The document presents a preformulation study in drug development, focusing on the investigation of the physical and chemical properties of drug substances before they are formulated into stable and effective dosage forms. It covers topics such as polymorphism, hygroscopicity, flow properties, solubility, and regulatory guidelines provided by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). Additionally, practical methods for analyzing and enhancing solubility and drug absorption, along with various tests and metrics, are discussed.







![Flow Properties
Angle of Repose (3)
It is the maximum Angle possible between surface of
the pile of the Powder and horizontal plane.
It is used to determine flow property of powders
Rough and irregular surface Higher Angle of Repose
Lower the Angle of repose Better the flow properties
θ is directly proportional to Surface roughness
Notes- 25-30[Excellent Flow Properties]
Carr's Consolidation Index
Also known as compressibility
Carr's index is the indication of the Flowability of
a powder
In a Flatter cone free flowing powder, the bulk
density and tapped density would be close in
value
therefore, the carr's index would Small
Notes- 1-10[Excellent Flow Properties]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preformulationstudyandregulation-240918105936-841fa95f/85/Preformulation-Study-and-Regulation-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![Wetting Agents
The wetting agent molecule has a portion with an affinity for the particle surface and portion with an affinity for
water. [HLB Value: 7-9]
Wetting is the extent of contact between a liquid and surface , when two are brought in contact with each other
First stage of wetting is Addition of a granulating agent to powder is characterized by- Pendular State
Act in suspension reduce contact Angle between substance and solvent
Contact angle [θ=0°] Complete wetting
Contact angle [θ=90°] Cohesive force=Adhesive force
Wa > Wc - wetting occurs
Wetting agent test
Drave Test :- it is the time taken for wet skin of cotton yarn to skin in wetting solution contained in 500 mL.
Emperic Test ,Trough Test ,Contact Angle method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preformulationstudyandregulation-240918105936-841fa95f/85/Preformulation-Study-and-Regulation-pptx-10-320.jpg)





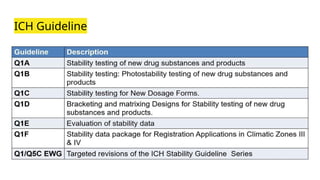
![ICH Guidelines
ICH Guideline "international council for Harmonisation of technical requirements for pharmaceuticals for
Human use"
"International conference on Harmonisation of technical registration for registration of pharmaceuticals
for Human use"
As per ICH Guideline India comes in Zone III and IV (whole world divided into 4 zones)
ICH topics divided into 4 categories [QSEM]
Q- Quality [Q1-Q2]
S- Safety
E- Efficacy
M- Multidisciplinary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preformulationstudyandregulation-240918105936-841fa95f/85/Preformulation-Study-and-Regulation-pptx-16-320.jpg)