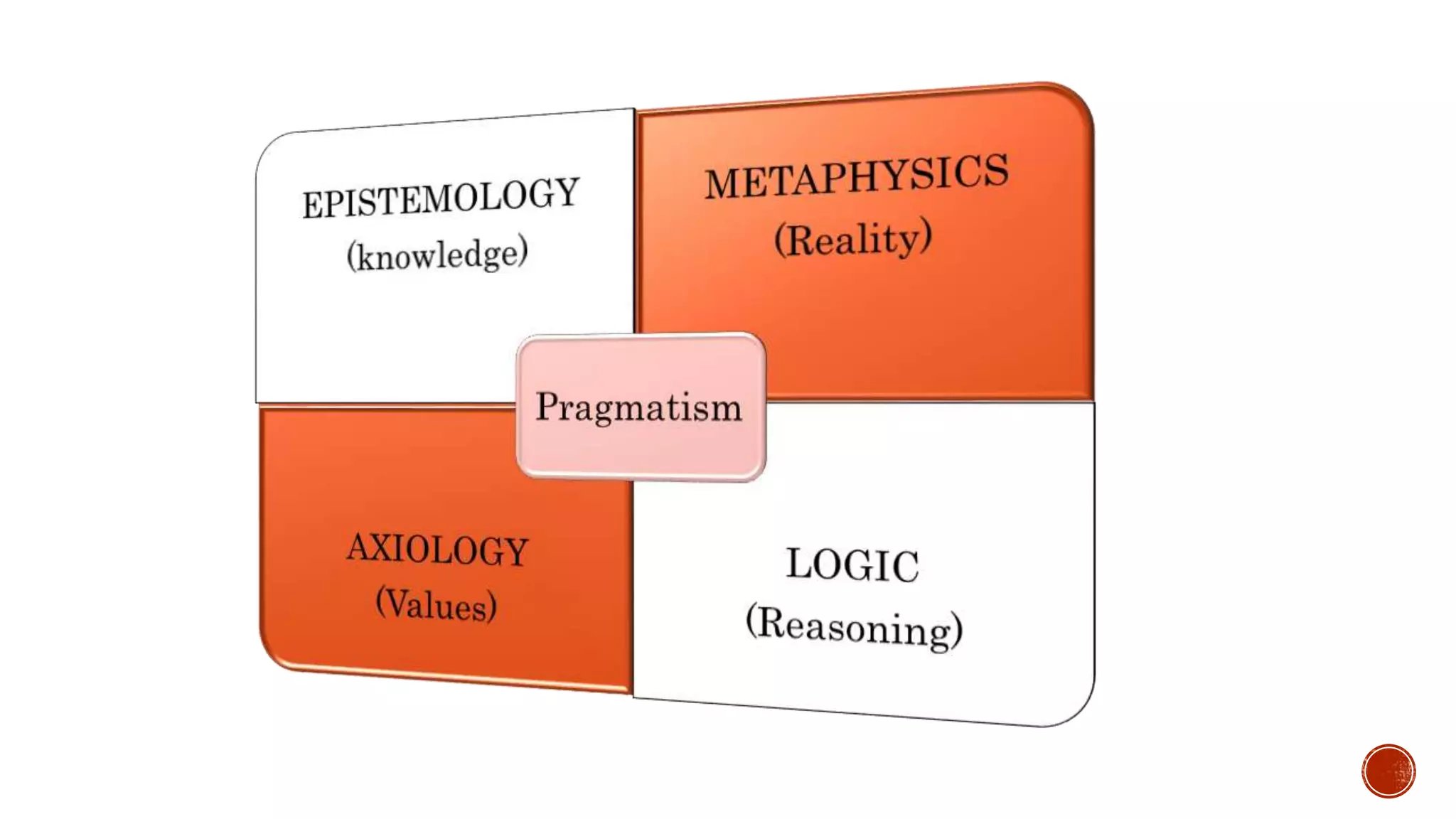
The document outlines the principles of pragmatism and reconstructionism. It discusses the founders and key exponents of pragmatism, including Charles Sanders Peirce, William James, and John Dewey. The fundamental principles of pragmatism are presented, including that theories are true if they work and there is no absolute knowledge or reality. Pragmatism's epistemology, metaphysics, axiology, and logic are defined. Reconstructionism is described as being rooted in pragmatism and emphasizing addressing social questions and reforming society. The goals, nature of curriculum, roles of teachers and students, and teaching methods of pragmatism and reconstructionism in education are also summarized.