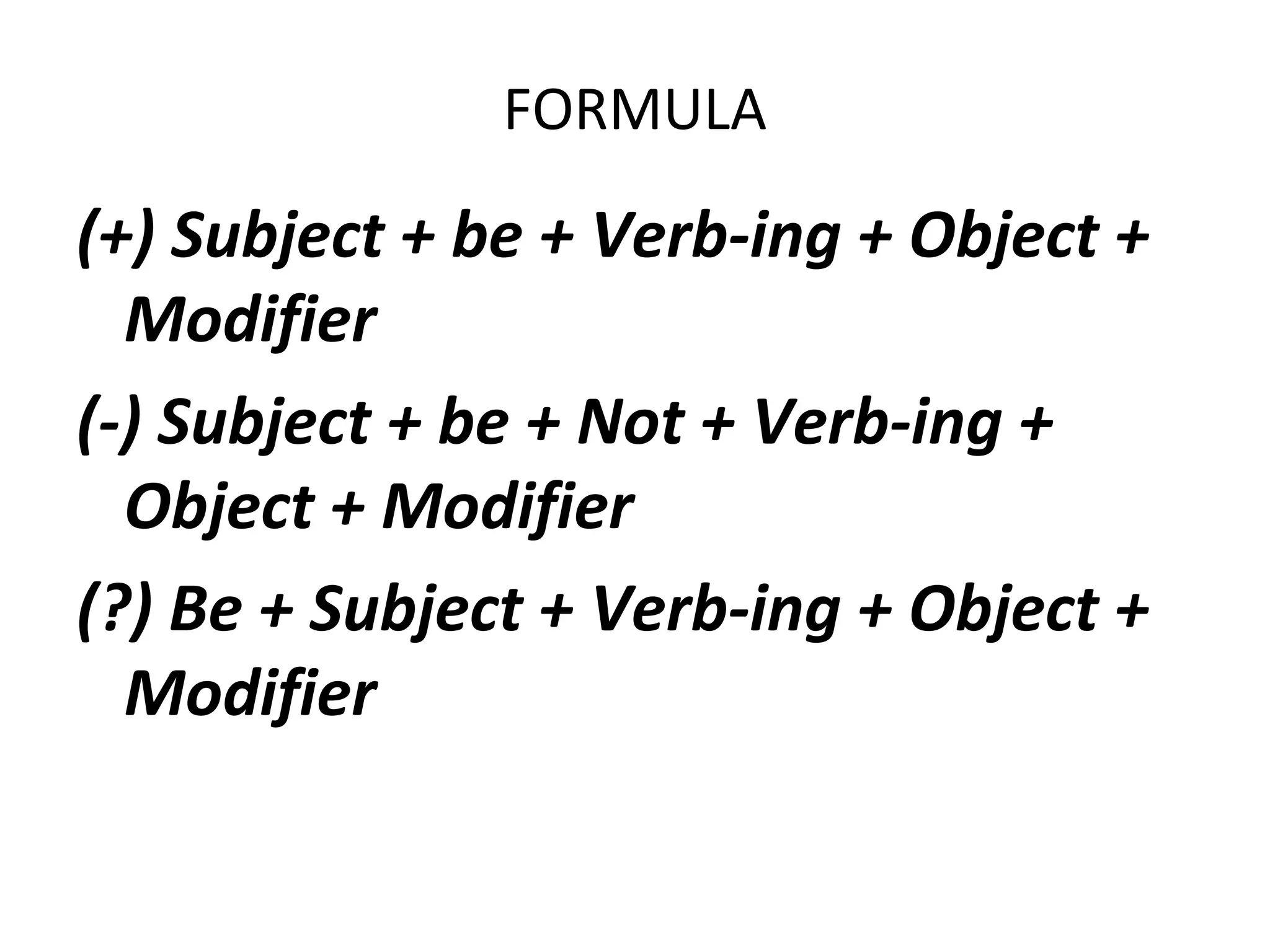
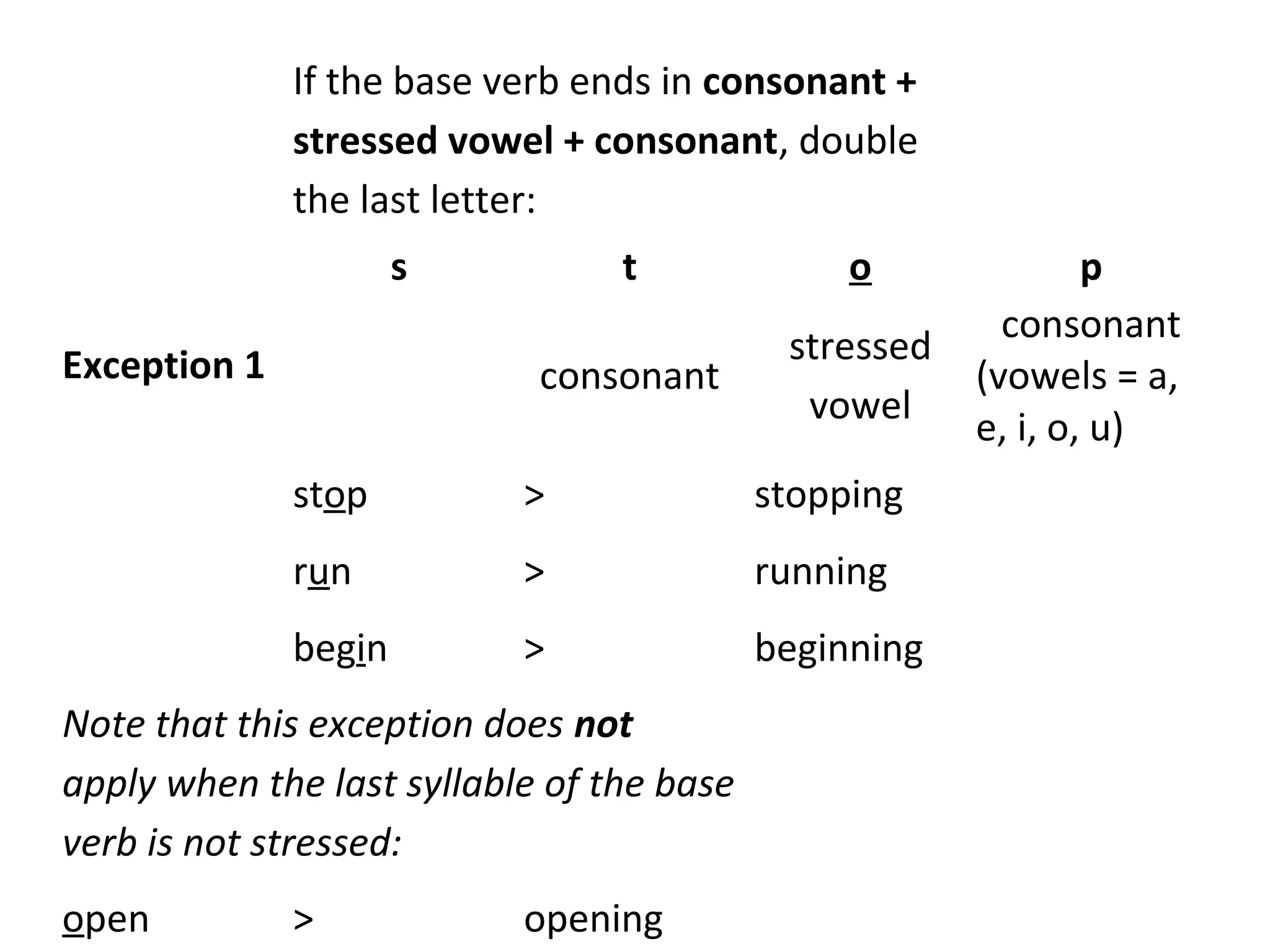
The document describes the use of the present continuous tense in English. It discusses four main uses: (1) actions happening now, (2) longer actions in progress now, (3) planned events in the near future, and (4) repetition or irritation with words like "always." It provides examples for each use and notes some irregular verb forms. The document also covers adverb placement, non-continuous verbs that don't use the present continuous form, and rules for spelling verbs in the -ing form.